![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Frontal lobe |
Associated with Attention, Motivation, Emotional social And sexual control, verbal expression, judgement, spontaneity, problem solving, decision making, motor integration, voluntary movement, sequencing |
Many young male TBI patients |
|
|
Temporal lobe |
Short term memory, receptive language, language comprehension, musical awareness, selective attention, object categorization, locating objects, face recognition, aggressive behavior visual memory, processing auditory and visual sensory input |
|
|
|
Gyrus |
Grooves of brain |
|
|
|
Sulcus |
Valleys between gyrus |
|
|
|
Name the four lobes of the brain |
Frontal, parietal, temporal, occupital |
|
|
|
Paraparesis
|
Partial paralysis of LE |
|
|
|
Tetra paresis |
All 4 limbs weak |
|
|
|
Tetra paresis
|
All 4 limbs weak |
|
|
|
Paraplegia |
Complete OR incomplete LE and trunk |
|
|
|
Neuron |
Basic building blocks of brain |
|
|
|
Neuron |
Information processing units in the brain receiving and transmitting information. They have three main parts cell body, axon and dendrites |
|
|
|
Neuron |
Information processing units in the brain receiving and transmitting information. They have three main parts cell body, axon and dendrites |
|
|
|
Neuron |
Special nerve fiber carries messages can have so many branches they can carry messages to thousands. They are covered by myelin sheath. Three different types: sensory neurons, motor neuron, inter neuron |
|
|
|
Sensory neuron |
Carry impulse from sense organs to the CNS |
|
|
|
Motor neuron |
Carry messages from CNS to muscle and glands in our body |
|
|
|
Interneuron |
Connect various neurons within brain and spinal cord carries info BETWEEN motor and sensory neurons |
|
|
|
Interneuron |
Connect various neurons within brain and spinal cord carries info BETWEEN motor and sensory neurons |
|
|
|
Meninges |
Three protective layers protecting the brain and spinal cord. Dura mater, arachnoid, and Pia mater |
|
|
|
Interneuron |
Connect various neurons within brain and spinal cord carries info BETWEEN motor and sensory neurons |
|
|
|
Meninges |
Three protective layers protecting the brain and spinal cord. Dura mater, arachnoid, and Pia mater |
|
|
|
Dura mater |
Outer most protective covering of brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
Interneuron |
Connect various neurons within brain and spinal cord carries info BETWEEN motor and sensory neurons |
|
|
|
Meninges |
Three protective layers protecting the brain and spinal cord. Dura mater, arachnoid, and Pia mater |
|
|
|
Dura mater |
Outer most protective covering of brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
Arachnoid layer |
Middle protective layer |
|
|
|
Interneuron |
Connect various neurons within brain and spinal cord carries info BETWEEN motor and sensory neurons |
|
|
|
Meninges |
Three protective layers protecting the brain and spinal cord. Dura mater, arachnoid, and Pia mater |
|
|
|
Dura mater |
Outer most protective covering of brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
Arachnoid layer |
Middle protective layer |
|
|
|
Pia matter |
Innermost protective layer |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Arteriorvenous Malformation |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Arteriorvenous Malformation |
|
|
|
AVM |
Collection of dysplastic plexiform vessels that is supplied by one or more arterial feeders and drained by one or more venous channels
Arteriovenous shunting occurs
There is direct communication between arterial and venous channels
Vast majority of all AVM's are located in the cerebral hemispheres only 15 o/o occur In the posterior fossa |
|
|
|
Clinical features of AVM |
Both genders equally affected -peak of presentation is between 20-49 - majority become symptomatic by age 50 - 50 o/o of pts present w/sx caused by hemorrhage: SAH 30o/o of cases, parenchyma line 23o/o, and IVH 16o/o, combined bleed occurs in 31o/o - overall risk of bleed is estimated at 2 to 4 o/o per year ( increases by that much each year so as it gets older higher the risk) |
|
|
|
Cortex |
the outer layer of the cerebrum (the cerebral cortex ), composed of folded gray matter and playing an important role in consciousness. |
|
|
|
Parietal lobe |
Posterior to the frontal lobe and superior to the temporal lobe, houses the cortex for sensation, optic radiations carrying sensory input from the eyes for visual interpretation, language centers including Broca's and Wernicke's areas. |
|
|
|
Occipital lobe |
Posterior aspect of the brain on top of the tentorium responsible for vision and interpretation of visual sensory signals also contains the primary visual cortex |
|
|
|
Basal ganglia |
Group of nuclei that serves as a coordinating center for several nerve tracts including muscle movement |
|
|
|
Limbic system |
A group of nuclei and cortical structures that encode memory and regulate autonomic nervous system and endocrine function in response to emotional stimuli. Consists of Hypothalamus, Amygdala, Cingulate gurus, Hippocampus. |
|
|
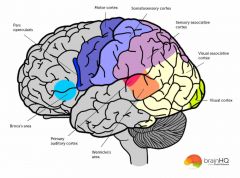
Front (Term) |
Different brain activity areas |
|
|
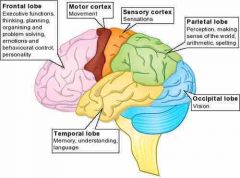
Front (Term) |
More activity centers |
|
|
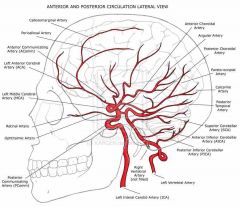
Front (Term) |
Brain circulation |
|
|
|
Neuron |
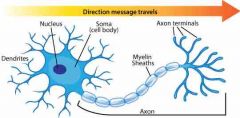
Image |
|

