![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Corticospinal tracts
|
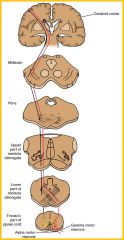
pathways concerned with voluntary, discrete, skilled movements (especially those of distal parts of limbs)
|
|
|
Reticulospinal tracts
|
facilitate or inhibit activity of alpha and gamma motor neurons in anterior gray columns and thus can facilitate or inhibit voluntary movement or reflex activity
|
|
|
Tectospinal tract
|
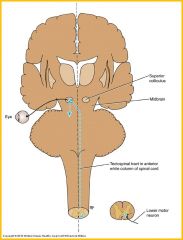
concerned with reflex postural movements in response to visual stimuli
|
|
|
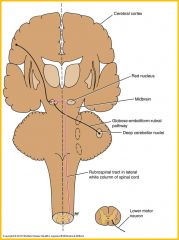
Rubrospinal tract
|
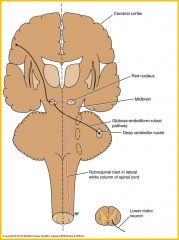
acts on both alpha and gamma motor neurons in anterior gray columns and facilitates activity of flexor muscles and inhibits activity of extensor or antigravity muscles
|
|
|
Vestibulospinal tract
|
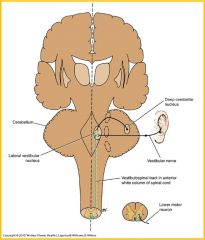
facilitates activity of extensor muscles by acting on motor neurons in anterior gray columns, inhibits activity of flexor muscles and is concerned with postural activity associated with balance
|
|
|
Olivospinal tract
|
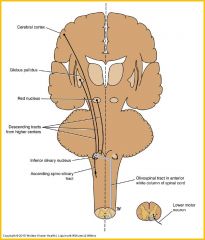
may play a role in muscular activity
|
|
|
Descending autonomic fibers
|
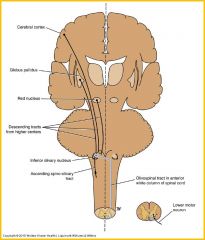
concerned with control of visceral activity
|
|
|
Cerebellar circuits
|
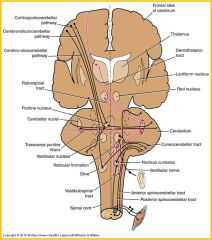
Cerebellum receives information from cerebral cortex, including motor areas and is also informed of changes in lengths and tensions of muscles, position and angular movements of the head
Output of cerebellar nuclei: primary a supplementary motor areas, through a relay in the posterior division of the ventral lateral thalamic nucleus (VLp) Other cerebellar efferents influence lower motor neurons through connections with vestibular nuclei and nuclei of reticular formation |
|
|
Basal Ganglia
|
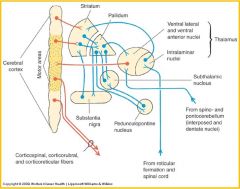
Motor circuitry of basal ganglia involved in transfer of information from whole of neocortex to motor areas, in particular the premotor and supplementary
motor areas Striatum serves as repository of instructions for fragments of learned movements |

