![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
175 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
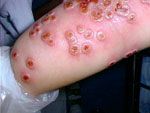
What disease? What class of virus?
|
Vaccinia/Cowpox "milkmaid's blisters"
Poxvirus class |
|
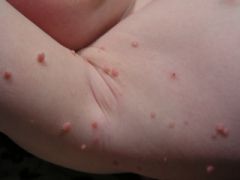
What disease is this? What class does its etiology fall under?
|
Molluscum contagiosum. Poxvirus.
|
|
|
Are boosters needed when a live attenuated vaccine is given?
|
No
|
|
|
Complementation refers to
|
When 1 of 2 viruses that infect the cell has a mutation that results in a nonfunctional protein. The nonmutated virus "complements" the mutated one by making a functional protein that serves both viruses.
|
|
|
Live attenuated vaccines include
|
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR), Sabin polio, VZV, yellow fever, smallpox
|
|
|
Killed vaccines include
|
Rabies, Influenza, Salk Polio, and HAV (RIP Always, salK=Killed)
|
|
|
Recombinant vaccines include
|
HBV(antigen = recombinant HBsAg), HPV (types 6,11,16, and 18)
|
|
|
DNA viral genomes are predominantly double stranded or single stranded. What is the exception?
|
Double stranded. Parvoviridae are ssDNA ("part-of-a-virus")
|
|
|
Name all of the DNA viruses
|
Herpesviruses, Hepadnavirus, Adenovirus, Parvovirus, Papillomavirus, Polyomavirus, Poxvirus (HHAPPPy viruses)
|
|
|
All DNA viral genomes are linear except
|
Papilloma, polyoma and hepadnaviruses (circular)
|
|
|
RNA viruses are predominantly double stranded or single stranded. What is the exception?
|
Single stranded. Reoviridae is dsRNA "repeat-o-virus"
|
|
|
Which of these are infectious when purified? dsDNA, dsRNA, (+) ssRNA, (-)ssRNA
|
dsDNA and (+)ssRNA
|
|
|
All viruses are haploid except what virus
|
Retrovirus - have 2 identical ssRNA molecules (diploid)
|
|
|
All DNA viruses replicate in the nucleus except
|
Poxvirus
|
|
|
All RNA viruses replicate in the nucleus except
|
Influenza and retrovirus
|
|
|
Naked (nonenveloped) viruses include
|
Calicivirus, Picornavirus, Reovirus, Parvovirus, Adenovirus, Papillomavirus, and Polyomavirus (Naked CPR and PAPP smear)
|
|
|
Name the enveloped DNA viruses
|
Herpesvirus (HSV 1 and 2, VZV, CMV, EBV), HBV, smallpox
|
|
|
Name the nucleocapsid DNA viruses
|
Adenovirus, papillomaviruses, parvovirus
|
|
|
Name the enveloped RNA viruses
|
Flavivirus (HCV, Yellow fever, West nile), Togavirus (Rubella), Retrovirus (HIV, HTLV), Coronavirus ("common cold" and SARS, Orthomyxovirus (Influenza), Paramyxovirus (Parainfluenza, RSV, Rubeola/Measles, Mumps), Rhabdovirus (Rabies), Filovirus (Ebola/Marburg hemorrhagic fever), Arenavirus (LCMV - Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus), Bunyavirus (Hantavirus), Deltavirus (HDV)
|
|
|
Name the nucleocapsid RNA viruses
|
Reovirus (Colorado tick fever, Rotavirus), Picornavirus (Poliovirus, Echovirus, Rhinovirus, Coxsackievirus, HAV), Hepevirus (HEV), and Calicivirus (Norwalk virus)
|
|
|
Name 4 characteristics that all DNA viruses share
|
1. Double stranded (EXCEPT Parvo). 2. Linear (EXCEPT Papilloma and polyoma - circular, supercoiled and Hepadna - circular, incomplete) 3. Icosahedral (EXCEPT pox - complex) 4. Replicate in the nucleus (EXCEPT Pox which carries its own DNA-dependent RNA polymerase)
|
|
|
What DNA virus carries its own DNA-dependent RNA polymerase and does not replicate in the nucleus?
