![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nucleus (10-20um) |
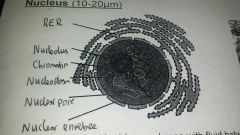
N.envolope: double membrane with fluid between,contains nuclear pores to allow substances through. Controls entry/exit of materials in nucleus N.pores: allows passage of large molecules like mRNA,3000 pores in a nucleus histones Nucleoplasm: jelly like material that makes up the bulk of nucleus,contains linear DNA & histones Nucleolus: small dense spherical region within the Nucleoplasm which makes rRNA & ribosomes Nucleolus: small dense spherical region within the Nucleoplasm which makes rRNA & ribosomes |
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
●series of flattened membrane bound sacs called cisternae ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM: (Studded with ribosomes) ●provide large SA for protein synthesis & glycoproteins synthesis made on attached ribosome ● provide pathway for the transport of proteins SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ●no ribosomes,so appear smooth ●function to synthesise,store & transport lipids & carbohydrates Cells that make & store large amounts of CPL have a large number of extensive ER E.g. Liver Cells & Epithelial Cells line the intestine |
|
|
Mitochondria (1-10um) |
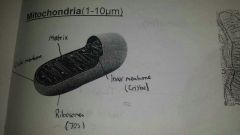
●spherical or sausage shaped with double membrane,controls entry/exit of materials ●Inner membrane highly folded into cristae,provides large surface area for attachment of enzymes for respiration ●central part is the matrix, contains proteins,lipids,ribosomes & mitochondrial DNA that allows the mitochondria to control production of their own proteins
Provides/synthesis ATP by aerobic respiration
|
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
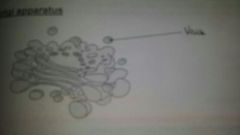
●stacks of membrane bound flattened sacs called cisternae with small ronded hollow structures called vesicles ●recieves proteins & lipids from ER & may modify them (+carb) ●labels them allowing them to be sorted & sent to the right destination ●once labelled they are transported to the vesicle & pinched of from the ends of the golgi cisternae ●vesicles may move to the cell surface,fuse with the membrane and release the contents to the outside E.g. secretory enzymes ●●golgi also form lysosomes ●well developed in secretory cells like epithelial cells
|
|
|
Chloroplasts (2-10um long & 1um diameter) |

●found in plant cells & protocists ●2 membranes separated by fluid filled space ●chloroplasts carry out photosynthesis● carry out photosynthesis ● carry out photosynthesis●C.Envelope is a double plasma membrane that surrounds the organelle & controls what enters/leaves the cell ●Inner membrane is folded into sacs called thylakoids (stack = granum) Provides large SA ●chlorophyll molecules are on the thylakoid membrane & in integranal lamella.This is where the 1st stage of photosynthesis takes place ●Stroma is a fluid filled matrix where the 2nd stage of Photosynthesis takes place ●contains all the enzyme needed ●starch granules can be found here ●chloroplasts contain DNA & ribosomes so they can manufacture some proteins needed for photosynthesis |
|
|
Lysosomes |
Spherical Sacs with single membrane Contain powerful digestive enzymes/lysozymes to break down/hydrolyse materials |
|
|
Vesicles |
Membrane bound sacs Carry different substances around cells Contains phospholipid bilayer |
|
|
Ribosomes |
●No membrane ●found in ER & cytoplasm ●have 2 subunits ●both subunits contain rRNA & protein 80s = eukaryotic 70s = prokaryotic |
|
|
Vacuoles |
●fluid filled sacs surrounded by a single membrane called a tonoplast ●Contains water,mineral salts,sugars,amino acids,waste & pigments ●maintains cell stability by pushing cytoplasm against cell wall to make the cell turgid ●support plant structure when lots of cells are together ●Involved in isolation of unwanted chemicals |
|
|
Cell wall |
●In plants made up of cellulose ●provide strong wall for strength & support ●In fungi made up of chitin ●In bacteria/prokaryote made up of peptidoglycan/murein |

