![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
235 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
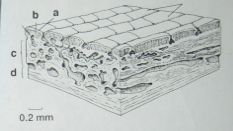
identify the labeled structures |
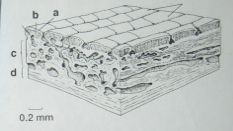
a:Enamel |
|
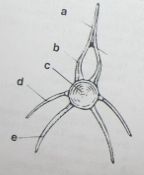
identify the labeled structures |
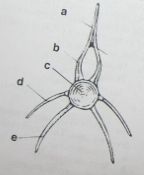
a: Neural Spine |
|
|
Kidney tubules and ducts are derived from the… |
-Intermediate mesoderm (Mesomere) |
|
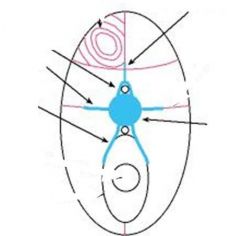
Identify structures at arrows |
Ventral rib is also the remnant of the hemal arch |
|
|
Kidneys are not derived from… |
-Dermis nor epidermis |
|
|
The notochord is derived from the… |
-Mesoderm-chordamesoderm |
|
|
The smooth muscle layers in the wall of the digestive tract are derived from… |
- Lateral plate mesoderm (Hypomere), splanchnic |
|
|
The pericardium is a derivative of the… |
-Lateral plate mesoderm (Hypomere) |
|
|
The vertebrate coelom forms by the splitting (delamination) of the… |
-Lateral plate mesoderm (Hypomere) |
|
|
The vertebrae are derived from… |
-Mesoderm-epimere (dorsal) |
|
|
The ventral body cavity is also called the… |
-Coelom (Celom) |
|
|
The transverse septum in a shark separates the… |
-Pericardial and (pleuro)peritoneal cavities. |
|
|
The inner ear is derived from the… |
-Epidermal placodes |
|
|
Epaxial muscles of the trunk are derived from… |
-Somites |
|
|
Muscles in the throat and floor of the oral cavity that arise as anterior extensions of myotomes from the trunk are called the… |
-Hypobranchial muscles |
|
|
Muscles that originate in the trunk but grow posteriad ventral to the gills and ultimately connect to the lower jaw. |
-Hypobranchial muscles |
|
|
Wide, thin, sheet-like muscles that develop below the horizontal skeletogenous septum of the posterior trunk are called… |
-Hypaxial muscles |
|
|
The process of _?_ produces the dorsal hollow nerve cord |
-Neurulation |
|
|
The dorsal hollow nerve tube, a chordate characteristic, is formed from _?_, in a process called _?_. |
-Ectoderm (neural plate)…neurulation. |
|
|
Which of the following extraembryonic membranes is found in embryos of all vertebrate classes? |
-Yolk sac |
|
|
Which of the following extraembryonic membranes do reptilian avian, and mammalian embryos possess? |
-Allantois |
|
|
The eggs of a bird are _?_, and its cleavage pattern is _?_. |
-Macrolecithal, extremely telolecithal…meroblastic. |
|
|
An unidentified vertebrate lays eggs that are microlecithal and isolecithal. What type of cleavage do you expect to occur in this vertebrate embryo? |
-Holoblastic, equal |
|
|
Glands that release their secretion by concentrating it in the tips of the secretory cells, and then “pinch off” the tips (i.e., with loss of cytoplasm from their secretory cells) are called… |
-Apocrine glands |
|
|
Glands that release their secretion by exocytosis (i.e. with no loss of cytoplasm from their secretory cells) are called… |
-Merocrine (Eccrine) glands |
|
|
Glands in which cells contain their secretion in the cytoplasm, break free of the epithelium and lyse to release their secretion (and must be replaced by mitosis in stem cells) are called… |
-Holocrine glands |
|
|
outermost (i.e. most superficial) layer of the vertebrate epidermis is the… |
-Stratum corneum |
|
|
The outermost, dead (and highly keatinized) layer of the mammalian epidermis is the… |
-Stratum corneum |
|
|
The epidermis contains a layer of actively dividing cells. This layer is the… |
-Stratum basale |
|
|
The horny (cornified) protein that gives the stratum corneum of the epidermis its name is… |
-Keratin |
|
|
Feathers are composed of… |
-Keratin |
|
|
Feathers are derived from… |
-epidermis |
|
|
The unguis is a part of a… |
-Claw |
|
|
Human teeth are derived from… |
-Both dermis and epidermis |
|
|
The integumentary chromatophore that contains a dark brown pigment is the… |
-Melanophore |
|
|
Sebaceous glands… |
-Secrete an oily substance that lubricates skin and hair |
|
|