|
Poxvirus
|
|
|
What diseases does HSV-1 cause?
|
Gingivostomatitis, Keratoconjunctivitis, Temporal lobe encephalitis (most common cause of sporadic encephalitis in the US), herpes labialis
|
|
|
How is HSV-1 spread?
|
Respiration secretions, saliva
|
|
|
What diseases does HSV-2 cause?
|
Herpes genitalis, neonatal herpes
|
|
|
How is HSV-2 spread?
|
Sexual contact, perinatal
|
|
|
What diseases does VZV cause?
|
Varicella-zoster (shingles), encephalitis, pneumonia
|
|
|
How is VZV spread?
|
Respiratory secretions
|
|
|
What diseases does EBV cause?
|
Infectious mononucleosis, Burkitt's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma
|
|
|
How is EBV spread?
|
Respiratory secretions, saliva
|
|
|
What diseases does CMV cause?
|
Congenital infection, mononucleousis (negative Monospot), pneumonia. infected cells have characteristic "owl's eye" appearance
|
|
|
How is CMV spread?
|
Congenital, transfusion, sexual contact, saliva, urine, transplant
|
|
|
Where does VZV remain dormant in?
|
Trigeminal and dorsal root ganglia
|
|
|
What class of viruses is EBV and CMV in?
|
Herpesviruses
|
|
|
What virus is Kaposi's sarcoma associated with in AIDS patients?
|
HHV-8
|
|
|
HHV-8 causes what disease?
|
Kaposi's sarcoma in HIV patients
|
|
|
How is HHV-8 spread?
|
Sexual contact
|
|
|
What is a Tzanck test used for?
|
HSV-1, HSV-2, and VZV detection
|
|
|
What is done in a Tzanck test?
|
A smear is taken from an opened skin vesicle to detect multinucleated giant cells
|
|
|
Infected HSV cells also have intranuclear __________ inclusions
|
Cowdry A
|
|
|
What cells does EBV infect?
|
B cells
|
|
|
Name some common symptoms of EBV infection
|
Fever, hepatosplenomegaly, pharyngitis, and lymphadenopathy (esp. posterior cervical nodes from B cells multiplying)
|
|
|
What is the peak incidence of EBV infection
|
15-20 years old
|
|
|
EBV does what to T cells
|
Abnormal circulating cytotoxic T cells (atypical lymphocytes)
|
|
|
Explain how a positive Monospot test works
|
Blood of a person infected with EBV has Ab against EBV that cross reacts and agglutinates sheep RBCs.
|
|
|
What diseases are EBV associated with?
|
infectious mononucleosis, endemic Burkitt's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma
|
|
|
Heterophil antibodies detected by agglutination of sheep RBCs reveal the presence of what virus?
|
EBV
|
|
|
Adenovirus possesses an envelop. True or false
|
FALSE
|
|
|
What symptoms does Adenovirus cause
|
Febrile pharyngitis, pneumonia, conjunctivitis ("pink eye"
|
|
|
What disease does Parvovirus cause
|
Aplastic crises in sickle cell disease, "slapped cheek" rash aka erythema infectiosum (fifth disease), hydrops fetalis
|
|
|
What is hydrops fetalis? What DNA virus is it associated with?
|
Accumulation of fluid/ascites. A prenatal form of heart faiulre usually stemming from fetal anemia. Parvovirus B19 virus
|
|
|
What disease does Papillomavirus cause?
|
HPV - warts, CIN, cervical cancer
|
|
|
What disease does Polyomavirus cause?
|
JC virus - progressive multifucal leukoencephalopathy (PML) in HIV
|
|
|
What class of viruses does JC virus belong to?
|
Polyoma virus
|
|
|
What diseases fall under the Poxvirus class?
