![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
week 0 |
Fertilization by sperm, forming zygote, initiating embryogenesis |
|
|
|
week 1 |
HCG secretion begins around the time of implantation of blasticyst |
|
|
|
Week 2 |
Bilaminar disk (epiblast, hypoblast) |
2 weeks=2 layers |
|
|
3 weeks |
Trilaminar disk. Gastrulation. Primitive streak, notochord, mesoderm and its organization, and neural plate begin to form. |
3 weeks= 3 layers |
|
|
Weeks 3-8 (embryonic period) |
Neural tube formed by neuroectoderm and closes by week 4. Organogenesis Extremely susceptible to teratogens |
|
|
|
Week 4 |
Heart begins to beat. Upper limbs and lower limbs begin to form |
4 weeks=4 limbs |
|
|
Week 6 |
Fetal cardiac activity visible by transvaginal ultrasound |
|
|
|
Week 10 |
Genitalia have female and male characteristics |
|
|
|
Gastrulation |
Process that forms the trilaminar embryonic disk. Establishes - Ectoderm - mesoderm - endoderm |
|
|
|
How does gastrulation begin? |
with the epiblast invaginating to form the primitive streak. |
|
|
|
What structures derive from surface ectoderm? |
adenohypophysis lens of the eye epithelial linings of oral cavity sensory organs of the ear olfactory epithelium epidermis parotid, sweat, mammary glands Anal canal below pectinate line |
Brain Eye Ear Mouth Skin Glands Butthole |
|
|
Neuroectoderm derivatives |
Brain (neurohypophysis, CNS neurons, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, pineal gland) Retina and optic nerve Spinal Cord |
Brain, spinal cord Eye nerves
|
|
|
Neural Crest Derivatives |
Bones of the skull Pia and arachnoid PNS(ANS, dorsal root ganglia, cranial nerves, celiac ganglion, shwann cells) melanocytes chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla parafollicular C cells of thryroid aorticopulmonary septum |
skull, PNS, cells |
|
|
Mesoderm derivatives |
- muscle, bone, connective tissue, peritoneum - CV structures, gut tube wall - spleen, kidneys, adrenal cortex - vagina, testes, ovaries - blood, lymphatics |
tissue, tubes & testes |
|
|
Regional specification of developing brain |
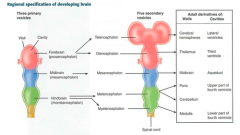
|
|
|
|
CNS/PNS origins neuroectoderm |
CNS neurons; Ependymal cells(inner lining of ventricles,make CSF); oligodendroglia;astrocytes |
|
|
|
CNS/PNS origins Neural crest |
PNS neurons,schwan cells |
|
|
|
CNS/PNS oringins Mesoderm |
Microglia,(Like Macrophages) |
|
|
|
One of the leading causes of congenital malformations in the united states |
Fetal alcohol syndrome |
|
|
|
Congenital abnormalities of Fetal alcohol syndrome |
intellectual disability, pre and postnatal developmental retardation, microcephaly, heart defects, facial abnormalities, holoprosencephaly |
|
|
|
mesoderm defects |
VACTERAL Vertebral defects Anal atresia Cardiac defects Tracheo-esophageal fistula Renal defects Limb defects |
VACTERAL |
|
|
Endoderm derivatives |
- Anal canal above pectinate line - Urethra - Gut tube epithelium Epithelial derivatives: lungs, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, eustachian tubes, thymus, parathyroid, thyroid follicular cells |
Epithelial linings |
|
|
Regulatory proteins that control cell cycle events |
Cyclins |
|
|
|
what is the difference between a deformation and a malformation? |
A deformation is an extrinsic disruption and ocurrs after the embryonic period.
A malformation is an intrinic disruption and ocurrs during the embryonic period. |
|
|
|
What is the difference between Agenesis and Aplasia? |
Agenesis is absent organ due to absent primordial tissue
Aplasia is absent organ despite presence of primordial tissue (Hypoplasia is incomplete organ, present primordial tissue) |
|
|
|
What is sequence and disruption? |
Sequence - abnormalities result from a single embryological event (primary)
Disruption - breakdown of a previously normal tissue. (secondary) |
|
|
|
What Tumor suppressors control G1 to S progression |
P53 and Rb |
|
|
|
Mutations in p53 and Rb result in |
Unrestrained cell division (e,g,Li-Fraumeni syndrome) |
|
|
|
What does golgi do to modify aminoacids? |
- Modifies N-oligosaccharides on asparagine. - Adds O-oligosaccarides on serine and threonine. - Adds mannose-6-phosphate to proteins for trafficking to lysosomes.
|
AA: SAT |
|
|
What cells remain in G0? |
Nuerons, skeletal and cardiac muscle, RBCs. |
|
|
|
Describe the mechanism of |
Inherited lysosomal storage disorder, defect in phosphotransferase.
