![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
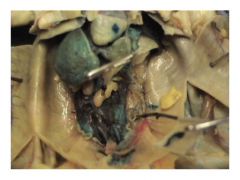
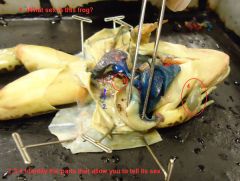
Q: What sex is this frog?
|
male
|
|
|
Q: What is the scientific name of the frog you studied?
|
Rana pipiens
|
|
|
Q: What are two things you can look for externally to tell if the frog is male?
|
vocal sacs and swollen thumbpads
|
|
|
Q: toward the head region
|
Anterior
|
|
|
Q: toward the hind region
|
Posterior
|
|
|
Q: the back surface
|
Dorsal
|
|
|
Q: toward or on or near the belly (front of a primate or lower surface of a lower animal)
|
Ventral
|
|
|
Q: the membrane of the ear that vibrates to transmit sound
|
tympanic membrane
|
|
|
Q: openings into the nasal cavity, both internally and externally, in the head of a vertebrate
|
nares
|
|
|
Q: a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach
|
esophagus
|
|
|
Q: the valve between the stomach and the small intestine
|
pyloric valve
|
|
|
Q: responsible for most chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients
|
small intestine
|
|
|
Q: organ that absorbs water from undigested material
|
large intestine
|
|
|
Q: dark, marble like organ usually near the stomach that produces, stores, and eliminates blood cells
|
spleen
|
|
|
Q: two long dark excretory organs that lie along back; they filter wastes (especially urea) from the blood and excrete them in urine
|
kidneys
|
|
|
Q: very obvious yellow stringy structures that provide warmth and store nutrients for hibernation and production of sex cells
|
fat bodies
|
|
|
Q: opening through which air enters trachea
|
Glottis
|
|
|
Q: two bumps in roof of mouth used to prevent prey from escaping
|
Vomerine Teeth
|
|
|
Q: stores bile until needed for digestion
|
gall bladder
|
|
|
Q: region in the back of the frog that allows passage of eggs or sperm and waste products of digestive and urinary systems
|
cloaca
|
|
|
Q: large, cream colored, muscular j-shaped organ that helps in mechanical and chemical digestion of food
|
stomach
|
|
|
Q: two stretchy grey organs in the chest that have lots of blood vessels since they are where blood picks up oxygen and loses carbon dioxide
|
lungs
|
|
|
Q: large blood vessel along the back that supplies oxygenated blood to several body parts
|
dorsal aorta
|
|
|
Q: a large vein that returns blood from lower body regions to the heart
|
inferior (posterior) vena cava
|
|
|
Q: two large veins that return blood from the upper body regions to the heart
|
left and right superior (anterior) vena cava
|
|
|
Q: major arterial branches from the conus arteriosus that each divide into 3 branches to carry oxygenated blood to body tissues
|
left and right truncus arteriosus
|
|
|
Q: arterial branch from the truncus arteriosus that supplies oxygenated blood to the head region
|
carotid arch
|
|
|
Q: middle arterial branch from the truncus arteriosus that loops around to meet the one from the other side, forming the dorsal aorta and supplying the forelimbs and lower body region with oxygenated blood
|
systemic (aortic) arch
|
|
|
Q: lower arterial branch from the truncus arteriosus which carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs and skin so it can pick up more oxygen
|
pulmocutaneous arch
|
|
|
Q: artery that branches off of the dorsal aorta to supply the stomach, liver, pancreas, intestines, spleen
|
coeliacomesenteric artery
|
|
|
Q: coeliacomesenteric artery branches to give two arteries - this one splits to give two gastric arteries that supply the stomach, liver and pancreas
|
coeliac artery
|
|
|
Q: coeliacomesenteric artery branches to give two arteries - this one supplies the intestines and spleen
|
mesenteric artery
|
|
|
Q: some of the arteries that supply the leg include
|
iliac artery, sciatic artery, femoral artery
|
|
|
Q: this vein lies along the belly; it was attached to the body wall when you opened the frog
|
ventral abdominal vein
|
|

|
amplexus
|
|
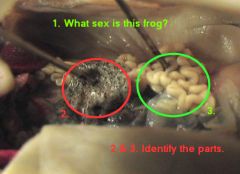
|
1. female
2. ovary 3. oviduct |
|