|
Smallpox, Vaccinia-cowpox, Molluscum contagiosum
|
|
|
What diseases does Reovirus cause?
|
Reovirus - Colorado tick fever, Rotavirus - #1 cause of fatal diarrhea in children
|
|
|
Diseases of Picornavirus
|
Poliovirus, Echovirus - aseptic meningitis, Rhinovirus - "common cold," Coxsackievirus, HAV (acute viral hepatitis) - PERCH
|
|
|
What are some of the physical manifestations of Coxsackievirus infection?
|
Aseptic meningitis, herpangina (mouth blisters, febrile pharyngitis), hand, foot, and mouth disease, myocarditis
|
|
|
Aseptic meningitis, herpangina (mouth blisters, febrile pharyngitis), hand foot and mouth disease, myocarditis can all be manifestatiosn of this virus
|
Coxsackievirus
|
|
|
Coxsackievirus is classifed as what RNA virus family?
|
Picornavirus
|
|
|
HEV virus can be classified as a RNA or DNA virus? In what class?
|
RNA virus; Hepevirus
|
|
|
What disease does the Norwalk virus cause? What class is it in?
|
Viral gastroenteritis; Calicivirus
|
|
|
Which of the RNA viruses are segmented?
|
Bunyaviruses, Orthomyxoviruses, Arenaviruses, and Reoviruses (BOAR)
|
|
|
How many segments does the influenza virus have?
|
8
|
|
|
What class of viruses is Rubella in?
|
Togavirus
|
|
|
What diseases does Togavirus class have?
|
Rubella (German measles), Eastern equine encephalitis, Western equine encephalitis
|
|
|
HCV, Yellow fever, dengue, St. Louis encephalitis, West Nile virus are all in what class?
|
Flavivirus
|
|
|
HTLV causes what disease? What class?
|
T-cell leukemia. Retrovirus
|
|
|
What diseases is Coronavirus responsible for?
|
"common cold" and SARS
|
|
|
Influenza virus is what class of virus?
|
Orthomyxovirus
|
|
|
What type of capsid does orthomyxovirus have?
|
Helical
|
|
|
Coronavirus has a + or - SS of RNA?
|
Plus
|
|
|
Rhabdovirus causes what disease? + or - RNA? What shape capsid?
|
Rabies, Minus, Helical
|
|
|
Do flaviviruses have envelopes? + or - RNA? Icosahedral or helical capsid?
|
Yes envelope; + RNA; Icosahedral
|
|
|
How many segments do reoviruses have?
|
10-12 segments
|
|
|
What diseases are Paramyxoviruses responsible for?
|
Parainfluenza - croup, RSV - bronchiolitis in babies, Rubeola (Measles), Mumps
|
|
|
What is the treatment for RSV?
|
Ribavirin
|
|
|
What disease is caused by Filoviruses?
|
Ebola/Marburg hemorrhagic fever which is often fatal!
|
|
|
What class of virus is responsible for Ebola/Marburg hemorrhagic fever?
|
Filoviruses
|
|
|
What class of viruses is responsible for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) and Lassa fever encephalitis?
|
Arenaviruses
|
|
|
What spreads Lassa fever encephalitis?
|
Mice
|
|
|
What class of viruses does Hantavirus fall under?
|
Bunyaviruses
|
|
|
What are the sx of Hantavirus?
|
Hemorrhagic fever, pneumonia
|
|
|
What class does HDV fall under?
|
Deltavirus
|
|
|
Deltavirus has what virus in it?
|
HDV
|
|
|
Which RNA viruses are negative stranded? What must they have bring with it to reproduce?
|
Arenaviruses, Bunyaviruses, Paramyxoviruses, Orthomyxoviruses, Filoviruses, and Rhabdoviruses (Always Bring Polymerase Or Fail Replication); RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
|
|
|
Which Picornaviruses can cause aseptic meningitis?
