![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Required rate of return (r)
|
r = (r* + IP) + DRP + LP + MRP
r* - real risk-free rate of interesst IP - inflation premium DRP - default risk premium LP - liquidity risk premium MRP - maturity risk premium |
|
|
Risk free rate (rf)
|
rf = (r* + IP)
- usually 3-month T-bills r* - real risk-free rate of interesst IP - inflation premium |
|
|
Nominal (=)
|
nominal = r* + IP + [(r*)(IP)]
|
|
|
Pure Expectations Hypothesis (PEH)
|
yield curve depends on investors expecations about future interest rates
- if interest rates are expected to increase: L-T rates will be higher than S-T rates |
|
|
Treasury Securities MRP
|
MRP = 0
|
|
|
Risks associated with overseas investing
|
- exchange rate risk
- country risk |
|
|
bond
|
long term debt instrument in which a borrower agrees to make payments of principle and interest to holders of bond (> 12 months)
|
|
|
Par value (of a bond)
|
face amount of the bond which paid at maturity
|
|
|
coupon interest rate
|
nominal stated contract rate (annual) - what you'll get for year based on payment incraments
|
|
|
maturity date
|
years until bond must be repaid
|
|
|
issue date
|
date when the bond was issued
|
|
|
yield to maturity
|
rate of return earned on bond held until maturity
|
|
|
accrued interest
|
interest owed of due from the last interest payment due (based on last paid)
|
|
|
callable bond
|
company can buy it back (call it back)
|
|
|
sinking fund
|
forces trustee to pay off a percentage of bonds per year (reduces risk of default)
|
|
|
convertible bond
|
when stock goes up owners buy stock -> automatically move from debt to equity
|
|
|
warrant
|
L-T option to buy stated # of shares at specified price (sweeten to buy debt)
|
|
|
putable bond
|
allows holder to sell the bond back to the company prior to maturity (low quality company)
|
|
|
income bond
|
only pays interest if the company earns interest
|
|
|
indexed bond
|
interest rate paid based upon a specific index
|
|
|
catastrophic bond (cat bond)
|
amount paid at maturity is a function of some defined contingency
|
|
|
zero coupon bond
|
no interest and at end of bond like get back principle (really high rate of return)
|
|
|
discount rate (rd)
|

the rate that could be earned on alternative investments of equal risk
|
|
|
value of financial assets
|
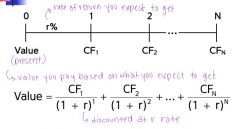
value paid based on expected return
|
|
|
value bond with calculator
|
par value - FV
coupon - PMT _______ - PV t - I/YR time held - N |
|
|
bond values over time (if rd remains constant)
|
- value of a premium bond would decrease until par value
- value of a discount bond would increase until par value - value of par bond remains consistant |
|
|
Expected total return - Yield to maturity (YTM)
|
![YTM = [expected CY] + [expected CGY]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/49/05/89/4490589_m.jpg)
YTM = [expected CY] + [expected CGY]
|
|
|
YTM on calc
|
N - time held
I/YR - __________ PV - sells for (neg) PMT - par value (coupon) FV - par value |
|
|
Current Yield (CY)
|
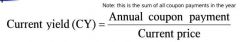
|
|
|
Capital gains yield (CGY)
|
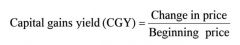
|
|
|
Semiannual bonds
|
- multiply years by 2 # of pds = 2N
- divide nominal rate by 2: periodic rate (I/YR) = rd/2 - divide annual coupon by 2: PMT = annual coupon/2 |
|
|
Semiannual bond's effective rate
|
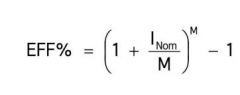
|
|
|
rate of return on investment
|

- number is a percentage
- rate that you are earning money |
|
|
Investment risk
|
degree of variability of possible outcomes (greater variability - greater risk)
|
|
|
Expected rate of return (ȓ)
|

|
|
|
standard deviation (σ)
|

|
|
|
coefficient of variation (cv)
|

high CV - in order to get high rate of return you are taking on a high level of risk
|
|
|
risk aversion
|
investors dislike risk (require higher rates of return for risks)
|
|
|
risk premium
|
the difference between return on a risky asset and a riskless asset
|
|
|
weight average (ȓp)
|
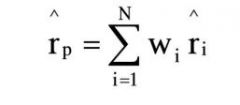
|
|
|
CVp
|
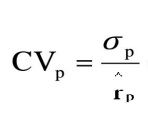
σp - decreases as stocks added
|
|
|
market risk
|
part of the total risk you can't get rid of
|
|
|
diversifible risk
|
part of the total risk you can get rid of
|
|
|
capital asset pricing model (CAPM)
& security market line |

draws a line (security market line that describes rate of return you should get (risk after diversification)
|
|
|
beta
|
measures of securities reaction
- beta = 1, security just as risky as market - beta > 1, security riskier than market - beta < 1, security is less risky than market |
|
|
common stockk
|
represents ownership; source of money to supply cash
|
|
|
intrinsic value
|
estimate of what it is worth vs. the marketplace
|
|
|
dividend growth model
|
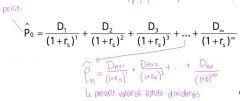
|
|
|
constant dividend growth stock
|

stock whose dividends are expected to grow forever at a constant rate
|
|
|
if growth is constant
|
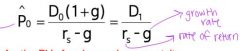
|
|
|
Constant growth rate model can only be used if...
|
- rs > g
- g is expected to be constant forever |
|
|
dividend yield
|
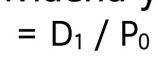
|
|
|
capital gains yield
|
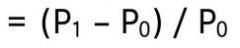
|
|
|
total return (rs)
|

|
|
|
growth is zero
|
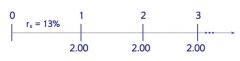
|
|
|
price
|

|
|
|
Corporate Value Model (CVM) - MV of equity
|
MV of equity = MV of firm - MV of debt - MV of preferred
|
|
|
Corporate Value Model (CVM) - value per share
|
MV of equity / # of shares
|
|
|
Preferred stock
|
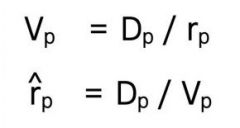
hybrid security
|

