![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
114 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ovary/fruit |
The swollen basal part of the carpel in angiosperms, which contains the ovules
|
|
|
Ovule/seed
|
The female gamete and its protective and nutritive tissue, which develops into the dispersal unit or seed after fertilization in seed plants
|
|
|
Beak |
A narrow or prolonged tip
|
|
|
Dehiscent |
Opening at maturity
|
|
|
Indehiscent |
Not opening at maturity |
|
|
Pericarp |
The wall of a fruit, derived from the maturing ovary wall
|
|
|
Endocarp/mesocarp/exocarp |
Innermost layer/middle/outer layer
|
|
|
Suture
|
A line of fusion
|
|
|
Valve |
One of the segments of a dehiscent fruit, separating from other such segments at maturity
|
|
|
Achene |
Any simple one-seeded indehis-cent dry fruit that develops from a monocarpellary ovary (Echinacea)
|
|
|
Caryopsis |
A fruit that resembles an achene except that the seed wall fuses with the carpel wall during embryo development (corn)
|
|
|
Nut |
A dry indehiscent fruit with a single seed
|
|
|
Nutlet |
A small nut |
|
|
Winged Nutlet
|
A winged nut
|
|
|
Nutlet in a bladder |
|
|
|
Samara |
A type of achene with a pericarp extended into a membranous wing, which aids wind dispersal of the seed
|
|
|
Schizocarp |
A dry fruit that is derived from two or more one-seeded carpels that divide into one-seeded units at maturity (the units can be achenes, berries, follicles, etc.)
|
|
|
Capsule |
Any dry dehiscent fruit derived from two or more many-seeded fused carpels
|
|
|
Folicle |
Dry dehiscent many-seeded fruit derived from one carpel, which on ripening splits down one side only (Milkweed)
|
|
|
Legume |
Dry dehiscent many-seeded fruit derived from one carpel, which on ripening splits down two sides
|
|
|
Silique |
Dry dehiscent fruit typically more than twice as long as wide, with two valves separating from the persistent placentae and septum
|
|
|
Silicle |
Dry dehiscent fruit typically less than twice as long as wide, with two valves separating from the persistent placentae and septum
|
|
|
Berry |
A many-seeded fleshy indehiscent fruit
|
|
|
Drupe |
A fleshy indehiscent fruit in which the seed or seeds are surrounded by a hardened schlerenchymatous endocarp (peach)
|
|
|
Hesperidium |
Fleshy berry-like fruit with a tough rind (citrus)
|
|
|
Pepo |
Fleshy indehiscent many-seeded fruit with a tough rind (cucumber)
|
|
|
Accessory fruit |
A fleshy fruit developing from a succulent receptacle rather than the pistil. The ripened ovaries are achenes on the surface (strawberry) |
|
|
Hip |
A berry-like structure composed of an enlarged hypanthium surrounding numerous achenes |
|
|
Pome |
A fleshy, indehiscent fruit derived from an inferior, compound ovary, consisting of a modified floral tube surrounding a core (apple) |
|
|
Receptacle |
The portion of the pedicel upon which the flower parts are borne |
|
|
Hypanthium |
A cup-shaped extension of the floral axis usually formed from the union of the basal parts of the calyx, corolla and androecium commonly surrounding or enclosing the pistils (rose) |
|
|
Aggregate fruit |
Usually applied to a cluster or group of small fleshy fruits originating from a number of separate pistils in a single flower, as in the clustered drupelets of the raspberry
|
|
|
Multiple fruit |
Fruit formed from several separate flowers crowded on a single axis (pineapple)
|
|
|
Petal/corolla |
Collective term for petals
|
|
|
Sepal/calyx |
Collective term for sepals |
|
|
Perianth |
The calyx and corolla
|
|
|
Pedicel |
The stalk attaching individual flowers to the main axis
|
|
|
Peduncle |
The stalk of a solitary flower or an inflorescence
|
|
|
Receptacle |
The expanded region at the end of a peduncle to which the floral parts are attached
|
|
|
Involucre |
Whorl of bracts subtending a flower or flower cluster
|
|
|
Bract |
A reduced leaf or leaflike structure at the base of a flower or inflorescence
|
|
|
Hypanthium |
The flat or cup-shaped receptacle found in perigynous flowers
|
|
|
Actinomorphic/radially symmetric |
Radially symmetric. The arrangement of parts in an organ or organism such that any cut taken through the centre divides the structure into similar halves
|
|
|
Zygomorphic/bilaterally symmetry |
The arrangement of parts in an organ or organism such that it can only be split into similar halves along one given plane
|
|
|
Bilabiate |
Two lipped flower as in many irregular flowers
|
|
|
Tubular |
Form of a tube
|
|
|
Spur |
A tubular projection from a flower, usually from the base of a perianth segment (columbine)
|
|
|
Throat |
The orifice of a gamopetalous corolla or gamosepalous calyx
|
|
|
Complete |
With all of the parts typically belonging to it, as a flower with sepals, petals, stamens and pistils
|
|
|
Incomplete |
Lacking an expected part or series of parts, as in a flower lacking one of the floral whorls |
|
|
Apetalous |
Flower with no petals |
|
|
Tepals |
A segment of a perianth which is not differentiated into calyx and corolla
|
|
|
Stamen |
The male reproductive organ of a flower consisting of an anther and filament |
|
|
Anther |
The apical portion of a stamen, which produces the microspores or pollen grains
|
|
|
Filament |
The stalk of a stamen, bearing the anther at its apex
|
|
|
Monadelphous |
Describing stamen filaments that are all fused for the greater part of their length, so forming a tube around the style
|
|
|
Epipetalous |
Describing stamens that arise from the petals, as occur in many flowers with tubular corollas
|
|
|
Stamens exerted |
Stamens protruding above the perianth
|
|
|
Stamens inserted |
Stamens not protruding above the perianth
|
|
|
Pistil
|
A term used ambiguously to describe either a single carpel (simple pistil) or a group of fused carpels (compound pistil)
|
|
|
Stigma |
The receptive tip of the carpel, which receives pollen at pollination and on which the pollen grain germinates
|
|
|
Style |
The sterile portion of the carpel between the ovary and the stigma, which may be elongated or feathery, especially in wind-pollinated species, so that the stigma is presented in an effective place for pollination
|
|
|
Carpel |
The structure that bears and encloses the ovules in flowering plants
|
|
|
Monocarpous |
having a gynoecium that forms only a single ovary
|
|
|
Apocarpous |
having distinct carpels that are not joined together
|
|
|
Syncarpous |
Fused carpels
|
|
|
Locule |
A cavity within which specialized organs may develop, most usually the ovules
|
|
|
Septum |
Any partition, whether within a cell, as in a septate fibre, or in an organ, such as a fruit
|
|
|
Marginal placentation |
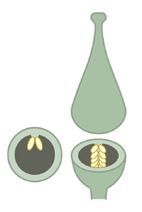
A form of placentation in which the placentae develop along the ventral suture of a simple ovary
|
|
|
Axile placentation |
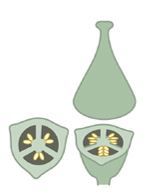
A form of placentation in which the placentae arise along the central axis of the ovary
|
|
|
Parietal placentation |