|
Poliovirus, Coxsackievirus, Echovirus
|
|
|
What is the Yellow fever virus transmitted by? What are the reservoirs of this virus?
|
Aedes mosquitos; humans or monkeys
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of a Yellow fever virus infection?
|
High fever, black vomitus, and jaundice. Counsilman bodies may be seen in the liver
|
|
|
What virus causes high fever, black vomitus, jaundice, and Councilman bodies in the liver?
|
Yellow fever virus
|
|
|
What are the sx of German measles? What is the virus that causes German measles?
|
Rubella virus: fever, lymphadenopathy, arthralgias, fine truncal rash.
|
|
|
What virus is the most important global cause of infantile gastroenteritis and is a segmented dsRNA virus?
|
Rotavirus
|
|
|
What does rotavirus do to the GI tract?
|
Villous destruction with atrophy leads to decreased absorption of Na+ and water.
|
|
|
What are the functions of hemagglutinin and neuraminidase of influenza viruses?
|
Hemagglutinin: attach to host sialic acid receptors. Neuraminidase: dissovles mucus
|
|
|
What is croup?
|
Seal like barking cough that is a manifestation of parainfluenza
|
|
|
What is diagnostic of measles?
|
Koplick spots - red spots w/ blue-white center on buccal mucosa
|
|
|
What are signs of rubeola virus infection?
|
Koplik spots, SSPE (subacute sclerosing panencephalitis), encephalitis, and giant cell pneumonia (rarely, in mmunosuppressed). Rash spreads from head to toe.
|
|
|
What are the three C's of measles?
|
Cough, coryza (head cold), conjunctivitis
|
|
|
What virus casues parotitis, orchitis, and aspetic meningitis?
|
Mumps virus
|
|
|
What are Negri bodies?
|
Characteristic cytoplasmic inclusions in neurons infected by rabies virus
|
|
|
What shape does the rabies virus capsid take?
|
Bullet shaped
|
|
|
How long is the incubation period for rabies?
|
Weeks to months
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of rabies virus infection?
|
Fatal encephalitis with seizures, hydrophobia, hypersalivation, and pharyngeal spasm
|
|
|
What virus casues Fatal encephalitis with seizures, hydrophobia, hypersalivation, and pharyngeal spasm
|
Rabies virus (rhabdovirus)
|
|
|
How is rabies virus commonly transmitted
|
More from bat, racoon, and skunk bites than from dog bites
|
|
|
How does rabies affect the CNS
|
Migrate in a retrograde fashion up nerve axons
|
|
|
What are arboviruses?
|
Viruses transmitted by arthropods (mosquitos, ticks)
|
|
|
What is the difference between Rubella and Rubeola?
|
Rubella - togavirus, German 3 day measles; Rubeola - Paramyxovirus, measles
|
|
|
What diseases does Varicella cause?
|
Chickenpox and zoster
|
|
|
What is the difference between Varicella and Variola?
|
Varicella - herpesvirus: chickenpox and zoster. Poxvirus - smallpox
|
|
|
HAV has a short or long incubation? How long?
|
Short - 3 weeks
|
|
|
Can anybody be a HAV carrier?
|
No
|
|
|
How is HBV transmitted?
|
Parenteral, sexual, and maternal-fetal routes.
|
|
|
HBV has a short or long incubation? How long?
|
Long - 3 months
|
|
|
Can anybody be a HBV carrier?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Describe the replication mechanism of HBV
|
HBV is a DNA hepadnavirus. Host cellular RNA polymerase transcribes RNA from the DNA template. Reverse transcriptase from virus transcribes - strand DNA genome from RNA intermediate. Then viron DNA dependent DNA polymerase transcribes + strand of DNA to make complete replication.
|
|
|
HCV is transmitted by
|
Blood primarily
|
|
|
Can there be carriers of HCV?
|
Yes
|
|
|
HCV is a common cause of hepatitis among which populations
|
Post-transfusion and IV drug users in US
|
|
|
What are the four Cs associated with HCV?
