![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What type of joints are the D2-5 MCPs? Another example of the same joint? |
Condyloid joints allow flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, and circumduction, and they can be seen in the MCP joints of the index through little fingers and in wrist joints. |
|
|
|
Most common FOOSH fracture? |
After distal radius fracture, the next most common fracture of the wrist is scaphoid, followed by triquetrum, trapezium, and lunate.
|
|
|
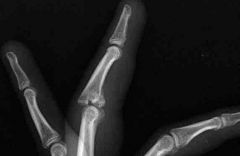
What type of arthroplasty for this 6 wk old injury? |
Hemi-hamate arthroplasty |
|
|
|
How much angulation is tolerated in metacarpal shaft fractures of the small finger? Ring finger? Long & middle? |
Metacarpal shaft fractures generally require reduction for angulation greater than 30 degrees in the little finger, 20 degrees in the ring finger, and any angulation in the long and index fingers.
|
|
|
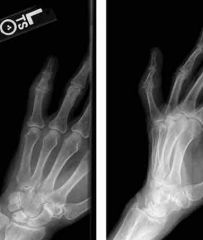
Best treatment for dorsal thumb dislocation? |
Closed Reduction, hyperextend at the joint & place pressure on dorsal base of proximal phalanx. |
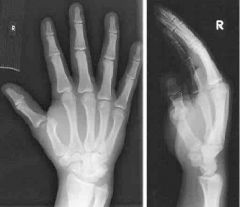
|
|
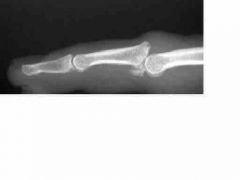
23-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after twisting the long finger of his dominant right hand while playing basketball. Physical examination shows dorsal instability of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint. X-ray study shows a volar buttress fracture involving 40% of the articular surface of the base of the middle phalanx. X-ray joint reduction is attained by passively flexing the PIP joint to 30 degrees. What is the most appropriate management? |
Extension block splinting since its stable when flexed. |
|
|
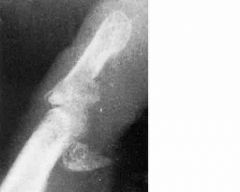
17-year-old boy is referred to the office by his primary care physician for consultation regarding lack of active flexion of the distal interphalangeal joint of the ring finger of the dominant right hand. Six weeks ago, he sustained an injury to the hand while practicing with his high school football team. Immediately after the injury, the team’s trainer initiated alternating application of hot and cold packs to the hand and gave the patient a finger splint, which he wore intermittently for five weeks. Current physical examination shows a tender mass at the distal interphalangeal joint of the ring finger. A radiograph is shown. What is the most appropriate next step? |
ORIF for this jersey finger since there’s a large bony fragment |
|
|
|
Physical examination and radiographs confirm a displaced Bennett fracture. Closed reduction of the fracture followed by percutaneous pin fixation is planned. In addition to longitudinal traction on the thumb while exerting pressure over the dorsoradial aspect of the metacarpal base, which of the following is the most appropriate reduction maneuver? |
Palmar abduction & thumb pronation |
What type of palmar motion? Pronation or supination? |
|
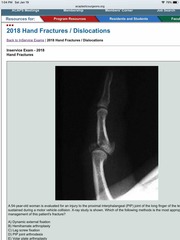
Front (Term) |
A) Dynamic external fixation |
|
|
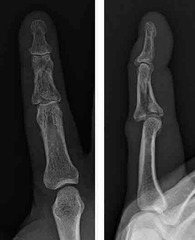
Best treatment? |
Dynamic traction reduction |
|
|
|
Injuries to the fifth carpometacarpal joint, including subluxation, dislocation, and fracture-dislocation, are often missed with standard two-view and three-view hand images. Two views have been suggested to help detect this subtle injury: What are they?
|
Anteroposterior view with forearm pronated 30 degrees from full supination. This view shows more clearly the profile of the articulation between the hamate and fifth metacarpal base. Lateral with 30 degrees of pronation. This view is especially helpful for detecting subluxation of the metacarpal dorsally off of the hamate. |
|

