![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Supine |
Face up |
Laying position |
|
|
Prone |
Face down |
Laying position |
|
|
Mediastinium |
Thoracic space between lungs |
Thoracic |
|
|
Pulmonary circulation |
To the lungs |
|
|
|
Systemic circulation |
To all the body except the lungs |
|
|
|
Midline |
Running down the centre of the body |
|
|
|
Lateral |
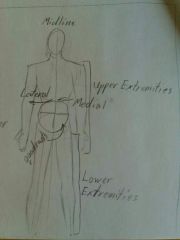
|
|
|
|
Medial |
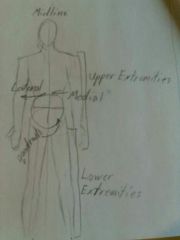
|
|
|
|
Quadrants |
Divide the abdominal cavity |
|
|
|
Ventricular Fibrillation |
Heart arrhythmia that doesn't provide adequate blood flow |
|
|
|
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) |
Heart arrhythmia that doesn't provide adequate blood flow |
|
|
|
Asystole |
Flatline |
Heart rythm |
|
|
Artery |
Carries blood away from the heart. |
|
|
|
NSR |
Normal Synus Rythm |
|
|
|
Aorta |
Main artery leaving the heart |
|
|
|
Superior Vena Cava |
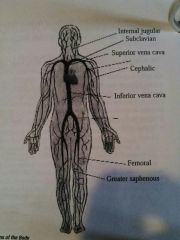
Vain that takes blood from the head, neck, shoulders, and upper extremities to the heart. |
Vein |
|
|
Inferior Vena Cava |
Vein that takes blood from the abdomen, pelvis, and lower extremities to the heart |
Vein |
|
|
Carotid pulse |
Felt in the anterior neck adjacent and just lateral to the thyroid cartilage |
|
|
|
Radial Pulse |
Felt at the wrist |
|
|
|
Femoral pulse |
Felt in the groin in the anterior crease between the leg and abdomen at the middle of the crease |
|
|
|
Systolic Pressure |
The maximum pressure occurring at the peak of the left ventricle contraction |
|
|
|
Diastolic pressure |
The minimum pressure during relaxation of the left ventrical |
|
|
|
Central nervous system |
Brain and spinal cord, connecting to the peripheral nerves |
|
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System |
Sensory and motor nerves that connect the central nervous system to the various body organs |
|
|
|
Sensory nerves |
Carry information about heat, cold, taste or pain to the central nervous system |
|
|
|
Motor nerves |
Carry messages to the muscles from the central nervous system, causing them to contract or relax |
|
|
|
Meninges |
Three layers of tissue that partially support the brain |
|
|
|
Occlusion |
Blockages usually caused by blood clots |
|
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) |
Clear, watery fluid suspending the brain |
|
|
|
Carotid Artery |
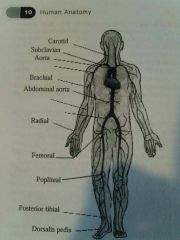
In the neck |
|
|
|
Subclavian artery |
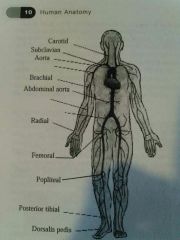
Just under the clavical (collarbone) |
|
|
|
Brachial artery |
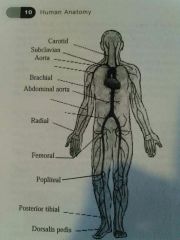
Upper arm artery |
|
|
|
Radial artery |
Artery in the wrist |
|
|
|
Femoral artery |
Artery on the inside of the thigh |
|
|
|
Popliteal artery |
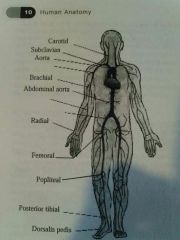
Artery on the inside of the knee |
|
|
|
Posterior Tibial artery |
Artery on the inside of the ankle |
|
|
|
Dorsalis pedis |
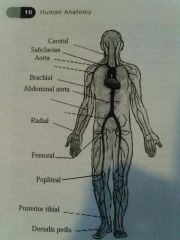
Artery on the top of the foot |
Artery |
|
|
Internal jugular |
Vein in the neck |
|
|
|
Subclavian vein |
Vein under the clavical |
|
|
|
Cephalic vein |
Vein in the upper arm |
|
|
|
Femoral vein |
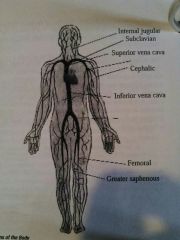
Vein in the inside of the thigh |
|
|
|
Greater sapheneous vein |
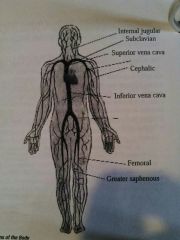
Vein on the inside of the knee |
|
|
|
Superior aorta |
Artery from the heart to the upper body |
|
|
|
Inferior Aorta |
Main artery from the heart to the lower body |
|
|
|
Anterior |
To the front |
|
|
|
Posterior |
To the back |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Lining of the abdominal cavity. One later covers the organs, another lines the cavity |
|
|
|
Cortex |
Hard outside of bones |
|
|
|
Periosteum |
A layers of connective tissue that covers the bones |
|
|
|
Zygoma |
Cheek bone |
|
|
|
Maxilla |
Upper jaw |
|
|
|
Mandible |
Lower jaw |
|
|
|
Cervical vertebra |
7 bones in the neck |
|
|
|
Thoracic vertebra |
12 bones in the upper back |
|
|
|
Lumbar vertebra |
5 bones that form the lower back |
|
|
|
Sacrum |
5 fused vertebra that are part of the pelvis |
|
|
|
Coccyx |
4 fused vertebra, the tailbone |
|
|
|
Scapula |
Shoulder blade |
|
|
|
Patella |
Kneecap |
Bone |
|
|
Carpals, metacarpals |
Hand bones |
|
|
|
Tarsals, metatarsals |
Foot bones |
|
|
|
Phalanges |
Fingers and toes |
|
|
|
Subcutaneous tissue |
A layer of connective tissue and fat that connects the skin to the muscles. |
|