A form of placentation in which the placentae develop along the fused margins of a unilocular compound ovary
|
|
|
Free central placentation |
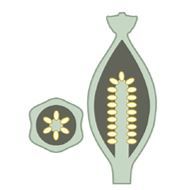
A form of placentation in which the placentae develop on a central dome or column of tissue
|
|
|
Basal placentation |
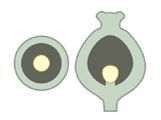
A form of placentation, found in ovaries containing only one ovule, in which the placenta develops at the base of the ovary
|
|
|
Superior(hypogynous) insertion |
The most commonly seen arrangement of floral parts in which the stamens, sepals, and petals are inserted below the ovary, giving a superior ovary
|
|
|
Perigynous insertion
|
The arrangement of floral parts, intermediate between hypogeny and epigeny
|
|
|
Epigynous insertion |
An arrangement of floral parts in which the stamens, sepals, and petals are inserted above the ovary, giving an inferior ovary
|
|
|
Adnate |
Describing unlike organs that are joined together, such as stamens fused with the petals
|
|
|
Connate |
Describing similar organs that are joined together, such as petals fused to form a tube
|
|
|
apo- |
Separate
|
|
|
gamo-/syn-
|
Fused
|
|
|
poly- |
Many separate
|
|
|
a-
|
Without
|
|
|
Dioecious |
Describing plants in which the female and male reproductive organs are separated on different individuals
|
|
|
Monoecious |
Describing plants in which the female and male reproductive organs are on the same plant
|
|
|
Polygamous |
With unisexual and bisexual flowers on the same plant
|
|
|
|
With both androecium and gynoecium on the same flower
|
|
|
Imperfect flower |
With the androecium OR gynoecium on the same flower |
|
|
Staminate |
Flower with only stamen
|
|
|
Pistillate |
Flower with only pistils |
|
|
Bract |
A leaflike organ subtending an inflorescence
|
|
|
Involucre |
A whorl of bracts around or beneath a condensed inflorescence, such as a capitulum or umbel. It resembles and performs the function of the calyx of a single simple flower
|
|
|
Rachis |
The main axis of an inflorescence
|
|
|
Scape |
The leafless stem of a solitary flower or inflorescence, such as that of the dandelion inflorescence
|
|
|
Solitary |
Single flower
|
|
|
Terminal inflorescence
|
Inflorescence from the tip of a twig
|
|
|
Axillary inflorescence |
Inflorescence from the axis of a twig |
|
|
Determinate
|
The youngest flowers are at the bottom of an elongated axis or on the outside of a truncated axis
|
|
|
Indeterminate |
The youngest flowers are at the top of an elongated axis or on the centre of a truncated axis
|
|
|
Spadix |
Flowers are sessile and borne on an enlarged fleshy axis
|
|
|
Spathe |
A large bract or pair of bracts subtending and often enclosing an inflorescence
|
|
|
Catkin(ament) |
An inflorescence consisting of a dense spike or raceme of apetalous, unisexual flowers |
|
|
Head (capitulum)
|

