![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define and explain the nature of risk?
|
- possibility or probability that something may occur that is unexpected, not anticipated.
- adds uncertainty - business exposed to operational and financial risks. - Operational risks impact upon day-to-day functions - Financial risks affect business cash flows and the value of balance sheet assets and liabilities. |
|
|
What is the purpose of risk management?
|
- ensure org is aware of risks with business operations.
- ensure personnel consider outcomes of decisions - establish objectives, policies, procedures and strategies that result in risk exposures being identified, measured and managed. - To mitigate risk. |
|
|
Who is responsible for the establishment of risk management objectives, policies, procedures and strategies in a corporation?
|
- The board of directors of an org is responsible for the determination and documentation of all objectives.
- it will determine related risk management policies; that is, how objectives will be implemented. - CEO and Exec will establish risk management procedures, strategies and reporting structures. |
|
|
It is often argued in risk management literature that risk must be identified, measured and managed, why?
|
- Before an org can begin to manage risk exposures it needs to know what they are - nature will vary.
Once identified it is necessary to measure impacts of - Based on this quantitative analysis, org will decide how, or if, the risk is to be managed. - Given a decision to manage a risk, the org will determine alternative strategies & put procedures in place to implement the strategy. |
|
|
If a company is highly reliant on its computer and communication systems. What category of risk best defines this type of risk exposure?
|
Operational risk is the principal or direct risk, but if a failure of the computer and
communications systems occur, then there will be a range of flow-on or consequential risks, particularly financial risks. |
|
|
Within the context of internal and external risk management,how can a company reliant on pc's may consider managing this risk exposure?
|
- A large corp may decide to manage this risk by building a secondary, system which must mirror primary one.
- Alternatively, an organisation may decide to out-source back-up arrangements to another provider. There are organisations that specialise in providing this service. |
|
|
What are the five major risk categories?
|
- Interest rate risk - the risk of an exposure to movements in current market interest rates.
- Foreign exchange risk - the risk that the value of one currency relative to another currency will change. - Liquidity risk - this risk has different aspects depending on the party concerned. - Credit risk - the risk that borrowers will not repay commitments when they are due. - Capital risk - is the risk that a corporation will not have sufficient capital to expand the business and maintain the desired debt to equity ratio. |
|
|
When a company expects existing high interest rates to slow activity in the local economy significantly. At the same time there are strong indicators that a number of major international economies are slowing, how are the interrelationships likely to eventuate between the five risk categories?
|
high interest rates mean debt finance cost will increase. Slowing consumer + business spending. Exchange rate changes, as will the slowing of the economy. The change in the exchange rate will affect cash flows, assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies as well as the level of imports and exports. Unemployment levels will rise and people will default on loans. Causing liquidity issues of the bank manager as well as being exposed to credit risk. If loan defaults exceed profits in a particular year, then losses will need to be written off
against capital or shareholder funds. |
|
|
What is a futures contract?
|
- A futures contract is an agreement between two parties to buy, or sell, a specified commodity or financial instrument at a specified date in the future at a price determined today.
- Futures contracts are standardised contracts traded through a formal exchange that enable the management of risk exposures associated with commodities and financial assets. |
|
|
A large fund manager has forecast that it will need to purchase at least $100 million worth of shares at the end of the next quarter. The fund manager has a policy that requires it to hedge the risk that the share price may rise over that period using a share index futures contracts. What transactions will he make?
|
- A future contract risk management strategy requires the risk manager to carry out a transaction in
the futures market today that corresponds with the physical market transaction risk that will occur in future - risk manager is planning to buy shares in future so s/he will buy share index futures contracts today. - In three mth, risk manager will close-out the futures market position be selling identical share index futures contracts. |
|
|
What are the cash flow implications for the funds manager of the futures contract risk management strategy?
|
- At commencement of strategy funds manager will be required to make an initial margin payment -specified % of the notional contract value.
- The futures contracts will be marked-to-market daily by futures exchange clearing house. If contract prices have moved against funds manager, required to top up the margin account with a maintenance margin call. - When the futures market position is closed out, the manager will have made either a P or L, being net difference between the initial buy price and sell price. - The profit or loss from the futures market transactions will be used to offset changes in the share prices in the share market. |
|
|
How can making a loss with the futures market strategy can result in the risk manager successfully hedging an identified risk exposure?
|
- Assume a company that has to roll-over a short-term debt facility in three months time. risk manager may use futures market strategy to hedge interest rate risk by selling a 90-day bank accepted bills futures contract.
- If interest rates fall over the contract period, then the mgr would make a loss on the futures transactions. - However the mgr would be able to borrow in debt market at the lower interest rate. - The loss made in the futures market is offset by the lower cost of borrowing in the debt market. The manager is satisfied because he/she had locked-in an interest rate; therefore, the risk has been hedged. |
|
|
Define an option and explain the premium and the exercise price.
|
- gives the option-buyer the right, but not obligation, to buy or sell a specified commodity or instrument at a specified price on or before a specified date.
- The price established in the option contract is known as the exercise price, or the strike price. - The exercise price determined today at which the buyer of the option is able to buy or sell the specified commodity or financial instrument at exercise date. - The option has value, therefore the writer (or seller) of an option contract will receive a premium from buyer - premium is paid up-front whether or not option is exercised at a later date. |
|
|
What is a call option?
|
A call option gives the option-buyer the right to buy the commodity or financial instrument
specified in the option contract at the exercise price either on a specified date, or alternatively at any time up to a specified date. |
|
|
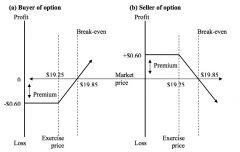
An investor enters into a call option on Santos Limited shares with an exercise price of $19.25 per share in two months, and pays a premium of $0.60 per share.
|
|