The type of scale seen in sharks is called a(n)… |
-Placoid scale |
|
|
The layer of dentin in placoid or ganoid scales is deposited by cells derived from the… |
-Dermis |
|
|
Scales on a snake are derived from… |
-Epidermis |
|
|
The layer of horn on a true horn is derived from… |
-Epidermis |
|
|
Dermal bone is not found in… |
-A horny tooth from a lamprey |
|
|
Dermal bone is found in… |
-A ganoid scale |
|
|
Osteoderms are derived from… |
-Dermis |
|
|
Unlike the situation in most vertebrates, a shark’s pectoral girdle contains no… |
-Elements derived from dermal bone |
|
|
An osteon or Haversian system is… |
-A concentric arrangement of cells and layers of extracellular matrix around a central tube. |
|
|
Bone development that occurs within a cartilaginous template is called… |
-Endochondral ossification |
|
|
When considered to be a joint, the epiphyseal plate of a long bone is an example of a… |
-Cartilaginous synarthroses |
|
|
In a fossorial mammal that uses its front limbs to dig, you would expect to find… |
-A relatively long olecranon process and short shaft of the radius and ulna |
|
|
The hyomandibula and stapes are part of the… |
-Splanchnocranium---second visceral arch |
|
|
The dentary bones are part of the… |
-Dermatocranium |
|
|
The first pharyngeal (visceral) arch does not contribute to the… |
-Hyoid apparatus (bone and/or cartilage). |
|
|
The hyoid bone is part of the… |
- Splanchnocranium---second visceral arch |
|
|
Which of the following elements of the visceral skeleton is not correctly paired with its derivative? |
-Second pharyngeal arch…malleus |
|
|
Mandibular (Meckel’s) cartilage and the malleus are part of the… |
- Splanchnocranium---first visceral arch |
|
|
Otic (Petrosal, Petrous) portion of the temporal is part of the… |
-Neurocranium- sense capsules |
|
|
The main power stroke in fishes comes from contraction of the… |
-Axial muscles |
|
|
In a muscle, the smallest unit that is capable of contraction is the… |
-Sarcomere |
|
|
The contractile unit within a skeletal muscle cell is the… |
-Sarcomere |
|
|
The basic, subcellular unit of muscle contraction in a skeletal muscle cell is the… |
-Sarcomere |
|
|
A sarcomere is… |
-The basic functional unit of skeletal muscle contraction |
|
|
In a muscle, the fascicle (fasciculus) is covered by a(n)… |
-Perimysium |
|
|
The connective tissue that wraps around a bundle of muscle cells (fascicle) is called the… |
-Perimysium |
|
|
In a first-class (first-order) lever… |
-The fulcrum lies between the force (effort) and the load (resistance) |
|
|
In a second-class (second-order) lever… |
-The load (resistance) lies between the force (effort) and the fulcrum. |
|
|
Which of the following simple tools works by using the principle of the second-order (second-class) lever? |
-A wheelbarrow |
|
|
In a third-class (third-order) lever… |
-The force (effort) lies between the fulcrum and the load (resistance). |
|
|
Contraction of _?_ cells is under voluntary control |
-Skeletal muscle |
|
|
Contraction of _?_ cells is not under voluntary control |
-Both cardiac and smooth muscle |
|
|
Control of contraction of these cells is involuntary… |
-Both cardiac and smooth muscle |
|
|
Striations are seen in the cells of… |
-Both cardiac and skeletal muscle |
|
|
Cells that exhibit striations… |
-Both cardiac and skeletal muscle |
|
|
Intercalated disks are unique characteristics of… |
-Cardiac muscle cells |
|
|
Cells that exhibit intercalated disks… |
-Cardiac muscle |
|
|
Cells that are multinucleated… |
-Skeletal muscle |
|
|
The internal anal sphincter is made of muscle cells that are… |
-Smooth and involuntary |
|
|
A motor unit is… |
-All skeletal muscle cells that are innervated by a particular motor neuron. |
|
|
In mammals, the respiratory and digestive systems share a common “tube” in the… |
-Pharynx |
|
|
Which of the following describes the respiratory portion of a vertebrate’s respiratory system? |
-It is a simple squamous epithelium |
|
|
