![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Fossil |
The preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past |

|
|
|
Mold fossil |
When sediments bury an organism and the sediments change into rock |

|
|
|
Cast fossil |
When a cast is filled with sand or mud that hardens into the shape of the organism |

|
|
|
Petrified/permineralized fossil |
When minerals soak into the buried remains, replacing the remains turning them into rock |

|
|
|
Preserved fossil |
When entire organism or parts of organisms are prevented from decaying from: Rock, ice, tar, and amber |

|
|
|
Carbonized fossil |
When organisms or parts are pressed between layers of soft mud or clay that hardens all the decaying of an organism away leaving the carbon imprint in the rock |

|
|
|
Trace fossil |
When the mud or sand hardens to a stone where a footprint, trail, or burrow of an organisms is left behind |

|
|
|
Law of superposition |
The relative age of rocks and fossils |
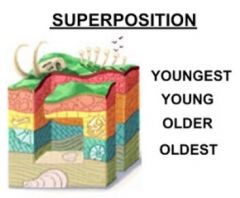
|
|
|
Relative age |
Relative age is the appropriate age , does not tell the exact age of an object |

|
|
|
Absolute age |
absolute age is the exact age (by chemically dating) |
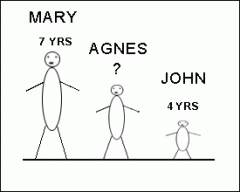
|

