![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
167 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ecologically tolerant |
Eurytopic |
|
|
Biogeography |
Patterns I'd species distribution, and the processes that result in such patterns |
|
|
What influences biogeography patterns |
Speciation Dispersal Extinction |
|
|
Barriers to dispersal |
Physical Ecological |
|
|
Name a species with a narrow distribution |
Devils hole pupfish (one hole in nevada) Redfinned blue eye (one spring in queensland) Hoatzin (S.A.) |
|
|
Name a species with a wide distribution |
Peregrine falcon Daphnia |
|
|
Place he likes to use to talk about endemism |
Lake Tanganyika |
|
|
Interesting species found in Lake Tanganyika |
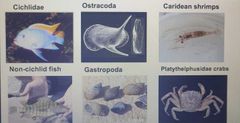
|
|
|
Population |
Group of organisms of the same sp. occupying a particular space at a particular time |
|
|
Community |
Population of populations Organisms of various sp. occupying a particular space at a particular time |
|
|
3 main types of distribution patterns |
Random Regular Clumped |
|
|
What causes random distribution patterns |
Neutral interactions |
|
|
What causes regular distribution patterns |
Antagonistic interactions |
|
|
What causes clumped distribution patterns |
Attraction between individuals or to a common resource |
|
|
Dispersion indecies |
Mean crowding (Lloyd's index) Nearest neibour techniques Parameter k of negative binomial Variance to mean ratio and dept. from poisson distribution |
|
|
Population descriptors |
Abundance Size distribution |
|
|
3 types of rarity (I guess? He says it like it's a fact but idk) |
Small local pop Narrow habitat tolerance Restricted range, narrow habitat and small pop |
|
|
Example of something with restricted range, narrow habitat and small populations |
California condor |
|
|
Example of something with extensive range, broad habitat and small populations |
Peregrine falcon |
|
|
Example of something with extensive range, narrow habitat and large populations |
Passenger pidgeon |
|
|
Liebig law of the minimum |
Basically no matter how much of one resource you have you can only stay somewhere if the least abundant thing is good enough (e.g. if there's enough food and space for 50 elephants, but only enough water for 3, then 47 elephants are gonna die) |
|
|
Types of dispersal |
Diffusion Jump Secular |
|
|
Diffusion dispersal |
Happens slowly over generations spreading out (African honey bee) |
|
|
Jump dispersal |
Happens over the course of basically a single generation (e.g. invasive species) |
|
|
Secular dispersal |
Dispersal so slow you're basically a new species by the time you get there |
|
|
Example of secular dispersal |
Lesser black backed gull & herring gull They both circled the Arctic in different directions, both live in ireland but used to be the sane species on the other side |
|
|
Increasing performance allows a species to... (3) |
Survive Grow Reproduce |
|
|
Peak of performance |
Species optimum |
|
|
Who described the niche |
G. Evelyn Hutchinson |
|
|
Fundamental niche |
An n-dimensional hypervolume |
|
|
Fundamental vs realised niche |
Realised niche is fundamental niche with competition |
|
|
No niches guy |
Steve Hubbell |
|
|
No niche theory |
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity |
|
|
Experiment against neutral theory |
Pond drought (J.M.Chase) Similar within pond sp richness (22) Perma ponds (71 total sp) Drought ponds (39 total sp) |
|
|
What do ecologists call random chance |
Stochastic |
|
|
Types of alien species |
Cultivated Casual Naturalised Invasive |
|
|
Cultivated |
Deliberately planted or sown by people |
|
|
Casual |
Not self perpetuating Maintained only by repeated introductions |
|
|
Naturalised |
Species thar has become established forming a self perpetuating population |
|
|
Invasive |
Spreading to the extent of causing ecological or economic harm. Generally has a negative impact on native species |
|
|
Can native species be invasive? |
Yes. If it disrupts by dominant colonisation |
|
|
Example of a native invasive species |
Bracken |
|
|
Rule of tens |
10% likelihood on each step on the invasion process |
|
|
Invasion process |
Transport Introduction Establish Spread |
|
|
Who did the rule of tens |
Williamson 1996 |
|
|
Reason of intentional introduction (5) |
Food and game Medicinal Pretty Science and conservation Biological control |
|
|
Example of a species introduced for medicinal value |
St. John's wort |
|
|
Example of a species introduced for biological control |
Cane toad |
|
|
Economic impacts and alien species relationship |
More economic the country, more alien species, cause of like transport n stuff |
|
|
Why was kudzu introduced |
To stop soil erosion |
|
|
Problem with kudzu |
Grows super fast, can suffocate anything. Remember that one image of a guy at his car but the car is all plants? Yea that one. |
|
|
How fast does kudzu spread |
20m/yr |
|
|
Example of an ornamental intruduction |
Ruddy duck |
|
|
