![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Schedule of quantities offered for sale at allposible prices in a market. |

Supply |
|
|
Combination of desire, ability, and willingnessto buy a produc. |

Demand |
|
|
Production needed if the firm is to recover itscosts; production level where total cost equals total revenue |

Break even point |
|
|
Productive resources that make up the fourcategories of land, capital, labor, and entrepreneurship. |

Factors of production |
|
|
The natural fluctuation ofthe economy between periods of expansion (growth) and contraction(recession). |
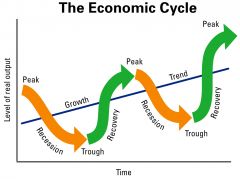
Economic cycle |
|
|
Program whereby a government or private agency programs that provide general economic and social assistance to needy individuals. |

Welfare State |
|
|
An approach to economicsand social studies in which control of economic factors is shifted from thepublic sector to the private sector. Drawing upon principlesof neoclassical economics, neoliberalism suggests that governments reduce deficit spending, limit subsidies, reform tax law to broadenthe tax base, remove fixed exchange rates, open up markets to trade by limiting protectionism, privatize state-runbusinesses, allow private property and back deregulation. |

Neoliberalism |
|
|
The tendency of investment funds and businesses to move beyond domestic and national markets to other marketsaround the globe, thereby increasing the interconnectedness of differentmarkets. Globalization has had the effect of markedly increasing not onlyinternational trade, but also cultural exchange. |

Globalization |
|
|
Institutional arrangementsdesigned to facilitate the free flow of goods and services and to coordinateforeign economic policies between countries in the same geographic region. |

Regionalism |
|
|
Prohibition on the exportor import of a product. |
Trade embargo |
|
|
An economic arrangementbetween different regions marked by the reduction or elimination of tradebarriers and the coordination of monetary and fiscal policies. The aim of economicintegration is to reduce costs for both consumers and producers, as well as toincrease trade between the countries taking part in the agreement. |

Economic integration |
|
|
Treaty (such as FTAA orNAFTA) between two or more countries to establish a free trade area where commerce ingoods and services can be conducted across their common borders, withouttariffs or hindrances but (in contrast to a common market) capital or labor maynot move freely. |

Free Trade Agreement |
|
|
Limit on the amount of agood that can be allowed into a country. |

Quota |
|
|
Tax placed on an imported product |
Tariff |
|
|
Is the rate at which the general levelof prices for goods and services is rising and, consequently, the purchasingpower of currency is falling. |

Inflation rate |
|
|
It is the monetary value ofall the finished goods and services produced within a country's borders in aspecific time period. |
GDP |
|
|
Excess of supply overdemand of products being offered to the market. |

Overproduction |

