![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is an income Statement |
A profit and loss account
Shows a companies income v expenditure, or, trading performance, over a given period, which may be a month, a quarter, or a financial year |
TRADING PERFORMANCE |
|
|
What is a Balance Sheet |
A snapshot in time of a companies financial position
Produced at the end of the financial year
Shows Assets, Owns, Debits, =, Liabilities, Owes, Credits |
POSITION
END
DR = CR |
|
|
What assets are displayed on a Balance Sheet |
Non Current Assets
Fixed Long Term Assets with a remaining useful life of greater than 12 months, I E, Land, Buildings, Equipment and Machinery, Plant and Vehicles
Current Assets
More Liquid assets, retained for less than 12 months, I E, Inventories, Trade Receivables, Cash and Cash Equivilent |
> 12 MONTHS
< 12 MONTHS |
|
|
What are Non-Current Assets and what are they used for |
Assets that have a remaining useful life of more than 1 year
Acquired for use within a business with a view to earning profit
Not sold during the normal course of business
|
USEFUL LIFE
EARNING PROFIT
NORMAL COURSE |
|
|
What is displayed on the liabilities section of a balance sheet |
Equity
Share Capital, Retained Earnings, Accumulated Profit
Non Current Liabilities
Borrowings, I E, long term loans
Current Liabilities
Trade Payables, Wages, Overheads, Short term borrowing, I E, Bank Overdraft |
|
|
|
What are Trade Payables |
Monies owing to suppliers for goods or services bought on credit
Can be thought of as a short term interest free loan |
CREDIT
INTEREST FREE |
|
|
5 Facts about Retained Earnings |
1. The percentage of profits not paid out to shareholder as a dividend
2. Retained by the company for re-investment or to pay off debts
3. Belongs to the shareholders
4. A businesses most important source of finance
5. Calculated at the beginning of the financial year |
PROFITS
RE-INVESTMENT
BELONGS
IMPORTANT
BEGINNING |
|
|
What is Accumulated Profit |
Similar to Retained Earnings but may include Reserve Accounts |
RESERVE |
|
|
How does Cash Flow around the Working Capital Cycle |
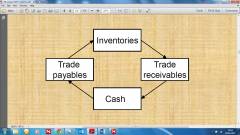
|
|
|
|
How do we calculate the Book Value of a Company |
Book Values = Equity, minus, Current Liabilities |
|
|
|
What financial controls can be implemented for inventories |
Hold Maximum
Re-order Levels
Hold Minimum |
|
|
|
Name some of the problems associated with holding Inventories |
Too High
Increased cost of holding, Uses Working Capital, Obsolescence
Too Low - Interrupted Operations |
INCREASED
CAPITAL
OBSOLESCENCE
INTERRUPTED |
|
|
What are the main financial controls associated with giving customers credit |
Customer Credit Ratings
Company Policies
Collection Periods, I E, 30, 60, or 90 days |
RATINGS
POLICIES
COLLECTION |
|
|
What are the main problems associated with giving customers credit |
Too High
Uses working capital, issues with cash flow
Too Low
Loss of customers |
CAPITAL
ISSUES
LOSS |
|
|
In which 3 areas of the cash flow cycle can we exert financial controls |
Inventories
Trade Receivables, A, K, A, Credit
Cash |
|
|
|
What are the main financial controls associated with cash |
Budgeting
&
Forecasting, Daily, Weekly, Monthly |
|
|
|
Name 4 cash flow control systems |
RAC - Record, Analyse, Control
Pareto, the 80 20 rule
Input, Process, Output, Feedback
ABC Analysis |
|
|
|
Name 2 financial accounting standards |
the I F R S, International Financial Reporting Standards
The I A S, International Accounting Standards |
|
|
|
Explain cash accounting |
An accounting method where financial events are only recognized after cash has changed hands
Income is recorded once it has been received
Expenses are recognised when they are actually paid |
CHANGED HANDS
RECEIVED
PAID |
|
|
List 1 advantage and 1 disadvantage of cash accounting |
An advantage is that, a business may appear to be better off than it actually is
A disadvantage is that, it provides an incomplete picture of liabilities incurred but not yet paid |
BETTER OFF
INCOMPLETE PICTURE |
|
|
Explain Accruals Accounting |
An accounting method that, measures the performance and financial position of a company, by recognising financial events, in the period they occur, irrespective of when cash changes hands