An inflorescence consisting of a head of small closely packed stalkless flowers or florets arising at the same level on a flattened axis
|
|
|
Spike |

The flowers are sessile and borne on an elongated axis
|
|
|
Spikelet |
A small spike or secondary spike (as in grass)
|
|
|
Raceme |

the flowers are formed on individual pedicels on the main axis
|
|
|
Umbel |
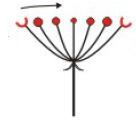
the flowers are borne on undivided pedicels originating from a common node on the main axis
|
|
|
Corymb |
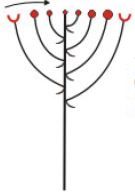
the flowers are formed on lateral stalks of different lengths, the longest at the base, resulting in a flattopped cluster of flowers
|
|
|
Cyme |

A flat-topped or round-topped determinate inflorescence
|
|
|
Panicle |

flowers are formed on stalks (peduncles) arising alternately or spirally from the main axis
|
|
|
Compound umbel |
An umbel of umbels |
|
|
Compound corymb |
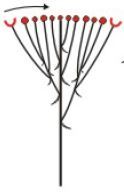
A corymb of corymbs
|
|
|
Compound cyme |
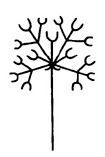
A cyme of cymes
|
|
|
Panicle of heads |
A panicle of heads |
|
|
Clustered axillary |
|

