![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Goblet cells extend to what area in the lung?
|
just to bronchi
|
|
|
Type I pneumocytes are what cell type?
|
Squamous; thin for optimal gas diffusion
|
|
|
What lung cells proliferate after lung damage?
|
Type II pneumocytes
|
|
|
Aspirating a peanut while sitting upright will likely lodge in what part of lung? how about supine?
|
upright- lower portion of right inferior lobe
supine- superior portion of right inferior lobe |
|
|
What is the relation of the pulmonary artery to the bronchus at each lung hilus?
|
Right-Anterior
Left- Superior RALS |
|
|
What are the muscles used in inspiration during exercise?
|
external intercostals, scalenes, sternocleidomastoids
|
|
|
What is deficient in neonatal RDS?
|
surfactant (lecithin)
|
|
|
What is the formula for physiological dead space?
|
tidal volume X (PaCO2-PeCO2)/PaCO2
pe=expired air |
|
|
At FRC, what is the
Airway pressure alveolar presssure intrapleural pressure |
airway and alveolar- zero
intrapleural- negative, prevents pneumothorax |
|
|
methemoglobin can be treated with what?
|
methylene blue
|
|
|
when treating cyanide poisoning, first use _____ then use ____ so it is renally excreted
|
nitrites (to oxidize hemo to methemoglobin)
then thiosulfate (binds to cyanide) |
|
|
The fact that hemoglobin has an increased affinity for O2 each time it binds an O2 is referred to as what
|
positive cooperativity
|
|
|
An increase in what causes a right shift in the hemoglobin dissociation curve
|
CO2
BPG exercise acid-altitude temperature |
|
|
What is a primary cause of pulmonary hypertension?
|
BMPR2 gene mutation, normally inhibits vascular smooth muscle proliferation
|
|
|
What are secondary causes of pulmonary hypertension?
|
COPD, mitral stenosis, recurrent thromboemboli, autoimmune disease(systemic sclerosis) left to right shunt, sleep apnea or living at high altitude (hypoxic vasoconstriction)
|
|
|
formula for pulmonary vascular resistance
|
P of pulmonary artery- P of left atrium
_______________________ CO |
|
|
Two causes of hypoxemia with a normal A-a gradient?
|
high altitude, hypoventilation
|
|
|
Majority of CO2 in blood is carried by what?
|
Bicarbonate
|
|
|
Sarcoidosis involves what
|
increase in ACE, and calcium
bilateral hilar lypmphadenopathy noncaseating granuloma |
|
|
What three drugs can cause a restrictive lung disease?
|
Bleomycin, busulfan, amiodarone
|
|
|
What is that pathophysiology of hyaline membrane disease?
|
neutrophilic substances, activation of coagulation cascade and free radicals...causes diffuse alveolar damage...increase alveolar capillary permeability...protein-rich leakage into alveoli
results in formation of hyaline membrane |
|
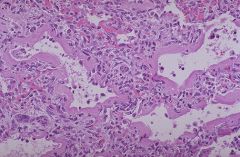
What disease?
|
Hyaline membrane disease...Neonatal ARDS
|
|
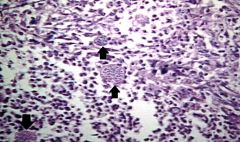
What disease? Hint: immunocompromised person
|
Coccidiomycosis
|
|
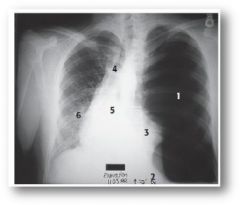
???
|
tension pneumothroax...mediastinal shift away from affected lung
|
|
|
What is Caplan's syndrome?
|
coal miner's pneumoconioses with rheumatoid involvement
|
|
|
Describe the lung region involved for the following:
Coal miner's pneumoconioses Silicosis Asbestosis |
Coal miner's- upper lobes
silcosis- upper lobes, and "eggshell" calcification of hilar lymph nodes abestosis- lower lobes |
|
|
fremitus is an indication of?
