![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
120 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Heterotrophic
|
An organism that is dependent on complex organic substances for nutrition because it cannot synthesize its own food
|
|
|
Absorptive
|
break down food by secreting digestive enzymes onto a substrate and then absorb the resulting small food molecules
|
|
|
Mycelium
|
the vegetative part of a fungus, consisting of a network of fine white filaments
|
|
|
Hyphae
|
each of the branching filaments that make up the mycelium of a fungus
|
|
|
Chitin
|
a fibrous substance consisting of polysaccharides and forming the major constituent in the exoskeleton of arthropods and the cell walls of fungi
|
|
|
Sporocarp
|
is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are borne.
|
|
|
Dikaryotic
|
Compatible cell-types can fuse cytoplasms (plasmogamy). When this occurs, the two nuclei of two cells pair off and cohabit without fusing.
|
|
|
Mycoses
|
disease caused by infection with a fungus, such as ringworm or thrush.
|
|
|
Mycorrhizae
|
a fungus that grows in association with the roots of a plant in a symbiotic or mildly pathogenic relationship.
|
|
|
Lichen
|
a simple slow-growing plant that typically forms a low crustlike, leaflike, or branching growth on rocks, walls, and trees
|
|
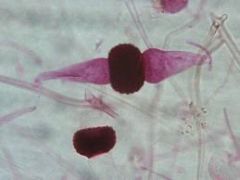
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Phylum: Zygomycota Zygospore |
|
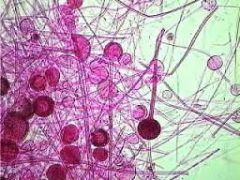
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Phylum: Zygomycota Rhizopus |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Phylum: Ascomycota Ascocarp |
|
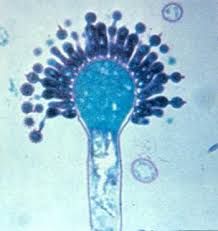
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Phylum: Ascomycota Conidia of Aspergillus |
|
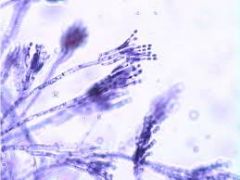
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Phylum: Ascomycota Conidia of penicillin |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Phylum: Basidiomycota Mushroom gill, basidia and basidiospores |
|
|
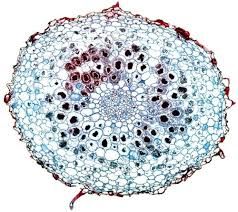
Mycorrhizae
|
|
|
Osculum
|
a large opening in a sponge through which water flows out of the sponge. Sponges may have more than one oscula
|
|
|
Ostia
|
a series of tiny pores all over the body of a sponge that let water into the sponge
|
|
|
Spicules |
structural elements found in most sponges
|
|
|
Silica
|
a hard, unreactive, colorless compound that occurs as the mineral quartz and as a principal constituent of sandstone and other rocks
|
|
|
Calcareous |
containing calcium carbonate, kind of support in sponges
|
|
|
Spongin |
A form of fibers that form the skeleton of certain sponges
|
|
|
Collagen |
The main structural protein found in animal connective tissue
|
|
|
Porocytes |
Cell that has a pore, lets water into sponge
|
|
|
Choanocytes |
Flagellated feeding cells create water flow
|
|
|
Pinacocytes
|
Outer surface of the organism
|
|
|
Archaeocytes
|
Cells that move around within the sponge
|
|
|
Mesoglea |
Jelly like structure between the epidermis
|
|
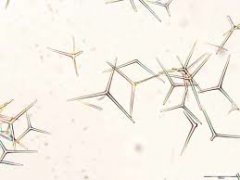
|
Calcareous spicule
|
|
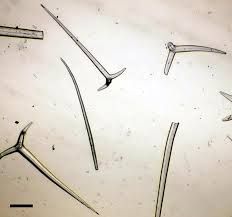
|
Silica Spicule
|
|
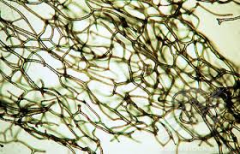
|
Spongin
|
|
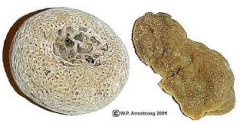
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Porifera Class: Calcarea |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Porifera Class: Hexactinellida |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Porifera Class: Demospongiae |
|
|
Sponges have _______________ level of structural organization in their bodies.
