![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
197 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
More fat/obese results in |
Less water in ICF and ECF |
|
|
What fraction of water makes up ECF |
1/3 |
|
|
What fraction of water makes up ICF |
2/3 |
|
|
What are the three parts of the ECF |
Intravascular: the liquid part of blood (plasma) Interstitial: Located between the cells and outside the blood vessels
Transcellular fluid: Example is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) |
|
|
More dilute than blood is |
Hypotonic solution |
|
|
More concentrated than blood is |
Hypertonic solution |
|
|
True or false: In certain parts of the body there are higher rates of a specific electrolyte because it is needed more in that place to carry out its specific function |
True |
|
|
Filtration |
Want to use to create a fluid balance in through the use of IV also |
|
|
True or false: Blood contains albumin and other proteins called colloids |
True |
|
|
Cause of edema relluated to pressure |
The body is not effectively bringing those pressures back to a balance. |
|
|
Water is important because it is a primary source of the body because |
Transports nutrients Bringing wastes in and out of cell Regulates temperature(sweat/evaporate) Tells how much muscle weight vs fat |
|
|
True or False: Thirst will impact fluid intake |
True |
|
|
The average daily intake of a healthy adult person |
2300ml |
|
|
Antidiuretic hornone (ADH) |
Made by neurons in the hypothalamus released from posterior pituitary gland |
|
|
What does too much ADH result in? |
Less urine excreted |
|
|
What is the result of having too little ADH? |
More urine excreted |
|
|
Which system indicated an indication of retention for the amount of sodium to water and cause a change in blood pressure |
Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System (RAAS) |
|
|
When is Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) released? |
Released when increased Extracellular fluid to influence sodium/ water excretion |
|
|
Major factor of Osmolality imbalance |
Osmotic shift of water (Ex:) Isotonic fluid |
|
|
Osmolality imbalance deficit |
Not enough Isotonic fluid SS: Hypovolemia |
|
|
Osmolarity imbalance excessive |
Excessive is ironic fluid Hypervolemia - high volume of something |
|
|
Hypernatremia |
Water deficit |
|
|
Hyponatremia |
Water excess |
|
|
Dehydration |
A combination of vascular volume and water deficit |
|
|
Low and high potassium results in |
Muscle weakness and can be life threatening |
|
True or False |
True |
|
|
High Calcium results in |
Muscle twitching |
|
|
Low Magnesium results in |
Lethargy |
|
|
True or false: Changes in the Extracellular fluid causes changes in the RAAS to maintain balance. |
True |
|
|
High Magnesium results in |
G |
|
|
Where are the cells of the Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) located |
Located in the atria of the heart |
|
|
ANP |
Can see heart and it’s ability of pumping, its ability to excrete sodium and water |
|
|
Osmolality |
Fluid inside the body (solute concentration in fluid by weight or the number of millimols in a kilogram of solution) |
|
|
Osmolarity |
Solute concentration in fluid by millimols per liter |
|
|
Osmolarity is fluid by ______ per _____ |
Millimols per liter |
|
|
Osmolality is fluid by ______ per _____ |
Millimols per kg |
|
|
True or False |
True |
|
|
True or False: Although there might be the same volume the changes in the level of solute concentration influences the movement of water in/out of components |
True |
|
|
Potassium, Calcium, and Magnesium are all low in |
Plasma concentration |
|
|
Potassium, Calcium, and Magnesium are found mostly in |
cells and bones that are necessary for the normal muscle and nerve function. |
|
|
Acid excretion in IV must match |
the same amount produced |
|
|
Factors in determining the acidity of blood |
Hydrogen ions and add pH |
|
|
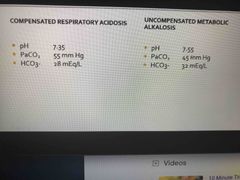
Normal arterial blood that is optimal for cell function is |
7.35 - 7.45 |
|
|
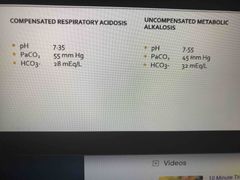
What are the 4 types of imbalances? |
Respiratory acidosis Respiratory Alkalosis Metabolic Alkalosis Metabolic Acidosis |
|
|
Kidneys excrete all acids except |
Carbon and Metabolic (bi carb) acid |
|
Reference |
;) |
|
|
Patient history |
Age Gender Body composition- environment, exercise, diet (a lot of salt? Foods rich in electrolyte, medications, surgeries/injuries |