|
Chronic, cirrhosis, carcinoma, carriers
|
|
|
Why can an individual be infected with multiple strains of HCV?
|
No 3'-5' exonuclease proofreading. RNA polymerase makes many errors --> individual with infection has many strains
|
|
|
What hepatitis virus is commonly associated with cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma?
|
HCV
|
|
|
Describe HDV
|
Defective virus that requires HBsAg as its envelope. HDV can coinfect with HBV or superinefect. Superinfect has a worse prognosis.
|
|
|
Can there be carriers for HDV?
|
Yes
|
|
|
How are HBV, HCV, and HDV all transmitted?
|
Parenteral, sexual, and maternal-fetal
|
|
|
HEV is what class of virus? Envelope? RNA structure? Capsid symmetry?
|
Hepevirus. No envelope. SS + Icosahedral
|
|
|
What hepatitis virus has a high mortality in pregnant women?
|
HEV
|
|
|
What hepatitis virus causes water-borne epidemics?
|
HEV
|
|
|
What does the presence of HBsAg indicate?
|
Continued presence indicates carrier state
|
|
|
What is the function of HBsAb?
|
Provides immunity to hepatitis B
|
|
|
What is HBeAg
|
A second, different antigenic determinant in the HBV core besides HBcAg. Important indicator of active viral replciation and high transmissibility
|
|
|
What is the significance of HBeAb presence?
|
Antibody to e antigen (in core). Indicates LOW transmissibility
|
|
|
What is the significance of HBV DNA presence in the serum?
|
Index of infectivity
|
|
|
What is the signifcance of HBx?
|
Functions in deregulation of hepatocyte replication which causes hepatocellular carcinoma in those infected with HBV.
|
|
|
Do HBcAb provide immunity and why do we use them?
|
NOT protective, no immunity - but used to distinguish a new infection from an old infection (IgM vs. IgG)
|
|
|
What is the difference in significance between the presence of HBeAg and HBeAb
|
HBeAg = high transmissibility; HBeAb = low transmissibility
|
|
|
What would you find in the serum of acute HBV disease?
|
HBsAg and HBcAb
|
|
|
What would you find in the serum of a patient in the window phase after resolution of HBV infection?
|
HBcAb
|
|
|
What would you find in the serum of a patient who is a chronic carrier of HBV?
|
HBsAg and HBcAb. Failed to develop protective HBsAb.
|
|
|
Somebody who is a chronic carrier of HBV has failed to develop what?
|
HBsAb
|
|
|
Somebody who is immunized for HBV has what in his serum?
|
HBsAb
|
|
|
What is greater in viral hepatitis: ALT or AST
|
ALT > AST
|
|
|
What is greater in alcoholic hepatitis: ALT or AST
|
AST > ALT
|
|
|
What are the main components/divisions of the HIV genome?
|
LTRs, GAG, POL, ENV, TAT, REV, NEV
|
|
|
What is the function of LTRs in the DNA genome?
|
Long terminal repeat sequences: 1) Sticky ends - sequences that are recognized by integrase that are involved ininsertion into host DNA. 2) Promoter/enhancer fx: once incorporated into host DNA, proteins bind to LTRs that can modify DNA trnascription
|
|
|
What is the HIV gene that codes for proteins inside the envelope like nucleocapsid, capsid, and matrix?
|
GAG
|
|
|
What is another name for the capsid and matrix protein genes?
|
Capsid - p24. Matrix - p17
|
|
|
What envelope proteins are transmembrane through the envelope and what proteins are outside the envelope?
|
gp41env is transmembrane through envelope. gp120env is outside the envelope
|
|
|
What does the POL gene code for in the HIV genome?
|
Protease, RT, and integrase proteins
|
|
|
What is the function of protease in HIV?
|
Protease cleaves gag and pol proteins from larger precursor proteins.
|
|
|
What makes the HIV genome hard to vaccinate against?