|
Cellular
|
|
|
The method used by sponges to obtain food is _____________________.
|
Filter feeding
|
|
|
It has been hypothesized that sponges are derived from a free-swimming, colonial single-celled ancestor. Thus, perhaps sponges are descended from what protest group?
|
choanoflagellates
|
|
|
Diploblastic
|
having a body derived from only two embryonic cell layers (ectoderm and endoderm, but no mesoderm),
|
|
|
Radical symmetry
|
Top and bottom sides only (symmetry)
|
|
|
Polyp
|
Mouth up, sedentary of the cnidaria |
|
|
Medusa
|
Mouth down, motile, reproductive of the cnidaria
|
|
|
Sessile
|
A plant or animal structure attacked to its base with a stalk
|
|
|
Motile |
Able to move around
|
|
|
Cnidocyte |
An explosive cell containing a nematocyst
|
|
|
Nematocyst |
Coiled filament (jelly stings)
|
|
|
Gastrovascular Cavity |
Sac like gut
|
|
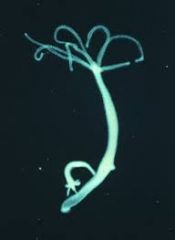
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Hydrozoa |
|
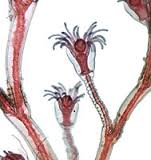
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Cnidaria Class Hydrozoa Polyp Stage |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Hydrozoa Medusa Stage |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Scyphozoa Strobila Stage |
|
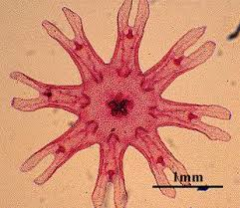
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Scyphozoa Ephyra Stage |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Scyphozoa Medusae Stage |
|
|
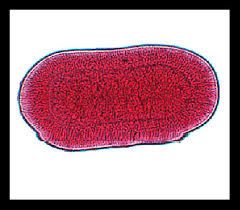
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Scyphozoa Planula Larvae Stage |
|
|
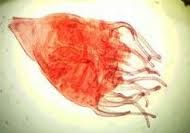
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Scyphozoa Scyphistoma (developing polyp) |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Anthozoa |
|
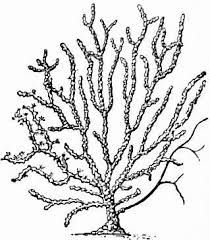
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Anthozoa |
|
|
Cnidarians typically have what tissue layers?
|
They only have two layers outer
|
|
|
What fills the space between tissue layers?
|
A matrix, jelly like.
|
|
|
The unique stinging cells possessed by members of this phylum are called _____________?
|
Nemyocyst
|
|
|
Cnidarians with a __________ adult body form are generally sessile and stationary. While those species with a ___________ adult body form are mobile and move throughout the ocean water.
|
Polyp Medusa |
|
|
Acoelomate
|
Invertebrate lacking a coelom
|
|
|
Triploblastic
|
Three derms, Endoderm, Exoderm, and Medsioderm
|
|
|
Hermaphroditic |
Both sexes
|
|
|
parasite |
feeds off other organisms
|
|
|
endoparasite |
Lives inside of its host |
|
|
Definitive host
|
|
|
|
Intermediate host |
Host that does not contain an adult |
|
|
Pharynx
|
Connects to the esophagus |
|
|
Ganglia
|
Ventral nerve cord for sensory input |
|
|
Cephalization
|
Development of a brain (concentration of nerves)
|
|
|
Scolex
|
What attaches tapeworms to host |
|
|
Proglottid
|
Segment in a tapeworm containing sexually mature reproductive system.