|
|
Acid excretion in IV must match |
the same amount produced |
|
|
Factors in determining the acidity of blood |
Hydrogen ions and add pH |
|
|
Normal arterial blood that is optimal for cell function is |
7.35 - 7.45 |
|
|
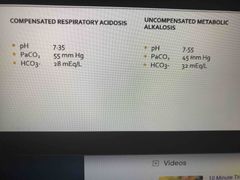
What are the 4 types of imbalances? |
Respiratory acidosis Respiratory Alkalosis Metabolic Alkalosis Metabolic Acidosis |
|
|
Kidneys excrete all acids except |
Carbon and Metabolic (bi carb) acid |
|
Reference |
;) |
|
|
Patient history |
Age Gender Body composition- environment, exercise, diet (a lot of salt? Foods rich in electrolyte, medications, surgeries/injuries |
|
|
Also ask i in Patient is there anything that would |
Impair secretion, increase secretion, or loss of fluid |
|
|
Acid excretion in IV must match |
the same amount produced |
|
|
Health promotion is also a part of |
Implementation |
|
|
Implementation: Health promotion includes |
Diet education , Health information, etc (table 42.4) |
|
|
Factors in determining the acidity of blood |
Hydrogen ions and add pH |
|
|
Normal arterial blood that is optimal for cell function is |
7.35 - 7.45 |
|
Reference |
;) |
|
|
Kidneys excrete all acids except |
Carbon and Metabolic (bi carb) acid |
|
|
Reference |
;) |
|
|
Patient history |
Age Gender Body composition- environment, exercise, diet (a lot of salt? Foods rich in electrolyte, medications, surgeries/injuries |
|

Front (Term) |
Where the mouse is the upper and lower number have such a huge difference in blood. “ There was not a high number when you draw blood from the vein) |
|
|
Physical Assessment ( |
Vital signs *I/O measurements (taken when person is receiving fluid intake) Respiratory status Cardiovascular status Neurological status GI/GU status |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Where the mouse is the upper and lower number have such a huge difference in blood. “ There was not a high number when you draw blood from the vein) |
|
|
Acid excretion in IV must match |
the same amount produced |
|
|
Health promotion is also a part of |
Implementation |
|
|
Implementation: Health promotion includes |
Diet education , Health information, etc (table 42.4) |
|
|
Enteral fluid replacements |
Are oral replacements of F&E or restrictions |
|
|
Factors in determining the acidity of blood |
Hydrogen ions and add pH |
|
Reference |
;) |
|
|
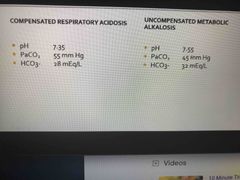
What are the 4 types of imbalances? |
Respiratory acidosis Respiratory Alkalosis Metabolic Alkalosis Metabolic Acidosis |
|
|
Kidneys excrete all acids except |
Carbon and Metabolic (bi carb) acid |
|
|
Reference |
;) |
|

Front (Term) |
Where the mouse is the upper and lower number have such a huge difference in blood. “ There was not a high number when you draw blood from the vein) |
|
|
Also ask i in Patient is there anything that would |
Impair secretion, increase secretion, or loss of fluid |
|
|
Physical Assessment ( |
Vital signs *I/O measurements (taken when person is receiving fluid intake) Respiratory status Cardiovascular status Neurological status GI/GU status |
|
|
Enteral fluid replacements |
Are oral replacements of F&E or restrictions/witholding |
|
|
Which fluid reinforces total intake with patient and family |
External fluid replacements |
|
|
Parenteral replacements |
Through a voxicular oxygenative device |
|
|
Which fluid reinforces total intake with patient and family |
External fluid replacements |
|
|
Parenteral replacements |
Through a voxicular oxygenative device |
|
|
G |
F |
|
|
Parenteral replacements |
Vascular access device equipment Starting IV (intravenous line) |
|
|
IV s |
Can quickly make fluid shifts happen quickly |
|
|
What are the two different types of of fluid replacements |
1 Colloids/blood 2 Crystalloid And they travel quickly through the membrane (no trouble getting in) |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
Problem with Lactated Ringers |
It gets metabolized by the liver and converts this lactate into bicarb |
|
|
True or False: Give lactated Ringers solution to patient with kidney problems who has a very Alkalotic pH |
False, Lactated Ringers should not be given to a patient with kidney problems who has a very Alkalotic pH because it will increase the amount of bicarbonate making the person more alkalotic |
|
|
Ringers solution |
