![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which lineages of large, multicellular eukaryotes occupy terrestrial environments?
|
land plants, animals, fungi
|
|
|
mutualists
-example? |
Organisms that live in close relationship with a host and that benefits its host.
-in exchange for sugars produced by host plants, fungi provide plant with key nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus. |
|
|
Mycorrhizal
|
Literally "fungal root".
Fungi that live in close assiciation w/plant roots. |
|
|
Saprophytes
|
Literally "rotten plants"
Fungi that make their living by digesting dead plant material. |
|
|
Peat
-importance? |
partly decayed plant material.
-Peat from Carboniferous period became coal after being buried under other sediments and subjected to heat and pressure |
|
|
Yeast
|
Any fungus growing as a single-celled form.
|
|
|
Mycelia
|
A mass of underground filaments that form the body of a fungus.
The form of a multicellular fungi. |
|
|
Hyphae
|
The individual filaments that make up a mycelium
|
|
|
Heterokaryotic
|
literally "different kernael"
a cell that contains 2 haploid nuclei-one from each parent |
|
|
Septa
|
Any wall-like structure. In fungi, cross-walls that divide fungul filaments into cell-like compartments.
|
|
|
Coenocytic
|
Containing many nuclei and a continuous cytoplasm through a filamentous body, w/o the body being divided into distinct cells. Some fungi are coenocytic.
|
|
|
4 groups (+ description) that fungi fall into reproductively
|
1)Chytridiomycota (live in H20, spores have flagella thus motile)
2) Zygomycota (literally “yoked-together fungi”. Hyphae are haploid and come in several mating types. When fuse together (mate) become spore-producing zygosporangium) 3)Basidiomycota (club fungi, mushrooms, puffballs, bracket fungi are reproductive structures of this group, basidia form at end of hyphae and produce spores) 4) Ascomycota (sac fungi, tips of hyphae produce sac-like cells called asci which produce spores) |
|
|
Zygosporangium
|
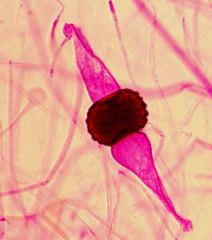
Spore-producing structure in fungi that are members of the Zygomycota.
|
|
|
Basidia
|

literally "little-pedestals"
Specialized spore-producing cells at the ends of hyphae in club fungi |
|
|
Asci
|
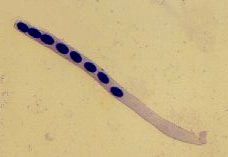
Specialized spore-producing cells found at the ends of hyphae in sac fungi.
|
|
|
Fungicides
|
molecules that are lethal to fungi
|
|
|
Chitin
|
Component of cell walls of fungi and other orgs.
|
|
|
Endophytic
|
literally "inside plants"
Fungi that live in the aboveground parts of plants |
|
|
Ectomycorrhizal Fungi (EMF)
|
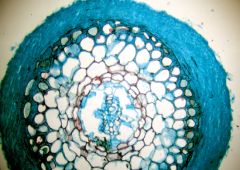
-Temperate forests
-hyphae extend outward -hyphae extend between cells -hyphae form dense sheath around root -Most are basidiomycetes, a few are ascomycetes |
|
|
Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (AMF)
or Vesicular-Arbuscular Mycorrhizae or Endomycorrhizal Fungi |
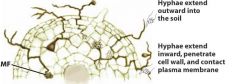
Grow into cells of root tissue. for a pipeline that extends from inside plant cells in the root to soil. are zygomycetes. found in 80% of land plants. dominant in grasslands/tropics.
|
|
|
Commensals
|
Species that are dependent on another species but are neither beneficial or harmful
|
|
|
Saprophyte
|
Oranism that feeds primarily on dead plant material.
|
|
|
Etracellular Digestion
|
Digestion that takes place outside of the organism.
|
|
|
Spore in fungi
|
Most fundamental reproductive cell in fungi. The dispersal stage in fungal life cycle, produced during asexual + sexual reproduction.
|
|
|
Plasmogamy
|
Fusion of cytoplasm of 2 individuals. Occurs in many fungi.
|
|
|
Karyogamy
|
fusion of nuclei
|
|
|
Sporangium
|
Spore-producing structure found in some plants and fungi.
|

