![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the functions of skeletal muscles |
action- movement produced when a muscle contracts concentrically in isolation Other roles: agonist- muscle producing the desired movement by contracting either concentrically or eccentrically antagonist - muscle which muse relax to allowed desired movement to occur Fixator- stabilises a body segment to allow another muscle perform an action synergist- cancels the unwanted action of the agonist |
|
|
Phases of soccer kick |
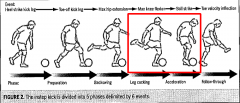
|
|
|
At the acceleration phase describe the predominant movement and the muscles responsible for producing the action |
The predominate movement: hip flexion List the muscle responsible for hip flexion: iliopsaos (major hip felxion) TFL (hip abduction & internal rotation) rectus femoris (knee extension) pectineus (hip adduction) sartorius ( hip abduction & external rotation) |
|
|
Which muscles are recruited first |
Which muscles are recruited first? - ones requiring the least synergy - muscles that cross one joint recruited first |
|
|
What is the role of the recruited muscle and what muscles are stabilizing the hip |
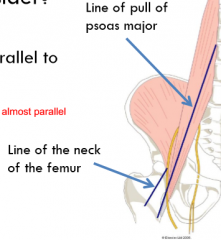
Role of recruited muscle: -prime mover Stabilizing the hip joint: -any muscle with a line of pull parallel to neck of femur -iliopsoas, pectineus |