Is similar to Lactated Ringers except There is no Lactate And it does not cause alkalization ppl |
|
|
What kind of solution is the D5W |
Isotonic |
|
|
True or false: DS5 is initially isotonic but when eneterinf the body it metabolizes and becomes a Hypotonic solution |
True |
|
|
Free water: _______ |
Hypotonic |
|
|
When will the health care provider see free water (water passes through membrane to ICF and ECF spaces in a patient? |
When the patient has high sodium level since water will normalize this sodium level |
|
|
True or false: D5W cannot be used to treat lack of volume because this patient needs a lot of volume and that’s not what D5W is used for |
True |
|
|
H |
H |
|
|
True or False: D5W is not good for any low BP, hemorrhaging circulatory/vascular collapse because it is does not stay Isotonic Seen early post op |
True |
|
|
What are two examples of colloids? |
Blood Proteins |
|
|
C |
F |
|
|
True or false Worry about any place where I am concerned about intracranial pressure |
True |
|
|
In Neuro patient I am concerned about Using D5W because it becomes when it becomes hypotonic and it renters the cell it can renter the tissues and makes grain swelling occur. The neuro patient already has a higher pressure in the brain |
R |
|
|
Intracellular Intravascular Inter spatial shifts Are needed when |
We’re trying to hydrate those cells |
|
|
Types of hypotonic solution |
0.45% sodium chloride 0.2% NaCl 2.5% Dextrose in water |
|
|
Hypertonic solutions |
When you want to take water out of the cell and increase the ECF volume |
|
|
Adding more than 5% dextrose would be considered a _______ solution |
Hypertonic |
|
|
Hypertonic solution would be used for someone who is |
Hypoglycemic because I need to correct it quickly |
|
|
Hypertonic solution is not used for |
Concern of someone with volume overload Ex: pulmonary edema, Depending on how high the amount of solution is given would need to change peripheral IV because it may be too caustic to the vessels |
|
|
G |
H |
|
|
Colloids |
Contain large molecules that do not pass through semipermeable membranes. They remain in the intravascular compartment and expand its volume by drawing fluid from the extra vascular spaces. |
|
|
Potassium is important because it influences how your _____ and _____ work |
Muscles and heart And is frequently being balanced in hospital because it is important |
|
|
Potassium chloride (KCL) |
Is a common additive to IV solutions and NEVER is administered through IV push
The solution must be diluted |
|
|
IV Push |
Injected directly into an IV |
|
|
V |
I |
|
|
True or false: The amount of potassium given will depend on how much volume, how fast, and if it is vital that they get a significant amount in over a certain period of time. May also need to choose a central access or catheter that is going into a central access like the superior vena cava. |
True |
|
|
True or false: Very often I will see medications, fluid replacements, blood administration, and more dilute slower administration of potassium that is mixed into IV fluids and given peripherally |
True |
|
|
Central catheters for to the |
Central vein |
|
|
True or False: Peripherally inserted central catheters (PICC) tend to last a little bit longer than the direct central catheters |
True |
|
|
Hospitals are very aware of CLABSI which are |
Central line associated blood stream infections and therefore typically do not like to have any central access if they don’t have to |
|
|
True or false: When giving IV start more distal and work more proximally across the hand |
True |
|
|
Crystalloids |
These are solutes (electrolytes or non-electrolytes) capable of crystallization and are easily mixed and dissolved in a solution. They are small and able to easily flow across semipermeable membranes Crystalloids allow for transfer from the bloodstream into the cells and the body tissue. |
|
|
Fluid resuscitation foR low ECF If worried about low ECF use |
Use normal saline 0.9% |
|
|
Low ECF symptoms |
Hemorrhage Sever vomiting or diarrhea Excessive drainage for GI secretions
|
|
|
Low ECF contributions to conditions |
Shock Mild hyponatremia Metabolic acidosis Hypercalcemia |
|
|
What is the only fluid to be used with administration of blood products |
0.9 Normal saline is the only |
|
|
Lactated Ringer’s |
Used in situation where patient has significant burn. Tho it is the only thing is closest to our own make up of everything that is the plasma and the blood |
