![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
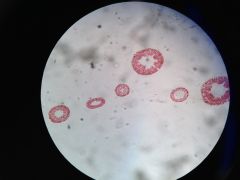
|
Hydra (P:Cnidaria;C:Hydrozoa;O:Hydroida;F:Hydridae)
|
|

|
Nematomorpha
|
|
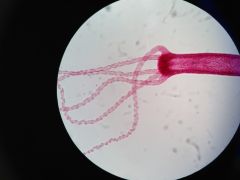
|
Hydra (P:Cnidaria;C:Hydrozoa;O:Hydroida;F:Hydridae)
|
|
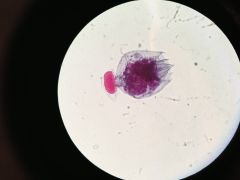
|
Rotifera
|
|

|
Nematoda
|
|
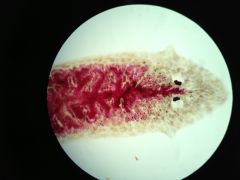
|
Planaria (P:Platyhelminthes)
|
|
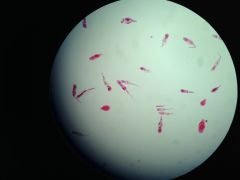
|
Rotifera
|
|
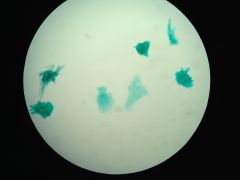
|
Amoeba (P: Tubulinae)
|
|
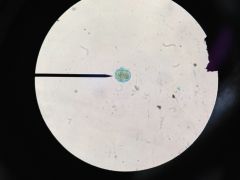
|
Peridinium (P: Dinoflagellata)
|
|
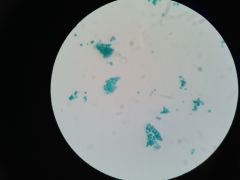
|
Chlamydomonas (P/D: Chlorphyta)
|
|
|
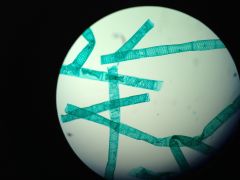
Spirogyra (P/D: Chlorophyta)
|
|
|
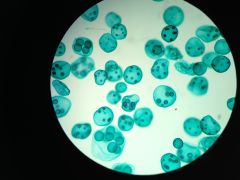
Volvox (P/D Chlorophyta)
|
|
|
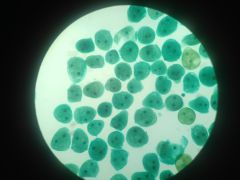
Stentor (P: Ciliophora)
|
|
|
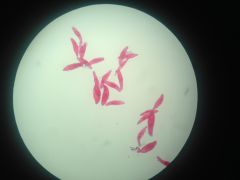
Paramecium (P: Ciliophora)
|
|
|
Eugelna (P: Euglenozoa)
|
|
|
Giardia (P: Metamonada)
|
|
|
Protozoa
|
Unicellular or acellular
Most reproduce by binary fission Multiple fission common in endosymbiont taxa |
|
|
Lugol’s Iodine
|
Used as a fixative and color, but don’t color all groups of protozoa
|
|
|
Protozoa sex
|
Gametogamy
» Gametes fuse as free‐swimming cells » flagellates » Autogamy » Gametes or gametic nuclei of same individual fuse » Heliozoa and ciliophora » Gamonotogamy » Mates unite to exchange gametes or gametic nuclei » Ciliophora |
|
|
Genus Spongilla
|
(P: Porifera, C: Demospongiae, O: Haploscleridae, F: Spongilidae)
|
|
|
Porifera Forms
|
– Encrusting
» Take form of structure they are living on – Rounded – Finger like |
|
|
Porifera Skeleton
|
– Siliceous spicules
– collagen |
|
|
Porifera sexual reproduction
|
» Gonochoristic
» With each separate sponge being entirely male or female » Gametes form from other cells: sperm (choanocytes); eggs (choanocytes or archaeocytes) |
|
|
Porifera asexual reproduction
|
» Simple fragmentation
» gemmule formation |
|
|
Porifera Digestion
|
Phagocytosis cells
» Porocytes » Pinacocytes » Choanocytes |
|
|
Cnidaria Body Plan
|
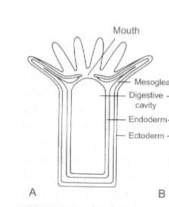
Polyp typically elongated along the oral-aboral axis
|
|
|
Cnidaria Body Plan
|
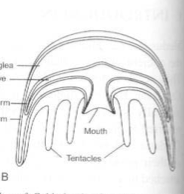
Medusa ~ bell shaped
|
|
|
Cnidaria cnidoblasts
|
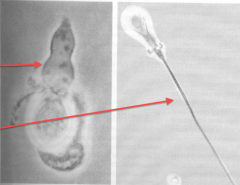
ectodermal cells that produce nematocysts
|
|
|
Cnidaria feeding
|
After being stung and encumbered by nematocysts
– Tentacles move victim to mouth – Opens to admit in to coelenteron – Gastric cells lining coelenteron secrete digestive juices |
|
|
Cnidaria Reproduction and Metamorphoses
|
Asexual and sexual reproduction
|
|
|
Platyhelminthes physiology
|
Gas exchange via body walls
|
|
|
Platyhelminthes Life History
|
Direct development
– Miniature worms hatch from eggs |
|
|
Platyhelminthes Sex
|
– Mostly Hermaphroditic
» Self-fertilization » Protandry = born one sex then turns into another – Asexual |
|
|
Platyhelminthes Functional Role in Ecosystem
|
predators
|
|
|
Nemertea Reproduction
|
Sexual with both male and female organs present
concurrently |
|
|
Nemertea Predation
|
Proboscis of mucus laced neurotoxins
|
|
|
Gastrotricha Ecological Role
|
Feed on bacteria
|
|
|
Gastrotricha Morphological Characteristics
|
– Spindle shaped
– Ventrally flattened – Cuticle usually with spines or scales |
|
|
Rotifera Lifestyle
|
planktonic (slowly sinking, rely on water current to stay up)
|
|
|
Rotifera Ecological Role
|
-Herbivores
• Feed on micro (pico) algae – Predators • Prokaryotes, protozoans, and metazoans |
|
|
Rotifera Morphological Characteristics
|
– Corona
• Apical ciliated region – Mastax • Muscular pharynx with complex set of jaws |
|
|
Nemotoda Ecological Role
|
Feed on bacteria, algae, protozoans
|
|
|
Nemotoda Morphological Characteristics
|
– Unsegmented worms
– Pseudocoel – Complete alimentary tract – Cylindrical body w tapering ends |
|
|
Nematomorpha Lifestyle
|
• Parasitic larvae on invertebrates
• Free living adults |
|
|
Nematomorpha Ecological Role
|
– Parasitic larvae
|
|
|
Nematomorpha Morphological Characteristics
|
– Unsegmented pseudocoelomates
– Non-functional alimentary tract – Anterior and posterior ends rounded |
|
|
Protozoa Ecological Role
|
Link microbial with autrophic trophic levels
|
|
|
Protozoa Lifestyle
|
Individual or colonial
|
|
|
Protozoa Morphological Characteristics
|
Unicellular or acellular
|
|
|
Porifera Ecological Role
|
– Often contain symbiotic algae
– Filter feed on bacteria and algae |
|
|
Porifera Morphological Characteristics
|
Tissue level of organization
|