Which of the following is least likely to describe the respiratory portion of a vertebrate’s respiratory system? |
-Its epithelium is keratinized |
|
|
Exclusive reliance on cutaneous respiration would be most likely in a… |
-Small, thin-skinned vertebrate in a moist forest |
|
|
In fishes, the complex arrangement of gills into primary lamellae (gill filaments) and secondary lamellae… |
-Creates a countercurrent system between the flow of blood in the capillary beds of the gill and the flow of water through the gills. |
|
|
Water enters the pharynx of a shark through two possible openings. These are the… |
-Mouth and spiracles (pseudobranchs). |
|
|
A fishes holobranch contains… |
-A gill arch |
|
|
Which of the following is a digestive secretion that is produced by the liver? |
-Bile |
|
|
The following is secreted by the Pancreas… |
-Amylase (Ptyalin) and bicarbonate ions |
|
|
The stomach secretes… |
-Pepsinogen/Pepsin |
|
|
The secretion found in lungs is… |
-Surfactant |
|
|
The salivary glands secrete… |
- Amylase (Ptyalin) |
|
|
The _?_ contains the epithelium that lines the lumen of the alimentary canal |
-Mucosa |
|
|
Contains the myenteric nerve plexus (of Auerbach). |
-Muscularis externa |
|
|
Contraction of muscles in this layer cause peristalsis and mixing movements. |
-Muscularis externa |
|
|
The layer next to the lumen of the alimentary canal |
-Epithelium |
|
|
The outermost (most peripheral) layer of the mucosa |
-Muscularis mucosae |
|
|
Which of the following structures is a remnant of the ventral mesentery? |
-Lesser omentum |
|
|
Lipids (Fatty acids) are absorbed in the _?_, where they directly enter the _?_. |
-Small intestine…lacteals. |
|
|
The muscle that regulates the movement of stomach contents into the intestine is the… |
-Pyloric sphincter |
|
|
A muscle that performs the same action as the prime mover is said to be the prime mover’s… |
-Synergist |
|
|
In mammals, the _?_ prevents the passage of food into the trachea |
-Epiglottis |
|
|
In mammals, the tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi is called the… |
-Trachea |
|
|
In mammals, the internal nares (choanae) are an opening into the… |
-Nasopharynx (Nasal pharynx). |
|
|
In mammals, the hard and soft palates form the floor of this region. |
-Nasal cavity |
|
|
In mammals, the thin-walled sacs that are arranged in grape-like clusters in the lungs and make up its respiratory surface are called the… |
-Alveoli |
|
|
The respiratory exchange surface of the mammalian respiratory system are located in the… |
-Alveoli |
|
|
In the mammalian lungs, the air in an alveolus; and the blood in an associated vascular capillary bed form a(n)… |
-Uniform pool flow system |
|
|
Normal inspiration (inhalation) in mammals is mainly the result of… |
-Contraction of the diaphragm. |
|
|
In a bird’s respiratory tract, which of the following makes up the actual respiratory surface where gas exchange occurs? |
-Parabronchi and air capillaries |
|
|
The sound-producing region located at the posterior end of a bird’s trachea is called the… |
-Syrinx |
|
|
In the bird’s lungs, the air that flows through parabronchi; and the blood in the capillary beds form a(n)… |
-Cross-current flow system |
|
|
In the avian respiratory system, the air sacs… |
-Have diverticula that enter the bones so that a “flight bellows” pumping system is created when the bird is flying |
|
|
Fishes whose swim bladders have no opening to the foregut during post-embryonic life are said to be… |
-Physocleistous |
|
|
Fishes whose swim bladders retain an opening to the foregut during post-embryonic life are said to be… |
-Physostomous |
|
|
A fish whose swim bladder has no opening to the foregut regulate the amount and composition of gases in the swim bladder by using its… |
-Red gland |
|
|
Which structures are responsible for regulating gas pressure in the swim (gas) bladders of fishes? |
-Retia mirable in red glands |
|
|
In amniotes, systemic veins carry blood to the… |
-Right atrium |
|
|
Which of the following are amniotes? |
-Birds, mammals, reptiles |