Income is recognized when, the right to receive consideration arrives
Expenses are recognized when, they actually occur |
FINANCIAL EVENTS
CONSIDERATION
ACTUALLY OCCUR |
|
|
When should income and expenses be recognized under accruals accounting |
When payment or part payment has been received or made
When customers agree to pay their bills
When a suppliers agreed credit period expires
|
PAYMENT
CUSTOMERS
SUPPLIERS |
|
|
When should assets and liabilities be recognized under accruals accounting |
An asset should be recognised if it has a remaining useful life of greater than 12 months
Liabilities should be recognised before the receipt of a suppliers invoice
|
USEFUL LIFE
BEFORE |
|
|
List 3 benefits of accruals accounting |
Provides a more complete picture of income earned and costs incurred
Assets and liabilities are recognized
Cash flow manipulation is removed |
COMPLETE PICTURE
RECOGNIZED
MANIPULATION |
|
|
What is an accrual |
Expenditure on goods or services for which the supplier has not yet invoiced or been paid |
NOT YET INVOICED |
|
|
How are accruals recorded in the financial statements |
Charged as an expense to the income statement
Deducted as an accrued expense from the current liabilities section of the balance sheet at the end of the financial period in which it occurred |
PAYMENT
DEBIT
CURRENT LIABILITIES |
|
|
What effect does an accrual have on expenses, liabilities and profit |
Increases expenses and liabilities
Decreases profit |
|
|
|
What is a prepayment |
Expenditure on goods or services for future benefit, which are charged to future operations, I E, insurance |
FUTURE |
|
|
How are prepayments recorded on the financial statements |
Charged as an expense to the income statement during the period in which it occurred
Added as a prepiad expense (of the relevant account) to the current assets section of the balance sheet |
PAYMENT
DEBIT
CURRENT ASSETS |
|
|
What effect does prepayments have on expenses liabilities and profit |
Decreases expenses and liabilities
Increases profit |
|
|
|
What are intangible assets |
Non financial assets which have no physical form, I E, Goodwill, Brand Names, IPR
|
NO PHYSICAL |
|
|
How are intangible assets identified and controlled |
Through custody or legal rights |
CUSTODY
LEGAL |
|
|
What is Depreciation |
A measure of the wearing out, consumption, or other loss of value, of non-current assets through, use, the passage of time, or obsolescence, due to technological or market changes |
CONSUMPTION
USE
TIME |
|
|
Name 2 methods of calculating Depreciation |
Straight Line Method
where, annual depreciation = original cost of asset minus estimated residual value, divided by expected useful life in years
Reducing Balance Method
where, Annual depreciation = Net Book Value, times, depreciation rate, expressed as a percentage |
STRAIGHT
REDUCING |
|
|
What is a Debtor |
A person or entity who owes money |
OWES |
|
|
What is a Creditor |
A person or entity to whom money is owed, for goods or services received, but not yet paid for |
OWED
NOT YET PAID |
|
|
What are Accounting Standards |
The rules under which financial accounts are prepared |
RULES |
|
|
Which body developed accounting standards in the UK |
The I,A,S,B
International Accounting Standards Board |
IASB |
|
|
How is annual depreciation recorded on financial statements |
Accumulated in the provision for depreciation account
Charged as an expense to the income statement
Deducted as annual depreciation from the Non-Current assets section of the Balance Sheet, to show, Net Book Value |
ACCUMULATED EXPENSE
DEDUCTED |
|
|
What is the formula for re-evaluating annual depreciation |
Annual Depreciation = Revised Value of Asset, minus, Residual Value, divided by Remaining Useful Life in years |
|
|
|
List 6 policies a company should have relating to offering customers credit |
1. Which customers should be offered credit
2. How much credit should they be offered
3. The length of time the credit will be offered over
4. Any discounts for prompt payment
5. Collection Policies
6. How to Manage the risk of non payment |
WHICH
HOW MUCH
