![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Evolutionary Significance of Fungi |
Once shared a lineage with plantsShared ancestor to animalsDecomposition mastersVery few fossils (because no hard tissue) |
|
|
How do fungi eat? |
Heterotrophically, by secretion of enzymesEnzymes to break down food. Decomposers Parasites (+,-) Mutualists (+,+) |
|
|
Are fungi multi cellular, or single celled? |
Trick question, the can be both. They are usually multi cellular, however the single celled ones are called yeasts. |
|
|
Fungal eating strategies |
1. Hyphae hoops – attack animals 2. Hyphae haustoria - extract from plant root 2A. Ectomycorrhizal fungi hug the root tissue 2B. Endomycorrhizal fungi puncture cell wallsAbout 90% of all plants make this +,+ relationship! |
|
|
Hyphae are... |
the filamentous fungal growths |
|
|
Mycellium are... |
The term used for many hyphae, hyphae have 2 types. 1. Septate – connected, but divided 2. Coencitic – connected without division |
|
|
How does fungas grow to increase surface area |
Lengthwise, not in girth |
|
|
Fungi have cell walls composed of_______. |
Chitin |
|
|
From memory, what do the 2 types of hyphae look like? |
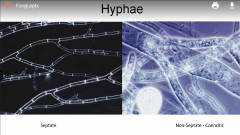
|
|
|
The "Fruiting body" of the mushroom is used for________. |
Reproduction |
|
|
Is fungal reproduction Sexual or asexual? |
Trick question, it can reproduce both ways |
|
|
Hyphae release pheromones as _______ ________ molecules. |
sexual signaling |
|
|
Plasmogamy is... |
the union of the cytoplasm of 2 parent mycellia. After fusion of the hyphae |
|
|
Heterokaryon is when... |
During plasmogamy the Nuclei do not fuse immediately, theycoexist. This makes a Dikaryotic cell |
|
|
Karyogamy is... |
when the 2 nuclei of a dikaryotic cell finally fuse making a diploid cell. |
|
|
Fungi and animals related distantly by... |
a flagellated ancestor. (posterior flagella)Evidence of mycorrhizal symbiosis as early as 420mya. |
|
|
So, where are fungi on the phylogenic tree |
Domain Eukarya Supergroup Unikonta Clade Opistohkonts (where the split occurred) Kingdom Fungi |
|
|
Alright, what are the 5 phyla of fungi we are studying? |
1. Chytridomycota - Small and flagella 2. P Glomeromycota - Are you with a plant? 3. Basidiomycota - The classic mushroom 4. Zygomycota–Hyphae+Q tip tight spores(bread? 5. Ascomycota – Cup, or loose spores (fruit?) |
|
|
What do you know about the chytrids |
1. Unique among fungi for having flagellated sporescalled Zoospores 2. Metabolism Similar to True Fungi 3. Primitive Fungi 4. Mutualistic (+,+) with some animals (typicallyundulates) helping break down plant material in stomachs. |
|
|
What do you know about Phylum zygomycota? |
1.Fast growing molds (Bread molds) 2. Genus Rhizopus: the common bread mold 3. Genus Pilobolus the shotgun fungi |
|
|
Zygomycota Reproduction |
Asexual and sexual reproduction. Plasmogamy makes Zygospores, a resting structure Isogamous = + and - not male and female. |
|
|
The common bread mold 1._________, have a 2. ________ that looks like a q-tip and is haploid and asexual. |
1. Rhizopus 2. Sporangium |
|
|
What do you know about phylum ascomycota |
1. It is home to geni Peziza, Penicillium, & Lichens. 2. They have an asci (a cup like structure for reproduction). 3. They can reproduce asexually via a conidiophore (the other q-tip like structure) |
|
|
What do you know about the lichens which are under the ascomycota phylum? |
1.form obligate mutualist (+,+) relationships 2. a mix between fungi and algae or cyanobacteria. 3. pioneer Organism (abiotic to biotic) and have very few requirements to survive 4. Lichens are exceedingly susceptible to environmental pollution 5. 3 types [ crustose, foliose, fruitocose] |
|
|
PHYLUM BASIDIOMYCOTA, what do you know about them? |
1. We're studying genus Coprinus 2. These are the classic mushroom 3.Their body is called a Basidocarp (reproduction) 4.Basidiomycota is also home to shelf fungi |
|
|
Draw and label a cross section |
Cap stalk gills basidia basidiaspores |
|
|
What do you know about phylum glomeromycota? |
1. All endomycorrhizae (live on/in plants) 2. Have Arbuscules (part that lives in plants) |