Golgi cannot add mannose-6-phosphate on proteins and they get lost (sent extracellulary instead of to lysosomes) |
|
|
|
What are some of the symptoms of I cell disease? |
- Course facial features - Clouded corneas - Decresed joint movement - High plasma levels of lysosomal enzymes. |
|
|
|
What proteins are in charge of vesicular trafficking? And what do they do? |
COPI: Golgi-->golgi (retrograde); golgi-->ER
COPII: Golgi-golgi (anterograde) ER-->golgi
Clathrin: - Trans golgi--> lysosomes - Plasma membrane--> endosome (recepted mediated endocytosis e.g LDL) |
|
|
|
What is Signal Recognition Particle (SRP)? What happens when its deficient? |
cytosolic ribonucleoprotein that traffics proteins from the ribosome to the RER.
Absence results in protein accumulation in the cytosol. |
|
|
|
I'm a membrane enclosed organelle that catabolizes very-long-chain acids and AA. Who am I? |
Peroxisome |
|
|
|
I degrade damaged or ubiquitin tagged proteins and am a barrel shaped complex. Who am I? |
Proteosome |
|
|
|
Drugs that act on microtubules |
Microtubules Get Constructed Very Poorly - Mebendazol - Griseofulvin - Colchicine - Vincristine/Vinblastine - Paclitaxel |
Microtubules Get Constructed Very Poorly |
|
|
Microtubules are conformed of... |
- Alfa and beta tubulin. - Helical, cylindrical - Each dimer has 2 GTP bound |
|
|
|
Kartageners Syndrome |
- Primary ciliary dyskinesia - Immotile cilia due to dynein arm defect - Sx: Infertility, ectopic pregnancy, bronchiectasis, recurrent sinusitus, situs invertus
|
|
|
|
Cilia structure |
9+2 arrangement of microtubules |
|
|
|
What is the structural difference between actin and myosin? |
Actins are long, structural polymers whereas myosins are dimeric, ATP driven motor proteins that move along actins. |
|
|
|
Actin and myosin provide cytoskeletal elements like... |
muscle contraction, microvilli, cytokinesis, adherins junctions |
|
|
|
Functions of microtubules |
Movement Flagella, cilia, mitotic spindles, axonal trafficking, centrioles |
movement |
|
|
What are the functions of Intermediate filaments |
Structure Vimentin, desmin, cytokeratin, lamins, glial fibrillary acid proteins (GFAP), neurofilaments |
structure |
|
|
The plasma membrane is composed of... |
An asymmetric lipid bilayer
Contains: cholesterol, phosholipids, sphingolipids, gylcolipids and protein. Fungal membranes contain ergosterol. |
|
|
|
Inmunohistochemical stains for intermediate filaments |
VimenTin - connective tissue DesMin - Muscle Cytokeratin - epithelial cells GFAP - neuroGlia neurofilaments - neurons |
|
|
|
Drugs that inhibit the sodium potassium pump |
Ouabain inhibits K Cardiac glycosides (digoxin and digitoxin) inhibits the Na-K ATPase |
|
|
|
What drugs inhibit the arachidonic acid products? |
- Corticosteroids-Phosphlipase A2 - Zileuton-Lipoxygenase - Cyclooxygenase-NSAIDS, aspirin, acetaminophen, COX-2 inh - Zafirlukast,montelukast- leukotiens |
|
|
|
Red infarcts occur where? |
Red=reperfusion
Loose tissues with multiple blood supplies, such as liver, lungs and intestine |
|
|
|
Where do pale infarts occur? |
Occur in solid tissues with a single blood supply such as heart, kidney and spleen. |
|
|
|
Acute inflammation is mediated by: |
Neutrophils, eosinophils and antibodies |
|
|
|
What is required for a molecule to enter into the nucleus into the nuclear pore? |
nuclear localization signals: 4-8 AA sequences Rich in lysine, arginine and proline |
|
|
|
Hypoxia meassured by the carotid body is done by which CN? |
Glosspharyngeal nerve (CN IX) |
|
|
|
Motor information for swallowing is done by which CN? |
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) Vagus nerve (CN X) |
|
|
|
Which cranial nerve measures blood pressure from the aortic arch? |
Vagus nerve (CN X) |
|
|
|
Which CN induces salivation from the sublingual glands? |
Facial nerve (CN VII) |
|
|
|
Which CN induces salivation from the parotid gland? |
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) |
|
|
|
Which CN measures blood pressure from the carotid? |
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) |
|