|
|
Tunicates are… |
-Urochordates |
|
|
In a fish’s heart (heart of a shark), what is the correct pattern of blood flow? |
-Sinus venosusatriumventricleconus arteriosus |
|
|
In fishes, amphibians, and most reptiles, blood from the veins enters the _?_ before entering the (right) atrium |
-Sinus venosus |
|
|
In a mudpuppy salamander, the lowest blood pressure would be found in the… |
-Sinus venosus |
|
|
Under normal circumstances, the primary pacemaker of the mammalian heart is the… |
-sinoatrial node |
|
|
The third aortic arch of amniotes… |
-Contributes to the carotid artery complex |
|
|
The carotid arch is derived from the… |
-Third pair of aortic (branchial) arches. |
|
|
Forms the “carotid arch” |
-Branchial arch II |
|
|
Connection of this arch to the dorsal aorta is called the ductus arteriosus (which closes at birth in mammals) |
- Branchial arch III |
|
|
Forms the “pulmonary arch” |
- Branchial arch VI |
|
|
Forms the “systemic arch” |
- Branchial arch IV |
|
|
The “arch of the aorta” is formed from its left side in mammals and its right side in birds |
- Branchial arch IV |
|
|
Which of the following statements comparing major lymphatic vessels to veins in mammals is false? |
-Both empty directly into the right atrium |
|
|
Which of the following statements comparing major lymphatic vessels to veins in mammals is true? |
-Both carry fluid toward the heart |
|
|
In vertebrates (except mammals) the renal portal system drains the blood from the… |
-Tail and hind limbs |
|
|
This system is absent in mammals… |
-Renal portal system |
|
|
Carries nitrogenous waste-rich blood from the site of waste production directly to the site of waste “treatment” |
-Renal portal system |
|
|
In air-breathing amphibians, pulmonary arteries receive blood from the… |
-Ventrical (there’s only one) |
|
|
The nitrogenous waste that requires the most energy to produce, but is the least toxic is… |
-Uric acid |
|
|
The nitrogenous waste that requires the least energy to produce, but is the most toxic and water-soluble is… |
-Ammonia |
|
|
The Wolffian duct is another name for the… |
-Mesonephric (Nephric) duct. |
|
|
The oviduct and uterus (if present) are derived from the… |
-Mullerian duct |
|
|
The fallopian (Uterine) tube is derived from the… |
-Mullerian duct |
|
|
The rectum is derived from the… |
-Cloaca-coprodeum |
|
|
The ureter is derived from the… |
-Metanephric duct |
|
|
The urogentital sinus derived from the… |
-Cloaca-urodeum |
|
|
In most amniotes, the _?_ is the functional adult kidney |
-Metanephros |
|
|
In mammals, birds, and reptiles, the _?_ is the functional adult kidney |
-Metanephros |
|
|
In most amphibians and sharks, the _?_ is the functional adult kidney |
-Opisthonephros |
|
|
In the mammalian kidney, this structure empties into a minor calyx… |
-Collecting duct |
|
|
The glomerulus is the site of… |
-Pressure filtration |
|
|
Receives filtrate that is “squeezed” out of blood vessels by blood (hydrostatic) pressure… |
-Glomerular (Nephric or Bowman’s) capsule. |
|
|
In mammals, the tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct is called the… |
-Vas (Ductus) deferens. |
|
|
The Vas (Ductus) deferens is derived from the… |
-Wolffian duct |
|
|
The labia majora of the human female are derived from the same tissues as the _?_ of the male. |
-Scrotum |
|
|
The spongy urethra inside of a male mammal’s penis is derived from the embryonic (uro)genital folds and is homologous with the female’s… |
-Labia minora |
|
|
The “midbrain” is the… |
-Mesencephalon |
|
|
The corpora quadrigemina are part of the… |
-Mesencephalon |
|
|
The myelin sheath is formed by the membranes of the… |
-Schwann cells (Neurilemmal cells). |
|
|
The myelin sheath that covers axons in the peripheral nervous system is produced by… |
-Schwann cells |
|
|
In a nerve cell, the dendrites… |
-Conduct nerve impulses toward the cell body |
|
|
In a neuron, the axon… |
-Conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body |
|
|
Interneurons are… |