|
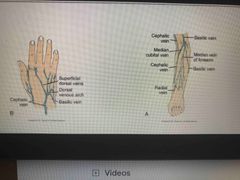
True or false: When giving IV start more distal and work more proximally across the hand |
True |
|
|
3 types of Osotonic |
G |
|
|
Problem with Lactated Ringers |
It gets metabolized by the liver and converts this lactate into bicarb |
|
|
True or False: Give lactated Ringers solution to patient with kidney problems who has a very Alkalotic pH |
False, Lactated Ringers should not be given to a patient with kidney problems who has a very Alkalotic pH because it will increase the amount of bicarbonate making the person more alkalotic |
|
|
Ringers solution |
Is similar to Lactated Ringers except There is no Lactate And it does not cause alkalization ppl |
|
|
What kind of solution is the D5W |
Isotonic |
|
|
True or false: DS5 is initially isotonic but when eneterinf the body it metabolizes and becomes a Hypotonic solution |
True |
|
|
Free water: _______ |
Hypotonic |
|
|
When will the health care provider see free water (water passes through membrane to ICF and ECF spaces in a patient? |
When the patient has high sodium level since water will normalize this sodium level |
|
|
True or false: D5W cannot be used to treat lack of volume because this patient needs a lot of volume and that’s not what D5W is used for |
True |
|
|
H |
H |
|
|
True or False: D5W is not good for any low BP, hemorrhaging circulatory/vascular collapse because it is does not stay Isotonic Seen early post op |
True |
|
|
What are two examples of colloids? |
Blood Proteins |
|
|
C |
F |
|
|
True or false Worry about any place where I am concerned about intracranial pressure |
True |
|
|
In Neuro patient I am concerned about Using D5W because it becomes when it becomes hypotonic and it renters the cell it can renter the tissues and makes grain swelling occur. The neuro patient already has a higher pressure in the brain |
R |
|
|
Intracellular Intravascular Inter spatial shifts Are needed when |
We’re trying to hydrate those cells |
|
|
Types of hypotonic solution |
0.45% sodium chloride 0.2% NaCl 2.5% Dextrose in water |
|
|
Hypertonic solutions |
When you want to take water out of the cell and increase the ECF volume |
|
|
Adding more than 5% dextrose would be considered a _______ solution |
Hypertonic |
|
|
Hypertonic solution would be used for someone who is |
Hypoglycemic because I need to correct it quickly |
|
|
Hypertonic solution is not used for |
Concern of someone with volume overload Ex: pulmonary edema, Depending on how high the amount of solution is given would need to change peripheral IV because it may be too caustic to the vessels |
|
|
G |
H |
|
|
Colloids |
Contain large molecules that do not pass through semipermeable membranes. They remain in the intravascular compartment and expand its volume by drawing fluid from the extra vascular spaces. |
|
|
Potassium is important because it influences how your _____ and _____ work |
Muscles and heart And is frequently being balanced in hospital because it is important |
|
|
Potassium chloride (KCL) |
Is a common additive to IV solutions and NEVER is administered through IV push
The solution must be diluted |
|
|
IV Push |
Injected directly into an IV |
|
|
V |
I |
|
|
True or false: The amount of potassium given will depend on how much volume, how fast, and if it is vital that they get a significant amount in over a certain period of time. May also need to choose a central access or catheter that is going into a central access like the superior vena cava. |
True |
|
|
True or false: Very often I will see medications, fluid replacements, blood administration, and more dilute slower administration of potassium that is mixed into IV fluids and given peripherally |
True |
|
|
Central catheters for to the |
Central vein |
|
|
True or False: Peripherally inserted central catheters (PICC) tend to last a little bit longer than the direct central catheters |
True |
|
|
Hospitals are very aware of CLABSI which are |
Central line associated blood stream infections and therefore typically do not like to have any central access if they don’t have to |
|
|
True or false: When giving IV start more distal and work more proximally across the hand |
True |
|
|
Crystalloids |
These are solutes (electrolytes or non-electrolytes) capable of crystallization and are easily mixed and dissolved in a solution. They are small and able to easily flow across semipermeable membranes Crystalloids allow for transfer from the bloodstream into the cells and the body tissue. |