|
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class: Turbellaria |
|
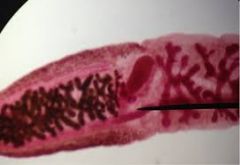
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class: Trematoda |
|
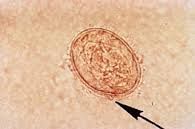
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class: Trematoda Trematoda egg |
|
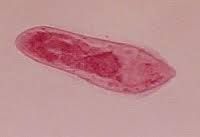
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class: Trematoda Trematoda Miracidium |
|
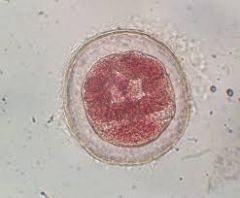
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class: Trematoda Trematoda Sporocyst |
|
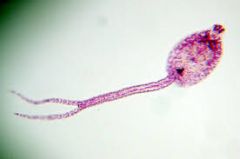
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class: Trematoda Trematoda Cercaria |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class: Trematoda Trematoda Adult |
|
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class: Cestoda Tape worms |
|
|
Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class: Trematoda Class Trematoda are? |
Primarily parasitic, has intermediate and definitive hosts.
|
|
|
What are the three "germ layers" from which all later tissues develop?
|
Ectoderm, Endoderm, Mesoderm
|
|
|
The platyhelminthes have ___________ body symmetry
|
Bilateral
|
|
|
Which of the three classes of Platyhelminthes you have you observed that is NOT primarily parasitic?
|
Turbellaria
|
|
|
Coelom
|
The intestinal cavity and the body of the cell wall |
|
|
Metanephridia
|
Type of excretory gland
|
|
|
Foot
|
Used for movement |
|
|
Mantle
|
Grows the shell |
|
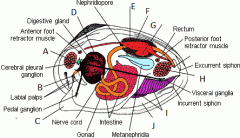
|
A) Anterior abductor muscle B) Mouth C) Foot |
|
|
Parapodia
|
Each number of paired muscular bristle bearing appendages used in locomotion, sensation, or respiration
|
|
|
Setae
|
Hair like or bristle like structures
|
|
|
Clitellum
|
A raised brand encircling the body of worms and some leaches |
|
|
Metamerism
|
The phenomenon of having a linear series of body segments |
|
|
Septa
|
Dividing wall between segments
|
|
|
Hydrostatic skeleton
|
Fluid filled cavity, the coelom, surrounded by muscles. |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Polyplacophora |
|
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Gastropoda |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Cephalopoda |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Bivalvia |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Annelida Class: Polychaeta |
|
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Annelida Class: Hirudinea |
|
|
Ecdysis
|
is the moulting of the cuticula in many invertebrates
|
|
|
Pseudocoelom
|
Cavity between the body wall and the intestine
|
|
|
Chemoreceptors
|
Process by which organisms respond to chemical stimuli in their environments
|
|
|
Facultative parasite
|
Can be free-living or parasitic
|
|
|
Free-living
|
Lives without a host |
|
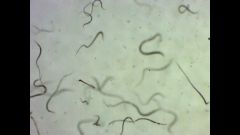
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Nematoda Class: Enoplea Vinegar worms |
|
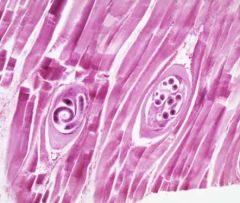
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Nematoda Class: Enoplea Parasitic |
|
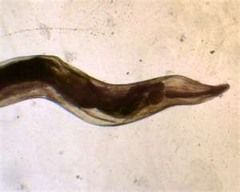
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Nematoda Class: Rhadbitea |
|
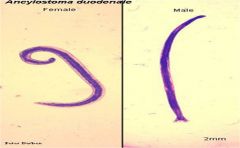
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Nematoda Class: Rhabditea |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Trilobita |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Subphylum: Chelicerata Class: Merostomata |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Subphylum: Chelicerata Class: Arachnida |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Subphylum: Chelicerata Class: Arachnida |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Subphylum: Myriapoda Class: Diplopoda |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Subphylum: Myriapoda Class: Chilopoda |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Subphylum: Crustacea Class: |
|

|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Subphylum: Crustacea Class: |
|
|
Clade: Opisthokonta Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Subphylum: Hexapoda Class: Insecta |