-Multipolar |
|
|
The two basic cell types that make up nervous tissue are… |
-Neurons and glial (neuroglial) cells. |
|
|
Choroid plexuses are found in the… |
-Ventricles of the brain. |
|
|
The connective tissue covering that surrounds a single muscle cell is the… |
-Endomysium |
|
|
An electroplax is… |
-A set of muscle cells that have been modified to produce an electrical discharge |
|
|
Electroplaxes are… |
-Modified muscle cells that act as electric organs in some fishes. |
|
|
In mammals, normal expiration results from… |
-Elastic recoil of lung tissues |
|
|
The ducts from both the liver and gall bladder fuse together to form a large duct called the… |
-Common bile duct. |
|
|
The duct that fills the liver is the… |
-Hepatic duct |
|
|
The membrane that lines the abdominal cavity (i.e., is attached to the inside of the body wall) is called the… |
-Parietal peritoneum |
|
|
True countercurrent flow is found between the blood and respiratory fluid (air or water) in the… |
-Gills of fishes. |
|
|
The elastic cartilage flap that covers the entrance to the trachea is called the… |
-Epiglottis |
|
|
In birds, the aorta (systemic arch) is derived from the… |
-Right fourth aortic arch |
|
|
Which of the following structures, when mature (functional), consists of a core of dermal bone covered by a keratinized sheath? |
-Bovine horn |
|
|
The pubic symphysis is an example of a… |
-Cartilaginous amphiarthroses. |
|
|
As plantigrade mammals walk, their _?_ come in contact with the ground |
-Tarsal/Carpal bones, metatarsal/metacarpal bones, and phalanges |
|
|
The region of the cloaca into which the reproductive and excretory systems empty is the… |
-Urodeum |
|
|
The shoulder (glenohumeral) joint is an example of a… |
-Synovial diarthroses. |
|
|
A synovial membrane and synovial fluid are found in a… |
-Diarthrosis |
|
|
Accordion-like pleats in the wall of the stomach that allow for its distension are called… |
-Rugae |
|
|
Large folds of the mucosa and submucosa that are found in the stomach… |
-Rugae |
|
|
Large folds of the mucosa and submucosa that are found in the small intestine… |
-Plicae circulares (Valves of Kerkring) |
|
|
Folds of the cell membrane found on individual epithelial cells… |
-Microvilli |
|
|
Multicellular, fingerlike projections found in the small intestine… |
-Villi |
|
|
Structures that contain lacteals… |
-Villi |
|
|
The photoreceptors of the eye are located in the… |
-Retina |
|
|
Maculae in the saccule (sacculus) and utricle (utriculus) are involved in… |
-Static equilibrium |
|
|
Pteridophores called xanthophores are… |
-Yellow in color |
|
|
Which of the following pigment cells contains yellow pigment? |
-Pteridophores |
|
|
Remnants of the prechordal cartilages (trabeculae) of the neurocranium are most clearly seen in the… |
-Ethmoid complex |
|
|
Ethmoid bone or complex of bones are part of the… |
-Neurocranium- parachordal or prechordal (tabecular) cartilages |
|
|
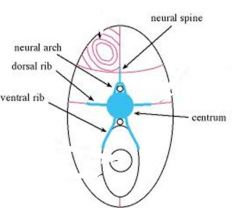
The neural arch is found in _?_ vertebrae, and the hemal arch is found in _?_ vertebrae. |
-All…caudal. |
|
|
To an anatomist studying human beings, supination is… |
-Returning the radius and ulna to anatomical position after they have been crossed. |
|
|
The scapula undergoes which of the following actions when a person shrugs the shoulders? |
-Elevation and depression. |
|
|
The extrinsic eye muscles are derived from… |
-Preotic somitomeres (somites) |
|
|
Teeth attaching to the side of the jawbones is called… |
-Pleurodont dentition. |
|
|
Teeth attaching to the surface (i.e. with a shallow socket) of the jawbones is called… |
-Acrodont dentition |
|
|
The function of trypsin is… |
-Digestion of proteins |
|
|
Many proteolytic enzymes (proteases) are secreted as inactive forms called proenzymes (zymogens) because… |
-The cells that secrete these enzymes must be protected from “self-digestion” |
|
|
The function of bile salts is… |
-Emulsification of lipids |
|
|