LENGTH
DISCOUNT
COLLECTION
RISK |
|
|
What is a Provision for Doubtful Debt |
An estimate of of the amount of customer debt, that a company expects not to be paid, based on previous experience
Can be thought of as a safety net
Helps avoid claiming profits which fail to materialise |
ESTIMATE
SAFETY NET
AVOID |
|
|
How do we record the provision of bad/doubtful debts on the financial statements |
If no provision already exists the full amount is taken as an expense into the Income Statement If a provision exists from the previous year
An increase will be taken into the income statement as and expense
A decrease will be taken into the Income Statement as an income
The full amount will be deducted from the trade and other receivables figure in the current liabilites section of the balance sheet |
EXPENSE
EXPENSE
INCOME
DEDUCTED |
|
|
What are Bad Debts |
Debts written off when it becomes reasonably certain the customer will never pay. The outstanding amount is written off as a bad debt |
CERTAIN
CUSTOMER
OUTSTANDING |
|
|
What is debt factoring |
An arrangement to have customer debts collected by a factoring company who advance the business a proportion of the total amount due to be collected |
PROPORTION
TOTAL |
|
|
What are the 3 main methods used to value inventories |
LIFO - Last In First Out
FIFO - First In First Out
AVCO - Average Cost |
|
|
|
List 6 costs associated with holding inventories |
1. Cost of Capital
2.Warehousing and Handling
3. Deterioration
4. Obsolescence
5. Insurance
6. Pilferage
|
|
|
|
What are the costs associated with procuring inventories |
Ordering Costs
Delivery Costs |
|
|
|
What are the costs associated with a shortage of inventories |
Profit from lost sales
Additional cost of emergency inventories |
PROFIT
EMERGENCY |
|
|
What assumptions are made when using the EOQ inventory management model |
Demand is constant,
Inventory is used up evenly over time, and, topped up just as it runs out |
CONSTANT
EVENLY
TOPPED UP |
|
|
What is the purpose of the EOQ inventory management model |
to determine the optimum inventory order level I, E, the amount of inventory to be ordered at one time, to ensure annual inventory costs are minimised
Formula
EOQ = Square Root (2 x Co x D) / Ch
where
Co = cost of placing one order
D = inventory usage in units for one period (demand)
Ch = holding cost per unit of inventory for one period |
OPTIMUM
MINIMISED
PLACING
USAGE
PER UNIT |
|
|
What sources of finance are available to a business |
Internal and External
Long Term and Short Term |
|
|
|
List 3 short term internal sources of finance |
Reduced inventory levels
Delayed payment of trade payables
Tighter credit controls
|
REDUCED
DELAYED
TIGHTER |
|
|
List a long term, internal source of finance |
Retained earnings |
RETAINED |
|
|
List 2 short term, external sources of finance |
Bank overdraft
Debt Factoring |
|
|
|
List 2 long term, external sources of finance |
Equity, e.g. ordinary shares
Debt, e.g. borrowings
|
|
|
|
List and explain 2 other forms of Borrowing |
Finance Lease Like a loan agreement for the purchase of Capital assets in installments
Sale and Lease Back Where a company raises finance by selling off a fixed asset to a financial institution and agreeing to lease it back so it can continue to use it |
FINANCE
INSTALLMENTS
LEASE BACK
SELLING OFF
|
|
|
List 4 things that should be considered when comparing Long Term v Short Term Borrowings |
Matching
Flexibility
Renewals
Interest Rates |
|
|
|
Describe 5 factors which should be considered when using borrowing as a primary source of finance for a business |
1. It is a cheaper source of finance than equity
2. Tax relief can be claimed on loan interest payments
3. Borrowings are secured on company assets
4. The lender has first claim on assets should the company go into liquidation
5. Repayments must be made as scheduled, irrespective of the company's financial postion |
CHEAPER
TAX
SECURED
LENDERS
REPAYMENTS |
|
|
List 3 advantages of a company being listed on the stock market |
1. Access to a wider pool of finance
2. Improved company image
3. Improved marketability of shares
|
FINANCE
IMAGE
MARKETABILITY |
|
|
