![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The purpose of Conceptual Framework |
Is to set out the various concepts that underpin financial reporting in order to assist 1. The IASB in developing new IFRS, evaluating existing IFRS and by providing a basis that enables it to reduce the number of alternatives currently allowed in the IFRS 2. The various national standard setters to develop national standards 3. Prepare-rs of financial statements in interpreting and applying difficult IFRS or creating their own policies where existing IFRS do not provide guidance or do not cater for the topic. 5. Users in interpreting financial statements that comply with IFRS 6. Other parties interested in how the IASB develop IFRS |
|
|
Concepts currently contained in the CF include |
1. Objective of general purpose Financial reporting. 2. Underlying assumption inherent in a set of financial statements 3. Qualitative characteristics of useful financial statements 4. Definitions of elements in financial statements 5. Recognition criteria to be met before the element may be recognized 6. Measurement bases that may be used when measuring the elements 7. Concepts of capital and capital maintenance |
|
|
The Structure of the CF |
Ch 1- The objective of general purpose financial reporting (new) Ch 2 The reporting entity (empty) Ch 3 Qualitative characteristics of useful financial information (new) Ch 4 Still to be named (Contains the text of the old framework) - Underlying assumption - Elements - Recognition - Measurement - Capital maintenance |
|
|
The objective of general purpose financial reporting is |
* To provide financial information about the reporting entity * that is useful to existing investors, lender and other creditors * in making decisions about providing resources to the entity |
|
|
The Accrual Basis |
* The effects transactions and other events and circumstances * on a reporting entity's economic resources and claims * in the periods in which those effects occur * even if the resulting cash receipts and payments occur in a different period |
|
|
The Cash Flow Basis entails recording |
* cash receipts and cash payments * in the periods in which they occur |
|
|
The CF admits that the cash flow basis provides additional useful information, |
but many users argue that the accrual system is inherently flawed because it allows, for example, the manipulation of profits through using various accounting policies and measurement methods |
|
|
For Financials to be useful to its users must have qualitative characteristics. The CF separates into 2 |
1. Fundamental Qualitative Characteristics * Relevance & faithful representation 2. Enhancing Qualitative Characteristics * Comparability * Verifiability * Timeliness * Understandability |
|
|
Relevance |
Must consider whether it could make a difference in the users decision making. Relevant information must have * Predictive value- financial info need not include predictions or forecasts simply offer info that users can input into their own predictions or forecasts and or * Confirmatory value- provides feedback regarding the users previous evaluations |
|
|
Materiality is not qualitative characteristic but is used in assessing what is relevant. Information is material if? |
The decisions of the users about a specific reporting entity could be influenced if it were misstated or omitted from the financial information |
|
|
Faithful representation |
*Complete- all info necessary for the user to understand the phenomenon *Neutral- Free from Bias (Bias = manipulation to get a response that is either favorable or unfavorable) * Free from Error- no errors or omissions in the description of phenomena & selection and application of processes used to produce the information. free from error does not mean perfect |
|
|
Applying the fundamental qualitative characteristics |
Steps 1. Identify the economic phenomenon that has the potential to be useful to the user 2. Identify what type of information would be most relevant 3. Determine whether the information is available and can be fairly represented. |
|
|
Enhancing Qualitative characteristics |
* Comparability- enables users to identify & understand similarities in items & differences among items. Comparability is the goal consistency helps achieve the goal. * Verifiability- means different knowledgeable and independent observers could reach consensus, although not necessarily complete agreement * Timeliness- in time to be capable of influencing their decisions * Understandability- Classified, characterized & presented, Clearly & concisely |
|
|
Underlying Assumption |
Going concern |
|
|
Assets |
* Resource * Controlled by the entity * As a result of a past event * From which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the entity |
|
|
Liability |
* Present obligation * Of the entity * As a result of a past event * The settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the entity of resources embodying economic benefit |
|
|
Equity |
* The residual interest in the assets * After deducting all liabilities |
|
|
Income |
* An increase in economic benefits * During the accounting period * In the form of increases in assets or decreases in liabilities * Resulting in increases in equity * Other than contributions from equity participants |
|
|
Expenses |
* A decrease in economic benefits * During the accounting period * In the form of decreases in assets or incurrence of liabilities * Resulting in decreases in equity * Other than distributions to equity participants |
|
|
Recognise = Journalise |
An element may only be recognised if it meets both the relevant definition & recognition criteria |
|
|
Recognition criteria |
Flow of future economic benefits must be probable and cost or value must be reliably measurable |
|
|
Disclosure |
Gives detail about items already recognised or not recognised but still considered relevant. |
|
|
Recognition of elements (that have met the definition) |
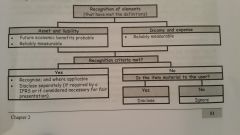
|
|
|
The historical Method |
- measures the assets at the actual amount paid for it at the time of acquisition - measures the liability at the amount of cash (or other asset) received as a loan or at the actual amount to be paid to settle the obligation in the normal course of business |
|
|
The Present Value method |
- measures an asset at the present value of the future cash flows (ie discounted) to be derived from it through the normal course of business and - measures liabilities at the present value of the future cash outflows (ie discounted) expected to be paid to settle the obligation during the normal course of business |
|
|
The Realisable Value Method |
- measures an asset at the cash amount for which it can be currently sold in an orderly disposal and - measures liabilities at the actual amount of cash (un-discounted) that would be required to settle the liability during the normal course of business |
|
|
The Current Cost Method |
- measures an asset at the amount that would currently have to be paid if a similar asset were to be acquired today and - measures liabilities at the actual amount of cash (un-discounted) that would be required to settle the liability today |
|
|
Capital maintenance and determination of profit |
Financial Capital Maintenance- a profit is earned if the financial (money) amount of the net assets is greater at the end of the period than at the beginning of the period, after excluding distributions to, or contributions from, owners during the period (eg dividends and having share issues). This can be measured in normal monetary units or units of constant purchasing power. Physical Capital maintenance- a profit is earned only if the physical productive capacity of the entity (or the resources or funds needed to achieve the capacity) at the end of the period exceeds the capacity at the beginning of the period, after excluding distributions to, or contributions from, owners during the period |
|
|
Answering Discussion Type Questions |
1. Definition- quote & discuss 2. Recognition criteria - quote & discuss 3. Conclude |
|
|
Summary Conceptual Framework for Financial Accounting |
- Objective of general purpose financial reporting - Underlying assumption - Qualitative Characteristics - Recognition & measurement of elements |