The glandular portion of the stomach that is specialized for chemical digestion in reptiles and birds is the… |
-Proventriculus |
|
|
Monosaccharides and amino acids are absorbed in the _?_, where they directly enter the _?_. |
-small intestine…blood capillaries |
|
|
Most amino acids and monosaccharides are reabsorbed here… |
-Proximal convoluted tubule |
|
|
Permeability of its walls is dependant upon the concentrations of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) in the blood. |
-Both collecting duct and distal convoluted tube |
|
|
The wall of its descending limb is permeable to water, while the wall of its ascending limb is impermeable to water… |
-Nephron loop (of Henle) |
|
|
After allowing microorganisms in the large intestine to digest cellulose, rabbits absorb the resulting simple sugars by… |
-Passing the digested food out of the digestive tract and re-ingesting it. |
|
|
Become T-cells and B-cells of the immune system… |
-Lymphocytes |
|
|
Formed elements that can initiate clotting… |
-Thrombocytes (Platelets) |
|
|
Formed elements that contain hemoglobin… |
-Erythrocytes |
|
|
Most numerous type of white blood cell... |
-Granulocytes |
|
|
Precursors of macrophages… |
-Monocytes |
|
|
The atria must completely empty before the ventricles begin to contract. The portion of the cardiac conducting (nodal) system that slows conduction of impulses to allow this to happen is the… |
-Atrioventricular (AV) node |
|
|
The epicardium is synonymous with the… |
-Visceral pericardium |
|
|
In the wall of a major blood vessel (i.e. artery or vein), the layer of smooth muscle cells is located in the… |
-Tunica media |
|
|
Valves are found in… |
-Lymphatic vessels |
|
|
A double-circuit system is most likely an evolutionary adaption that directly solved the need to… |
-Increase blood pressure in arteries that carry blood from the gills to the body tissues. |
|
|
The most consistently useful definition of the vein/venule group of blood vessels is… |
-“Blood vessesls that carry blood toward the heart” |
|
|
Carries hormone-rich blood from the site of hormone-production directly to the hormones’ target tissue |
-Hypophyseal (hypothalamic) portal system |
|
|
Carries nutrient-rich blood from the site of nutrient absorption directly to the site of nutrient storage |
-Hepatic portal system |
|
|
In this system, blood passes through two capillary beds connected by arteries/arterioles before returning to the heart. |
- Not of a portal system |
|
|
Closure of pre-capillary sphincters… |
-Causes blood to bypass the capillary bed and enter the arteriovenous shunts (throroughfare channels). |
|
|
What provides the force that is used to propel fluids though lymphatic vessels and veins? |
-Contraction of adjacent skeletal muscles |
|
|
Except in some teleost fishes, ovulation in vertebrates releases an egg or oocyte into the… |
-Celom |
|
|
Astrocytes are most closely associated with… |
-The blood-brain barrier |
|
|
White matter in the CNS looks white because of the presence of… |
-Oligodentrocytes (Oligodendroglia). |
|
|
Bundles of white matter in the peripheral nervous system are called… |
-Nerves |
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid is returned to the blood in the… |
-Arachnoid granulations (Arachnoid villi) |
|
|
The cerebral aqueduct of Sylvius connects… |
-The third ventricle to the fourth ventricle. |
|
|
Contains the auditory and optic lobes… |
-Mesencephalon |
|
|
Contains the cerebrum |
-Telencephalon |
|
|
Contains the eyes and pineal body |
-Diencephalon |
|
|
Contains the medulla oblongata |
-Myelencephalon |
|
|
Contains the pons varolii and cerebellum |
-Metencephalon |
|
|
The connective tissue covering that surrounds an individual nerve fiber is the… |
-Endoneurium |
|
|
Osteoclasts… |
-Digest bone matrix |
|
|
Blood vessels in compact bone are located in… |
-Central (Haversian) canals |
|
|
The area on the pelvic girdle with which the hindlimb articulates is called the… |
-Acetabulum |
|
|
Sutures in the skull are examples of a… |
-Fibrous synarthrosis |

