![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Producers |
Organisms in an ecosystem that produce biomass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs(.producers are the green plants in an ecosystem that can manufacture their own food through the process of photosynthesis |
|
|
|
Primary consumers |
Plant eaters. primary consumers can range in size from insects to elephants |
Herbivores |
|
|
Secondary consumers |
The fees on the primary consumers and are meat eaters |
Carnivores |
|
|
Tertiary consumers |
Organisms that feed on smaller primary and secondary consumers |
|
|
|
Decomposers |
Organisms that consume dead organisms and in doing so, carry out the natural process of decomposition. Like herbivores and predators, Decomposers are heterotrophic. This means that they use organic subtracted to get their energy, carbon. And nutrients for grow and development. Decomposers use deceased organisms and non-living organic compounds as their food source. The primary Decomposers are bacteria and fungi |
Bacteria and fungi |
|
|
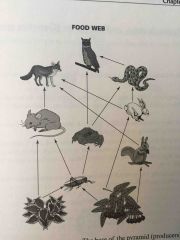
Food webs |
Interconnected energy systems. A food web demonstrates that alternate energy links available to an organism . Food webs help explain predator/prey relationships in an ecosystem and include networks of food chain |
|
|
|
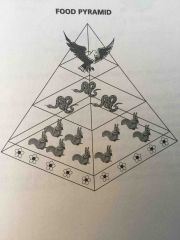
Food pyramids |
Illustrate energy flow in an ecosystem. The base of the pyramid (producers( supports all of the other levels of the pyramid. At each succeeding level of the food pyramid, there is a decrease in available energy |
|
|
|
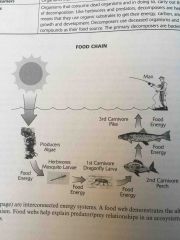
Food chain |
Food network describe the eating relationship between species within an ecosystem |
|