|
pneumomonia (lobar)
|
|
|
Complications from lung cancer (SPHERE)
|
Superior vena cava syndrome
Pancoast tumor Horner's syndrome Endocrine (paraneoplastic) Recurrent laryngeal symptoms Effusions |
|
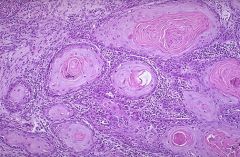
???
|
Squamous cell carcinoma---"keratin pearls"
|
|
|
Small cell carcinoma location and histology?
|
Central
neurodendocrine cells of kulchitsky (Small dark blue) assoc with ACTH Or ADH and possibly Lambert EatonM |
|
|
Most common lung cancer in females and nonsmokers?
|
Adenocarcinoma
affects peripheral (clara to type II pneumocytes) |
|
|
Squamous Cell CA location and characteristics?
|
Central
cavitation, linked to smoking, parathyroid like activity |
|
|
Psammoma bodies seen in what type of lung cancer?
|
mesothelioma
|
|
|
Patient presents with facial plethora, neck (JVD) and edema of upper extremities, what are you thinking?
|
Superior Vena Cava syndrome
|
|
|
H1 blockers..name them
|
1st gen-diphenhydramine, dimenhydrinate, chlorpehniramine
2nd- loratadine, fexofenandine, cetirizine |
|
|
Beta-2 agonists used for asthma
|
relac bronchial smooth muscle
albuterol- actue exacerbation salmeterol- long term prophylaxis |
|
|
salmeterol ADR
|
tremor, arrythmia
|
|
|
theophylline MOA
|
bronchodilation via
inhibiting phosphodiesterase, which decreases cAMP hydrolysis |
|
|
Ipratropium bromide MOA
|
competiive blocking of muscarinic receptors, prevents bronchoconstriction (asthma as well as COPD
|
|
|
What is the first line therapy for chronic asthma?
|
corticosteroids---beclomethasone, prednisone
inhibits NF-kB, which then decreased TNF alpha production, decrease inflammation |
|
|
Zileuton MOA
|
blocks 5-lipoxygenase pathway...blocks conversion of arachidonic acid to leukotrienes
|
|
|
Cromolyn MOA
|
prevents release of mediators from mast cells (Leukotrienes, histamine)
|
|
|
Montelukast and Zafirlukast MOA
|
block leukotriene receptors...really good for aspirin induced asthma
|
|
|
What can loosen mucus plugs in CF patients?
|
N-acetylcysteine
|
|
|
Guafenesin MOA
|
remove excess sputum but doesnt suppress cough reflex
|
|
|
Bosentan
|
MOA: antagonizes endothelin-1 receptors, which decreases PVR
use: pulmonary HTN |
|
|
Dextromethorphan
|
antitussive (antagonizes NMDA receptors)
synthetic codeine analog |
|
|
Organisms that cause bronchopenumonia
|
S. aureus, H. flu, klebsiella, s. pygoenes
|
|
|
Organisms that cause lobar pneumonia
|
pneumococcus (most common), Klebsiella
|
|
|
Organisms that cause interstitial pneumonia
|
RSV, adenoviruses, mycoplasma, legionella, chlamydia
|
|
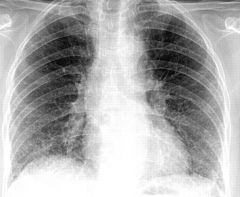
What is the most common cause?
|
Virus-- RSV, adenovirus
interstitial pneumonia |
|
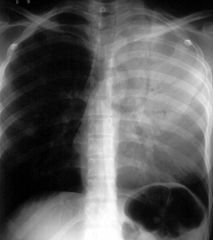
What is the most likely causative agent?
|
Pneumococcus...(s. pneumoniae)
|

