![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
EWG
|
carbonyl, ester, nitro, nitriles, sulfoxide
|
|
|
How can enolization process be catalysed?
|
using base to form the enolate ion |
|
|
How is the enolate ion stabalized?
|
By resonance |
|
|
What type of species are enolate ions?
|
nucleophiles |
|
|
What types of enolates are there?
|
singly stabilised and double stabilised |
|
|
single stabilised enolate + examples?
|
e.g. aldehydes, ketones, esters, nitriles, nitros, sulfoxides (make sure you know all of these |
|
|
pka's of CH-C=O protons(singly stabalised)? and base required to remove?
|
Strong base - lithium diisopropyl amide, BuLi, NaH, LDA |
|
|
Reaction conditions for irreversible deprotonation to enolate?
|
low temp, no H⁺ source, strong base |
|
|
How to alkylate an enolate(or derivitive)?
|
2) alkly halide that are Sn2 active |
|
|
What alkyl halides are Sn2 active?
|
primary maybe secondary but not tertiary |
|
|
exceptions to alkylation of enolates?
|
unsymmetrical ketones |
|
|
problem with alkylation of aldehydes?
|
enolate reacts in competition with undeprotonated aldehyde |
|
|
How to alkylate aldehydes?
|
use an enolate equivalent - enamines, silyl enol ethers, aza enolates |
|
|
making enamines as enolate equivalent?
|
carbonyl + secondary amine + H⁺
|
|
|
enamine back to carbonyl?
|
add water
|
|
|
What is enamines good for?
|
react with very reactive alkylating agents (allyl or benzyl systems) selectively |
|
|
Making silyl enol ethers as enolate equivalent?
|
carbonyl + trimethyl silyl chloride
|
|
|
silyl enol ether back to carbonyl?
|
acid or halogen compounds
|
|
|
What are silyl enol ethers good for?
|
less reactive than lithum enolates or enamines and will only react with strong electrophiles such as carbocation species formed from tertiary alkyl halides (Sn1 type alkylating reagents) and a lewis acid TiCl₄ |
|
|
making aza-enolates as enolate equivalent?
|
imine + strong base -> aza-enolate |
|
|
aza-enolate to carbonyl?
|
H⁺ + H₂O |
|
|
What are aza-enolates good for?
|
best for reactions involving Sn2 type alkylating reagents |
|
|
problem with unsymmetrical ketons?
|
may be more than one possible deprotonation route |
|
|
regioselective control?
|
kinetic or thermodynamic |
|
|
Kinetic control for deprotonation of an unsymmetrical ketone
|
large bulky strong bases like LDA will remove the least hindered H at low temperature |
|
|
Thermodynamic control for deprotonation of an unsymmetrical ketone?
|
1) base at higher temperature and longer reaction times to allow the more stable enolate to form 2) silyl enol ethers at room temperature |
|
|
Summary of which enolate equivalent for aldehyde is best for which alkylating agent type?
|
Sn1 type alkylating agents- silyl enol ether Sn2 type alkylating agents - aza-enolates |
|
|
Doubly stabilised enolates? + examples?
|
Two EWG are attached to a single carbon atom e.g. 1,3-Dicarbonyl
|
|
|
pka of double stabilised enolate hydrogens? + bases required?
|
10-15 ∴ only weak bases required e.g. K₂CO₃, NaOEt |
|
|
Dialkylation of doubly stabilized enolates?
|
can occur when there are two hydrogens on appropriate carbon, useful when synthesising carbocyclic rings |
|
|
Diester decarboxylation?
|
1)NaOH, H₂O -> carboxylate anion 2) HCl, Heat -> lose CO₂ |
|
|
Further reactions of enolates?
|
Michael addition reactions, aldol reactions, Claisen condensations |
|
|
Michael addition reactions?
|
michael acceptors are good electrophiles for enolates in conjugate addition reactions |
|
|
What is a michael acceptor?
|
α-β unsaturated carbonyl (carbonyl can be any EWG) |
|
|
Aldol reactions?
|
reaction of an enolate anion with a further >C=O system, which can be with the same carbonyl starting material (self condensations) or with a differert carbonyl (crossed aldol reactions)
|
|
|
E1cb elimination from aldol?
|
if the aldol reaction is carried out in excess base, it can eliminate to give the unsaturated carbonyl deriviative |
|
|
How to make the correct aldol?
|
-use one carbonyl that cannot enolize |
|
|
Claisen condensations?
|
|
|
|
When are claisen condensations most effective?
|
when the ester electrophile cannot enolise allowing useful acetylation reactions to be carried ou |
|
|
Oxidation level of oxygen containing functional groups?
|
aldehydes, ketones - 2 bonds acids, esters, acid chlorides, amides - 3 bonds |
|
|
Secondary alcohol to ketones?
|
(Jones oxidation) |
|
|
Primary alcohols to aldehydes?
|
Need to prevent overoxidation -TPAP, NMO -swern oxidation -TEMPO, NaOCl |
|
|
TPAP?
|
Tetra-n-propylammonium perruthenate (TPAP) is used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes. It is used catalytically alongside a cooxidant like NMO
|
|
|
Swern oxidation?
|
DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), oxalyl chloride and base (Et₃N) used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes
|
|
|
TEMPO?
|
|
|
|
What can NaBH₄ reduce?
|
ketones and esters to alcohol imine to amine slowly reduces ester to alcohol |
|
|
What can NaCNBH₃ reduce?
|
imine to amine slowly reduces aldehydes and ketones to alcohol |
|
|
What can LiBH₄ reduce?
