![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomical position |
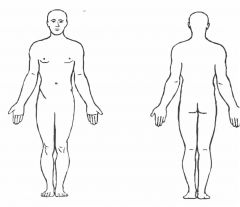
Stance at which human form is: head is level, eyes looking forward Hands with palms facing outward, at sides |
|
|
Supine |
Person lying face up |
|
|
Prone |
Person lying face down |
|
|
Right vs. Left (Anat. Position) |
"As if it were in your body." |
|
|
Axial |
Head and Trunk |
|
|
Appendicular |
Appendages (including girdles) |
|
|
Cranial |
Head |
|
|
Post-cranial |
Everything other than head. |
|
|
Dependent on Anat. Position: Inferior Anterior Posterior Medial Intermediate Lateral |
above below front back toward midline in between away from the midline |
|
|
Not dependent upon Anat. Position: Proximal Distal Dorsal Ventral Cephalic Caudal Superficial Deep |
nearer attachement to trunk further from point of attachment backside belly toward the head toward the tail (tailbone) toward body surface away from body surface (internal) |
|
|
Planes (4) |
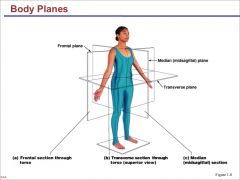
Saggital/Midsaggital Frontal (Coronal) Transverse Oblique: Any other angle, odd angle |
|
|
Process |
abony prominence (mastoid process)
|
|
|
Eminence |
abony projection; usually not as prominent as a process (mental eminence) |
|
|
Spine |
generallya longer, thinner, sharper process than an eminence (vertebral spines) |
|
|
Tuberosity |
alarge, usually rugose (roughened) eminence of variable shape; often the site oftendon or ligament attachment (deltoid tuberosity of the humerus) |
|
|
Tubercle |
asmall, usually rugose (roughened) eminence, often the site of tendon orligament attachment |
|
|
Trochanter |
large,blunt, rugose process (greater and lesser trochanters of the femur) |
|
|
Maleolus |
arounded protuberance (medial malleous of the tibia) |
|
|
Boss |
asmooth, round, broad eminence (parietal and frontal bossing in females) |
|
|
Condyle |
arounded articular process (occipital condyles, mandibular condyles) |
|
|
Epicondyle |
anonarticular projection adjacent to a condyle (lateral epicondyle of thehumerus) |
|
|
Head |
a large, rounded, usually articular end of a bone (head ofthe humerus and femur) |
|
|
Neck |
thesection of bone between the head and shaft of a bone (neck of the femur) |
|
|
Torus |
abony thickening (supraorbital torus on Homo erectus) |
|
|
Ridge |
alinear bony elevation, often roughened (supracondylar ridge of the humerus) |
|
|
Crest |
a prominent, usually sharp and thin ridge of bone (sagittalcrest found in apes) |
|
|
Line |
araised linear surface, not as thick as a torus or as sharp as a crest (inferiortemporal lines) |
|
|
Fossa |
adepressed area; usually broad and shallow (olecranon fossa on the distalhumerus) |
|
|
Fovea |
a pitlike, depressed area, usually smaller than a fossa(anterior fovea on a molar) |
|
|
Groove |
along pit or furrow (intertubercular groove on the proximal humerus) |
|
|
Sulcus |
a long, wide groove (preauricular sulcus in females illia) |
|
|
Fontanelle |
aspace between cranial bones of an infant |
|
|
Foramen |
an opening through a bone usually for the passage of bloodvessels or nerves (foramen magnum of the skull; nutrient foramina of the longbones) |
|
|
Canal |
atunnel-like, extended foramen (carotid canal at the base of the skull) |
|
|
Meatus |
ashort canal (external auditory meatus connects the middle and outer ear) |
|
|
Sinus |
acavity line with mucous membranes within a cranial bone. (Frontal sinus) |
|
|
Alveolus |
atooth socket |
|
|
Suture |
where adjacent bones of the skull meet (articulate) (cranialsutures) |
|
|
Facets |
asmall articular surface, or tooth contact (vertebral facets for articulationwith the ribs) |
|
|
Symphysis |
anearly immovable articulation (mental symphysis, pubic symphysis)
|