|
Hypervariable regions in the env proteins. Reverse transcriptase undergoes frequent mutation.
|
|
|
What does the TAT gene encode?
|
Viral transactivator protein that binds to viral genome and activates transcription.
|
|
|
What receptor proteins does HIV bind to on T cells? on macrophages?
|
CXCR4 and CD4 on T cells. CCR5 and CD4 on macrophages.
|
|
|
What protein mutation would give immunity or slow down the course of HIV infection?
|
Heterozygous CCR5 mutation = immunity. Heterozygous CCR5 mutation = slower course
|
|
|
What tests are used in the diagnosis of HIV?
|
ELISA first (sensitive, Rule out) then Western blot assaay (specific, rule in), or HIV PCR/virall load tests
|
|
|
What are the disadvantages of ELISA/Western blot tests?
|
Often falsely negative in the first 1-2 months of HIV infection and falsely positive initially in babies born to infected mothers (anti-gp120 crosses placenta)
|
|
|
What are the four F stages of HIV infection?
|
1. Flulike (acute) 2. Feeling fine (latent) 3. Falling count 4. Final crisis
|
|
|
Where does the HIV virus replicate during the latent phase?
|
Lymph nodes
|
|
|
What AIDS opportunitistic infections/diseases occur in the brain?
|
Cryptococcal meningitis, toxoplasmosis, CMV encephalopathy, AIDS dementia, PML (JC virus)
|
|
|
What AIDS opportunitistic infections/diseases occur in the eyes?
|
CMV retinitis
|
|
|
What AIDS opportunitistic infections/diseases occur in the mouth and throat?
|
Thrush (Candida albicans), HSV, CMV, oral hairy leukoplakia (EBV)
|
|
|
What AIDS opportunitistic infections/diseases occur in lungs?
|
Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PJP), TB, histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What AIDS opportunitistic infections/diseases occur in the GI tract?
|
Cryptosporidiosis, Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex, CMV colitis, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (EBV), Isospora belli (parasite)
|
|
|
What AIDS opportunitistic infections/diseases occur in the skin?
|
Shingles (VZV), Kaposi's sarcoma (HHV-8)
|
|
|
What AIDS opportunitistic infections/diseases occur in the genitals?
|
Genital herpes, warts, and cervical cancer (HPV)
|
|
|
Risk of what infections increases at a CD level <400 for AIDS patients?
|
Oral thrush, tinea pedis, reactivation VZV, reeactivation tuberculosis, other bacterial infections (H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae, Salmonella)
|
|
|
Risk of what infections increases at a CD level <200?'
|
Reactivation HSV, cryptosporidiosis, Isopora, disseminated coccidioidomycosis, Pneumocystis pneumonia
|
|
|
Risk of what infections increases at a CD level <100?
|
Candidal esophagitis, toxoplasmosis, histoplasmosis
|
|
|
Risk of what infections increases at a CD level <50?
|
CMV retinitis and esophagitis, disseminated M. avium-intracellulare, cryptococcal meningoencephalitis
|
|
|
Neoplasms associated with HIV
|
Kaposi's sarcoma (HHV-8), invasive cervical carcinoma (HPV), Primary CNS lymphoma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
|
|
HIV encephalitis occurs when in course of infection? How does it occur? What is the pathologic finding?
|
Late in course of HIV infection. Virus gains CNS access via infected macrophage. Microglial nodules with multinucleated giant cells.
|
|
|
What is a prion?
|
Proteinaceous infectious particles that do not contain RNA or DNA. Encoded by cellular genes.
|
|
|
What diseases do prions cause?
|
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJP-rapid progressive dementia), kuru, scrapie (sheep), and "mad cow disease"
|
|
|
Normal prions vs. pathologic prions differ how?
|
Normal: alpha helix conformation. Pathologic: B-pleated sheets.
|
|
|
Why do pathologic conformations of prions accumulate?
|
Resistance to proteinase digestion
|

