![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Solvent |
The component of a solution that is present in the greatest amount. |
It is the substance in which the solute is dissolved. |
|
|
Solute |
Substance that is dissolved in a solution. |
|
|
|
Oxyacid |
Any acid containing oxygen. |
|
|
|
Acid |
Hydrogen ions in a water solution that combined with bases. |
|
|
|
Oxyanion |
Onion containing one or more oxygen atoms bonded to another element. |
|
|
|
Anion |
A negatively charged ion |
|
|
|
Cation |
A positively charged ion |
|
|
|
Covalent bond |
A chemical bond that involves sharing of pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule |
|
|
|
Ionic bond |
A chemical bond between oppositely charged ions |
|
|
|
Chemical Bond |
Electrostatic force linking atoms |
|
|
|
reactant |
Substances that react in a chemical change |
|
|
|
Product |
Substances that are formed by the chemical change |
|
|
|
Subatomic particles |
Protons, electrons, neutrons |
|
|
|
Isotope |
Atoms of the same element that have different masses |
|
|
|
Electromagnetic radiation |
The form of energy that exhibits wavelike Behavior as it travels through space |
|
|
|
Frequency |
The number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time |
|
|
|
Wavelength |
Distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves |
|
|
|
Photoelectric effect |
Refers to the emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal |
|
|
|
Quantum |
The minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom |
|
|
|
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle |
States that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both position and velocity of an electron or any other particle |
|
|
|
Aufbau principle |
An electron occupies the lowest energy orbital that can receive it |
|
|
|
Hund's Rule |
Orbital's of equal energy are eight occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by say electron and all electrons are singularly occupy orbitals must have the same spin state |
|
|
|
Pauli Exclusion Principle |
No two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers |
|
|
|
Boyle's Law |
States that the volume of a fixed mass of gas varies inversely with the pressure at a constant temperature |
|
|
|
Solution |
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances in a single phase |
|
|
|
Electronegativity |
Attraction of an elemental particle to its valence electron measured on a number scale |
|
|
|
Lewis diagram / Electron Dot Structure |
A diagram system that represents covalent bonds and their shared electrons using lines and unshared the valence electrons with |
|
|
|
Overall charge of ionic compound |
Neutral |
|
|
|
Ionic bonds occur between? |
Metal and nonmetal |
|
|
|
Molecule |
The smallest particle of an element or compound capable of a stable, independent existence. |
|
|
|
VSEPR Model |
Assumes that electron pairs are arranged around the central element of a molecule or polyatomic ion so that there is maximum separation and minimum repulsion among regions of high electron density. |
|
|
|
Polar Covalent Image |
a type of chemical bond where a pair of electrons is unequally shared between two atoms. |
|
|
|
Structure formula |
a formula that shows the arrangement of atoms in the molecule of a compound. |
|
|
|
Carbonic acid |
H2C |
|
|
|
Carbon dioxide |
C2D |
|
|
|
Carbon monoxide |
CO |
|
|
|
Ammonia |
NH3 |
|
|
|
Spectator ion |
Ions in a solution that do not participate in a chemical reaction. |
|
|
|
Net ionic equation |
Equation that results from canceling spectator ions and eliminating brackets from a total ionic equation. |
|
|
|
Chemical equation |
Description of a chemical reaction by placing the formulas of the reactants on the left and the formulas of products on the right of an arrow. |
|
|
|
Aqueous solution |
Refers to a solution with water as solvent.
|
|
|
|
Single replacement |
a type of chemical reaction where an element reacts with a compound and takes the place of another element in that compound. |
|
|
|
Double replacement |
a type of chemical reaction where two compounds react, and the positive ions (cation) and the negative ions (anion) of the two reactants switch places, forming two new compounds or products |
|
|
|
Synthesis |
a type of reaction in which multiple reactants combine to form a single product. |
|
|
|
Decomposition |
analysis or breakdown is the separation of a chemical compound into elements or simpler compounds. |
|
|
|
Chemical reaction |
I |
|
|
|
Precipitate |
An insoluble solid formed by mixing in solution the constituent ions of a slightly soluble solution. |
|
|
|
Aufbau principle |
Means electrons are added to orbitals as protons are added to an atom |
|
|
|
Valence electrons |
an electron that is associated with an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond |
|
|
|
Atomic orbital |
Region or volume in space in which the probability of finding electrons is highest. |
|
|
|
Noble gas |
any of the gaseous elements helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon, occupying Group 0 (18) of the periodic table. |
|
|
|
Quantum mechanical model of an atom |
a model that explains how electrons exist in atoms and how those electrons determine the chemical and physical properties of elements. |
|
|
|
Schrödinger's wave equation |
an equation that describes thewave nature of elementary particles and is fundamental to the description of the properties of all matter. |
|
|
|
Photo effect |
the effect of high-energy radiation (as gamma rays) on an atomic nucleus; especially : photodisintegration. |
|
|
|
Ground state |
Lowest energy state or most stable state of an atom, molecule or ion. |
|
|
|
Electron configuration |
Specific distribution of electrons in atomic orbitals of atoms or ions. |
|
|
|
Heisenberg uncertainty principle |
That it is impossible to measure two properties of a quantum object, such as its position and momentum (or energy and time), simultaneously with infinite precision. |
|
|
|
Double bond |
Covalent bond resulting from the sharing of four electrons (two pairs) between two atoms.
|
|
|
|
Aufbau principle |
Outlines the rules used to determine how electrons organize into shells and subshells around the atomic nucleus |
|
|
|
Precipitate |
A solid that separates from solution. |
|
|
|
Single Bond
|
Covalent bond resulting from the sharing of two electrons (one pair) between two atoms. |
|
|
|
Formula Unit
|
The smallest repeating unit of a substance. The molecule for nonionic substances |
|
|
|
Metallic Bond
|
The smallest repeating unit of a substance. The molecule for nonionic substances |
|
|
|
Structure Formula
|
Depicts the bonding of atoms in a molecule. |
|
|
|
Single Replacement Formula |
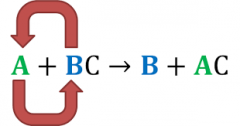
|
|
|
|
Double Replacement Formula |

|
|
|
|
Synthesis Formula |

|
|
|
|
Decomposition Formula |

|
|
|
|
Synthesis Reaction |
release energy in the form of heat and light, so they are exothermic.
|
|
|
|
Noble Gases |
They were long believed to be totally unreactive but compounds of xenon, krypton, and radon are now known. |
|