|
|
C |
G |
|
|
Fluid resuscitation foR low ECF If worried about low ECF use |
Use normal saline 0.9% |
|
|
Low ECF symptoms |
Hemorrhage Sever vomiting or diarrhea Excessive drainage for GI secretions
|
|
|
Low ECF contributions to conditions |
Shock Mild hyponatremia Metabolic acidosis Hypercalcemia |
|
|
What is the only fluid to be used with administration of blood products |
0.9 Normal saline is the only |
|
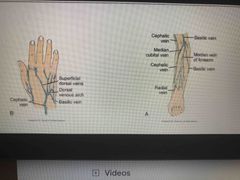
True or false: When giving IV start more distal and work more proximally across the hand |
True, this avoids any medication leaking out or any limitation for medication to beyond the area of infiltration and have the tissue bleed. |
|
|
Hypovolemic AKA |
AKA “from 3rd spacing”; a loss of Extracellular fluid (ECF) from the vascular to other body compartments. |
|
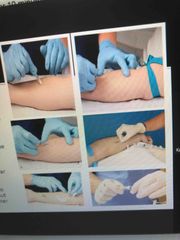
Giving Intravenous catheters (general) |
Need to have an order Know the (5) rights: right order, patient, time, route, medication Explain procedure Supplies: Turnequette 1. Decide where I am going to put the vein 2. Put turnequette on and see if I can palpate a vein 3. Clean the area 4. Determine what size IV needle (lumen) Giving Med or blood = size 20 Size 22 = small catheter for adult
IIC - Intermittent infusion cap Hep (heparin) lock/cap IIC and Hep lock mean that I am putting a catheter in the vein with a tube with a connector for that is finally taped. Only used to give fluid or medication through it. (There’s nothing that’s going to be hanging on it/in addition to it (medications or fluids) Need to have syringe with normal saline setup prior to inserting it 5. Insert beveled up (not attached to the patient) 6. Flush normal saline into the line to make sure that I have primed the line. Do not want any air in the line 7. Clean the area Hold the skin and with my dominant hand inserting at 15 degrees until I see a draw back of a flash of blood. This lets me know that I am in the vein, therefore, I don’t need to angle anymore. 8. Then I would go more parallel on the vein 9. Push and advance the father ahead so that the catheter only goes in and what is left is the blue color because the needle is all the way under the skin. 10 Use the safety lock and withdraw/remove 11 put catheter on in the same place 12 remove tourniquet (blue elastic band) 13 unclamp roller (white little thing) 14 Flush the line and see that it is able to flush the blood in easily and doesn’t hurt the patient 15 Secure it with a translucent dressing and then tape it down 16 If it’s going to have IV in place, insert it and then tape it down
|
|
|
How to Clean area for IV site |
Horizontally Vertically Then circularly Let it dry |
|
|
Many ways that an IV site can become contaminated |
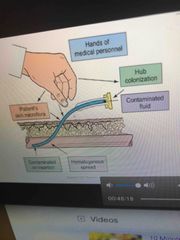
Back (Definition) |
|
|
IV fluid one Important to get right solution 2 Look at the bag make sure it’s clear and that there is no sediment, check expiration date, 3 Prime the line (Get fluid all the way through the chamber to the top of the head) 4 spike bag 5 clamp it off 6 pinch the chamber (but not too high) 7 make sure no air 8 Open the clamp and after I see that it went all the way through I would close the clamp We clean the IV ports with chlorhexidine before we give any med using IV
|
B |
|
|
The dressing for IV must have what things written on it? |
Date Time Size of IV |
|
|
ABO system |
Allows us to match blood in preparation for blood transfusions |
|
|
True or False: We have our own antibodies that help us fight off things |
True |
|
|
Universal recipient blood type |
AB |
|
|
The universal donor blood type |
Blood type O |
|
|
True or False: We have our own antibodies that help us fight off things |
True |
|
|
Universal recipient blood type |
AB |
|
|
The universal donor blood type |
Blood type O |
|
|
Type A blood |
A antigen and B antibody |
|
|
TPN |
Total parenteral nutrition nutrition through IV that has a high concentration which requires us to administer it centrally |
|
|
True or False: The TPN never stay hung more than 24 hours |
True |
|
|
True or False: with nutritional support the nurse will be coming and making sure that they are falling the recommendations And are monitoring for edema, looking at output. If they are following restrictions, plans and guidelines.
|
True |