What does an alien population need to overcome to be naturalised (3) |
Demographic stochasticity Environmental stochasticity Genetic problems of small populations |
|
|
How would one increase the liklihood of an introduction being successful |
Introduce large numbers |
|
|
Propagule pressure |
Also called introduction effect Composite measure of the number of species released into a region and also incorporates estimates of the absolute number of individuals involved in the release. |
|
|
What adaptations are the cane toads evolving |
Longer legs to spread faster |
|
|
Are the affects of an introduction seen quickly or slowly |
There is usually a time lag between Introduction and problems |
|
|
Largest threat to biodiversity |
Habitat loss & fragmentation |
|
|
Second largest threat to biodiversity |
Invasive species |
|
|
What did the ruddy duck do? |
Interbreed with native white headed duck |
|

OK I know I'm not meant to say this but this is the ruddy duck: |

And here's tge white headed duck. It's fugly. Let the ruddy duck live, this one's gross. It looks like a ****** up sneeze. |
|
|
How fast does Japanese knotweed grow |
Up to 10cm per day |
|
|
Are the Irish Japanese knotweed male or female |
Female |
|
|
Pseudoreplication |
Occurs when observations are bot statistically independent, but treated as if they are |
|
|
Why did the fox filled Islands have poorer plants |
Foxes killed birds which meant no bird **** to nutrition the plants |
|
|
What tends to be competed for |
Food Mates Territory |
|
|
Two types of competition (not inter and intra) |
Exploitation Interference |
|
|
Exploitation competition |
Individuals do not directly interact, but instead respond to resource levels |
|
|
Interference competition |
Individuals interact directly, usually by preventing access to a resource |
|
|
Density independence |
Density has no affect on the reproduction value, usually only seen at low density populations |
|
|
Undercompensating density dependance |
Density is playing a role, but it is still a lesser role than other factors, slows down r rate, but still not negative |
|
|
Overcompensating density dependance |
The density is having such a large impact that it is killing off the population |
|
|
Exactly compensating density dependsnce |
Number born = number die |
|
|
k |
Carrying capacity |
|
|
Exponential growth eqn. Discrete breeding seasons |

|
|
|
N |
Population size |
|
|
R |
Reproductive rate discrete seasons |
|
|
Model of pop. Inc. Limited by intraspecific competition (sigmoidal growth) |
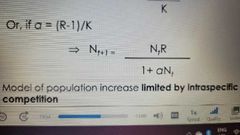
|
|
|
Exponential growth eqn. Continuous breeding seasons |

|
|
|
r |
Reproductive rate continuous breeding (intrinsic rate of natural increase) |
|
|
The Logistic Equation (Sigmoidal curve for continuous breeding) |
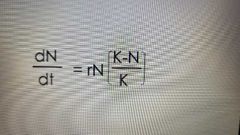
|
|
|
Law of constant final yield |
No matter how many organisms you cram into an area, you can only get so much biomass out of it. More individuals may grow, but they will grow smaller. |
|
|
Law of constant final yield eqn. |
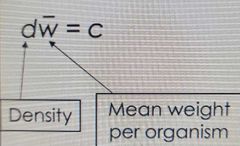
|
|
|
d |
Density |
|
|
w (with a a line on top) |
Mean weight per organism |
|
|
c (yield eqn.) |
A constant final yield |
|
|
k (lower case) |
Killing power |
|
|
Killing power |
Relative mortality rate =log (initial density/final density) |
|
|
b |
Log of density/killing power |
|
|
b=1 |
Pure contest competition |
|
|
Pure contest competition |
Exact compensation (b=1) Constant no. Of survivors |
|
|
b>>1 |
Pure scramble competition |
|
|
Pure scramble competition density dependance type |
Highly overcompensating density dependance |
|
|
Scramble graph |
Boom bust |
|
|
Contest |
Levels off at k nicely |
|
|
Types of interspecific interactions (6) |
Competition Predation Herbivory Parasitism Disease Mutualism |
|
|
Competition can result in... |
Exculaion of poor competitor Coexistence |
|
|
a |
Competition coefficient |
|
|
What equation is the lotka voltera model based on |
Logistic equation |
|
|
a12 meaning |
Effects of species 2 on species 1 |
|
|
Do numbers tend towards or away from zero isoclines |
Towards |
|
|
When can Stable equilibrium between two species happen |
When inter specific competition is less important than intra specific competition |
|
|
Gause's principle (competitive exclusion principle) |
If 2 species coexist, they do so as a result of niche differentiation If no differentiation exists, then one species is excluded |
|
|
Island |
Areas of appropriate habitat, surrounded by inappropriate habitat |
|
|
Arrhenius equation |
S=cA^z |
|
|
S |
No of species |
|
|
c in arrhenius |
Const. Measuring the no of species per unit area |
|
|
A |
Area of island |
|
|
z |
Const measuring slope of the line relating S and a, usually valued around 0.3 |
|
|
Dragonfly larva experiment (on impacts of predators) |
Without predators, 3 times more larvae survived, even though in the situation with predators those predators were kept separately. It was seemingly "fear" which killed the larvae. |