|
1. external nare
2. tympanic membrane |
|
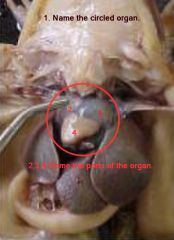
|
1. heart
2. right atrium 3. left atrium 4. ventricle |
|

|
1. heart
2. small intestine 3. large intestine |
|

|
nictitating membrane
|
|
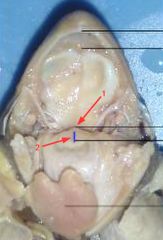
|
1. gullet
2. glottis |
|

|
1. dorsal
2. chromatophores |
|

|
gall bladder
|
|
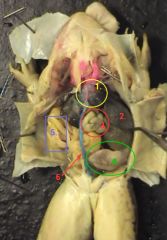
|
1. heart
2. liver 3. small intestine 4. stomach 5. fat bodies 6. ventral abdominal vein |
|
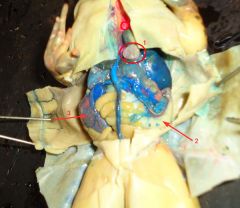
|
1. gall bladder
2. stomach 3. large intestine |
|
|
1. male
2. vestigial oviduct 3. testis 4. swollen thumbpad |
|
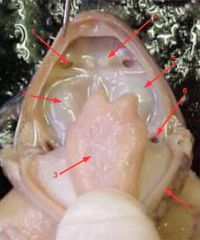
|
1. internal nare
2. eye orbit 3. tongue 4. vomerine tooth 5. other eye orbit (oops!) 6. eustachian tube opening 7. mandibular jaw |
|
|
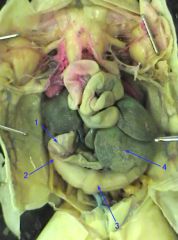
1. small intestine
2. pyloric valve 3. stomach 4. liver |
|
|
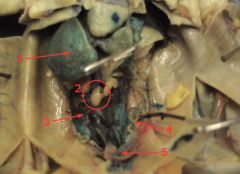
1. liver
2. testis 3. kidney 4. vestigial oviduct 5. urinary bladder |
|

|
ventral
|
|
|
Q: clear, third eyelid the protects the eye from debris, permits the frog to see underwater, and keeps the eye from drying out on land
|
nictitating membrane
|
|
|
Q: a tube that runs between the tympanic membrane and the mouth cavity; important for balance and pressure regulation
|
eustachian tube
|
|
|
Q: dark organ made up of 3-5 lobes which have many functions like detoxifying substances for safe excretion and producing bile for breaking up fats
|
liver
|
|
|
Q: folds in the stomach that allow it to expand and hold more food
|
rugae
|
|
|
Q: very thin, almost transparent tissue that holds abdominal organs like the small intestine and spleen in place; it has lots of blood vessels running through it
|
mesentery
|
|
|
Q: thin grey band of tissue that lies between the stomach and small intestine; it produces enzymes for digestion of food and hormones like insulin for regulation of blood sugar
|
pancreas
|
|
|
Q: dark grey, marble-like organ that lies in the mesentery and has a role in the immune system; it filters blood of bacteria, it destroys old RBCs and platelets, and it produces and stores RBCs, lymphocytes, and antibodies for when they're needed
|
spleen
|
|
|
Q: tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
|
ureter
|
|
|
Q: thin walled sac that stores urine until it is released into the cloaca and out the cloacal opening
|
urinary bladder
|
|
|
Q: membrane that surrounds and protects the heart
|
pericardium
|
|
|
Q: part of brain responsible for intellect, instinct and memory
|
cerebrum
|
|
|
Q: part of the brain responsible for balance and muscle coordination
|
cerebellum
|
|
|
Q: part of the brain responsible for life support (vital) functions like breathing, heartbeat, etc
|
medulla oblongata
|
|
|
Q: part of brain responsible for sight/vision
|
optic lobe
|
|
|
Q: part of brain responsible for the sense of smell
|
olfactory lobe
|
|
|
Q: What are the 2 main ways that frogs breathe?
|
1. through their skin
2. using their mouth and lungs |
|
|
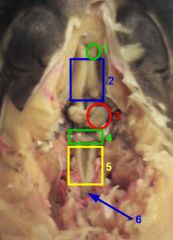
1. olfactory lobe
2. cerebrum 3. optic lobe 4. cerebellum 5. medulla oblongata 6. spinal cord |