List 3 disadvantages of a company being listed on the stock market |
1. More vulnerable to market fluctuations
2. Increased risk of hostile takeover
3. Subject to additional regulatory requirements |
VULNERABLE
RISK
SUBJECT TO |
|
|
List 4 ways in which a shareholder benefits from investing in shares of a company |
1. They are effectively the owners of the company
2. They share in the profits of the business through dividend payments
3. They have voting rights
4. They have limited liability should the company go into liquidation |
OWNERS
DIVIDEND
VOTING
LIMITED LIABILITY |
|
|
List 2 drawbacks of investing in shares of a company |
Shareholders have last claim on the companies assets in the event of liquidation
Value of investment can rise or fall depending on the stock market |
ASSETS
INVESTMENT |
|
|
What is a bonus share issue |
An issue of new shares in a company at no cost to the shareholders |
NEW
NO COST |
|
|
Explain how a bonus share issue works |
The shares are issued by converting some reserves (e.g. share premium) into capital
The new shares are issued at no cost to the shareholders and distributed in proportion to their existing shareholdings
No cash is raised by the company during the process |
PREMIUM
PROPORTION
NO CASH |
|
|
What is a rights issue |
An issue of new shares in a company for cash
Initially offered to existing shareholders in proportion to their current shareholdings
The issue price of the new shares is always below current market value of shares already in circulation |
CASH
PROPORTION
BELOW |
|
|
What is Share Capital |
Equity generated from the issue of shares in a company, which, can be in the form of cash, or, other considerations |
EQUITY
CASH
OTHER |
|
|
What is a share premium |
The excess paid to a company for a share over and above its nominal value
Share price = £7
Nominal value = £5
Share premium = £7 - £5 = £2 |
EXCESS
NOMINAL |
|
|
Explain Weighted Average Cost of Capital |
WACC is the average cost of a companies finance, weighted against the relative size of each element, compared to the total output
WACC = (% of Equity x Cost of Equity) + (% of Debt x Cost of Debt)
Cost of equity is the rate of return required by the ordinary shareholders on their investment
Cost of debt is the interest rate of a companies loans |
AVERAGE
WEIGHTED
RELATIVE
RATE OF RETURN
INTEREST RATE
|
|
|
What type of ratio is Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) |
A profitability ratio |
|
|
|
What type of ratio is the Liquid Assets ratio |
A liquidity ratio |
|
|
|
What type of ratio is Revenues Generation |
A profitability ratio |
|
|
|
What type of ratio is the Current Ratio |
A liquidity ratio |
|
|
|
What type of ratio is the Borrowing Ratio |
A gearing ratio |
|
|
|
What type of ratio is Profit Margin |
A profitability ratio |
|
|
|
What is the Liquid Assets Ratio also known as |
The acid test |
|
|
|
What type of ratio is Inventories Turn |
A liquidity ratio |
|
|
|
What type of ratio is the Income Gearing Ratio |
A gearing ratio |
|
|
|
What type of ratio is Trade Receivables Weeks |
A liquidity ratio |
|
|
|
What is Trade Receivables Weeks also known as |
Debt Collection Period |
|
|
|
What does Return on capital Employed indicate |
The overall return a company generates for every £1 invested |
RETURN |
|
|
What does Profit Margin indicate |
The average profit a company generates for every £1 of revenues |
REVENUES |
|
|
What does Revenues Generation indicate |
The revenues generated for every £1 of capital employed |
CAPITAL |
|
|
What does the Current Ratio indicate |
A companies ability to pay its way, in the short term
i.e. a liquidity test |
SHORT TERM |
|
|
What does trade receivables weeks indicate |
The length of time in weeks a company takes to collect its debts |
TIME |
|
|
What does Inventory Turn indicate |
The average number of times per year a company turns over its inventories |
AVERAGE |
|
|
What is the Acid Test Ratio |
A more stringent liquidity test |
STRINGENT |
|
|
What does the Borrowing Ratio Indicate |
The overall gearing of a company, or the number of times borrowing exceeds equity
i.e. a value of 8 indicates the company has borrowed £8 for every £1 invested |
GEARING |