|
|
Lotka volterra predation model |
dN/dt=rN-aPN |
|
|
What amount of energy gets passed on to each trophic level (roughly) |
10% |
|
|
Equilibrium model of island biogeography |
Immigration rate and extinction rate vs number of resident species. Where they cross is the no. of species |
|
|
Why are better dispensers less likely to speciate |
Continuous genetic input from "mainland" population |
|
|
Primary productivity |
Rate at which biomass is produced by autotrophs |
|
|
Biomass |
Mass of organisms per unity area if ground or unit volume of water |
|
|
Gross primary production |
Total fixation of carbon by photosynthesis |
|
|
Net primary production |
GPP less autotrophic respiration |
|
|
NPP |
Net primary production |
|
|
GPP |
Gross primary production |
|
|
Where has high ratio of NPP:B |
Open ocean |
|
|
Where has low ratio of NPP:B |
Rainforest |
|
|
Why do terrestrial ecosystems have such low NPP:B |
Because there's a lot of support biomass for the photosynthesis, eg tree trunks and branches, while in the ocean its just a lil guy photosynthesising like hell |
|
|
Autochthonous |
From said area |
|
|
Allochthonous |
From a different place |
|
|
Secondary productivity |
Rate of production of new biomass by heterotrophs |
|
|
TLTE |
Trophic level transfer efficiency |
|
|
TLTE is a combination of... |
Consumption efficiency Assimilation efficiency Production efficiency |
|
|
Consumption efficiency |
% of productivity at one trophic level that is consumed by the next trophic level |
|
|
Assimilation efficiency |
% of food energy that is assimilated across gut wall of consumer |
|
|
Production efficiency |
% assimilated energy incorporated into new biomass |
|
|
2 main life cycle strategies |
r species- Live fast die young K species- Slow and steady |
|
|
Are r or K species more likely to be pioneers |
r |
|
|
Are r or K species more likely to be the culmination of ecological succession |
K |
|
|
Raunkiaer's life forms |
Phanerophytes Chamaephytes Hemicryptophytes Cryptophytes Therophytes |
|
|
2 external factors which limit plants |
Stress Disturbance |
|
|
Low disturbance high productivity |
Competitors |
|
|
Low disturbance low productivity |
Stress tolerators |
|
|
High disturbance high productivity |
Ruderals |
|
|
2 things that positively impact population size |
Immigration Births |
|
|
2 things that negatively impact population size |
Deaths Emigration |
|
|
3 types of survivorship curve |
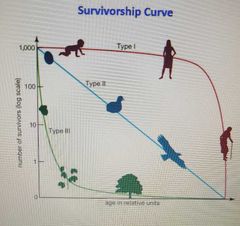
|
|
|
3 processes of vegetation change |
Physiographic Climactic Biotic |
|
|
Phisiographic vegetation change |
Plants changing the environment so other plants can no longer live there |
|
|
Climactic vegetation change |
Storms, drought, global warming |
|
|
Biotic vegetation change |
Grazing, invasive plants etc |
|
|
Whats the place that is a classic example for succession |
Glacier bay |
|
|
Glacier Bay succession plants: |
Moss & weed Dryas Alder Spruce |
|
|
Deterministic/relay floristics model of succession (4) |
Directional change Succeeding type dependent on preceeding type Ends in stable climax Catastrophe sends it back |
|
|
Objections to deterministic/relay floristics model of succession (4) |
Clear cut stages absent Composition of no two patches the same Unstable environment- no climax Modification of site overemphasised in importance for later species |
|
|
Secondary succession |
All present at beginning, but ratios change |
|
|
3 mechanisms of vegetation change |
Facilitation Inhibition Tolerance |
|
|
What is facilitation in relation to vegetative change |
One species leads to the next |
|
|
What is inhibition in relation to vegetative change |
One species stops the next |
|
|
What is tolerance in relation to vegetative change |
Species can be skipped |
|
|
Allelopathy |
Plants which excuse chemicals toxic to other plants eg *Deschampsia flexuosa* |
|
|
Examples of inhibition in relation to vegetative change |
Allelopathy Grazing |
|
|
Example of facilitation in relation to vegetative change |
Alder fixing nitrogen in soil |
|
|
Chronosequence |
Using different spaces to represent different times e.g. different bits of glacier bay being different ages |
|
|
Transition probabilities |
Probability of one tree replacing another during succession |
|
|
Marcov chains |
Statistical procedure in which chains of random events are constrained by current states |
|
|
Metapopulation |
Group of spatially separated populations of the same species which interact at some level |
|
|
Example of a metapopulation |
Checkerspot butterfly in San Francisco Bay area Fenders blue butterfly- kincaid's lupine (model) |
|
|
Conditions for metapop (4) |
Islands Even largest pop risk of extinction Patches close enough to repopulate after local extinction Dynamics of local populations nit synchronised |
|
|
Plants which excuse chemicals toxic to other plants eg *Deschampsia flexuosa* |
Allelopathy |
|
|
Allelopathic plant example |
Deschampsia flexuosa |