|
imine to amine aldehyde,ester and ketone to alcohol |
|
|
What can LiAlH₄ reduce?
|
imine to amine aldehyde, ester and ketone to alcohol amide to amine amide to aldehyde at 0⁰C carboxylic acid slowly to alcohol |
|
|
What can BH₃ reduce?
|
amide to amine carboxylic acid to alcohol aldehyde, ketone and ester slowly to alcohol |
|
|
Wolff-Kishner reaction?
|
|
|
|
What do we use DIBAL for?
|
ester -> aldehyde |
|
|
Summary reduction 1)Ketone -> secoundary alcohol 2)Ester -> aldehyde 3)Ester, amides -> primary alcohols 4)ketones to CH₂ |
1)NaBH₄, LiAlH₄ 2)DIBAL 3)LiAlH₄ 4)NH₂NH₂ + KOH |
|
|
What can reductive hydrogenation reduce?
|
C=C, C=N, C≡C, C≡N
|
|
|
Why can't hydrogen reduce carbonys? |
it is not nucleophilic enough |
|
|
Hydrogenation catalysts? |
Pd, Pt |
|
|
catalytic reduction of alkenes?
|
hydrogens mainly go on the same face |
|
|
catalytic reduction of alkynes
|
can be reduced all the way to saturated, or selectively reducet to cis-alkenes using Lindlar's catalyst, (Pd, CaCO₃ and Pb(OAc)₂)
|
|
|
Dissolving metal reductions?
|
as sodium and lithium metals release electrons in liquid ammonia the electrons can be trapped by either C≡C or aromatic systems in Birch reduction reactions
|
|
|
Birch reduction of alkynes? |
Na dissolving in NH₃, forms the more thermodynamically stable E-configuration (trans)
|
|
|
Birch reduction of aromatics ?
|
Li, NH₃(l), EtOH, Et₂O
gives dienes, different substituents gives different products |
|
|
electron withdrawing group on aromatic birch reduction? + examples of electron withdrawing groups?
|
|
|
|
electron donating groups effect on aromatic birch reduction? + examples of electron donating groups? |
ortho/meta reduction
EDG = CH₃, OMe, NH₂ etc |
|
|
anilines birch reduction?
|
gives conjugated dienamine |
|
|
Three types of elimination reaction?
|
E1, E1cb, E2 |
|
|
E1 elimination?
|
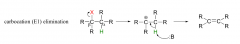
|
|
|
E2 elimination?
|
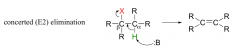
|
|
|
E1cb elimination?
|
reverse of E1, base is deprotonated first, then leaving group leaves
|
|
|
Julia Olefination reation?
|
Forms E-configuration by connection of two molecular fragments and a one electron reduction
|
|
|
Mechanism of Julia Olefination reaction?
|
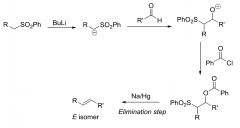
|
|
|
Modified one-step Julia Olefination reaction?
|
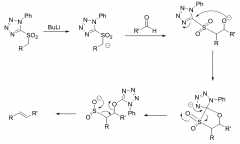
|
|
|
Peterson Reaction?
|
gives mainly Z-alkenes
|
|
|
Peterson Mechanism?
|
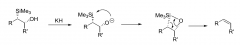
|
|
|
problem with peterson mechanism?
|
difficult to synthesise the diastereomer starting material |
|
|
Wittig Reaction(+reagents)?
|
1)alkyl halide + Ph₃P + BuLi 2) + carbonyl |
|
|
Making the phosphonium ylid?
|
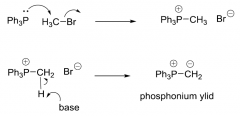
|
|
|
carbonyl + phosphonium ylid mechanism?
|
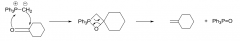
|
|
|
Stabilised ylids?
|
systems bearing EWG give predominantly E-alkenes (reasoning why is still debated) |
|
|
unstabilised ylids?
|
systems bearing EDG give predominantly z-alkenes |
|
|
Making Z-alkenes?
|
peterson base induced elimination Reduction of alkynes using Lindlar's catalyst |
|
|
Making E-alkenes?
|
julia and one-step julia reaction reduction of alkynes by dissolving metal reactions |
|
|
Monohydroxylation reactions?
|
hydroborylation |
|
|
Oxymercuration process?
|
1)Hg(OAc)₂ + H₂O 2)NaBH₄ Forms the most substituted alcohol |
|
|
Oxymercuration process mechanism?
|
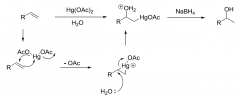
|
|
|
Hydroborylation?
|
1)BH₃ 2) H₂O₂, NaOH gives primary alcohols |
|
|
Dihydroxylation of alkenes?
|
mCPBA |
|
|
making cis diol from alkenes?(mechanism)
|
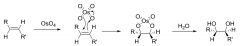
|
|
|
making trans-diols from alkenes?
|
meta-chloro-perbenzoic acid(mCPBA) followed by base induced ring opening |
|
|
Trans-diols from alkenes mechanism?
|
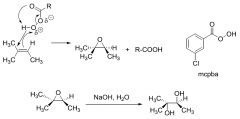
|
|
|
ozonolysis?
|
C=C cleavage using O₃ giving a range of products depending on the secound reagent added |
|
|
different reagents that can follow ozonolysis and their products?
|
NaBH₄ - > RCH₂OH + R'CH₂OH H₂O₂ -> RCO₂H + R'CO₂H |
|
|
|
|

