![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
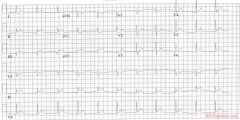
culprit laesion: RCX
* sinus rythm * normal conduction intervals * normal p-waver morphology * Q in II and AVF. Tall R wave in V2-V3 * ST elevation in II, III, AVF & V5, V6. ST depression in V2. * Conclusion: Infero- (II,III,AVF) postero- (depressions in V2-V3) lateral (V5,V6) infarct |
|
|
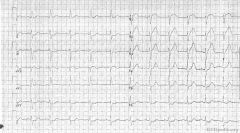
Culprit lesion: Left main
1. Sinus rhythm 2. Around 75 bpm 3. PQ normal, QRS interval 0.11 seconde, QT not prolonged 4. Left axis 5. normal p wave 6. QRS morphology: widened QRS, but not enough for LBBB diagnosis 7. ST elevation in AVR, V1, V2, V3. Reciprocal ST depression in II, III, AVF, V6. ST vector is upright ('pointing to heaven' (where the patient might go soon if not treated immediately) * Conclusion: Acute ischemia compatible with a left main blockage |
|
|
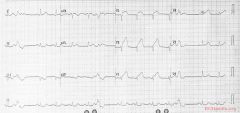
Culprit lesion: proximal LAD
1. sinus rhythm, with 3 ventricular premature beats 2. about 80 /min 3. normal conduction 4. horizontal axis 5. normal p wave morphology 6. Q in V1. slow anterior R-wave progression. 7. ST elevation in V1-V4, AVL. ST depression in II,III,AVF. The ST vector is upright. * Conclusion: Anterior MI with proximal LAD occlusion |
|
|
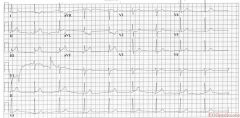
Culprit lesion: RCA
1. sinus bradycardia 2. about 55/min 3. normal conduction 4. intermediate (normal) axis 5. normal p wave morphology 6. tall R in V2, otherwise normal QRS morphology 7. ST elevation in II, III, AVF (in III > II). Depression in I, AVL, V2. * Conclusion: Inferoposterior MI caused by a RCA occlusion Arguments in favor of RCA occlusion (instead of RCX): * ST depression in I, AVL * bradycardia * ST elevation in III > II ('the highest ST elevation points at the culprit lesion') |
|
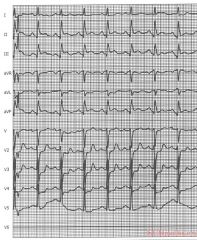
|
Culprit lesion: RCA
1. sinus rhythm 2. about 95/min 3. normal PQ and QRS interval. QT 360 ms, QTc 461ms (prolonged) 4. intermediate heart axis 5. tall p wave. possibly right atrial stress 6. No pathologic Q or LVH (however the inferior leads show small q waves) 7. ST elevation in II, III and AVF. ST depression in V2-V5. Lead V6 is missing (the electrode possibly fell off) * Conclusion: Infero-posterior MI caused by an RCA occlusion. |
|
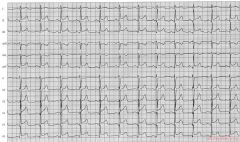
|
Culprit lesion: LAD
1. sinus rhythm 2. about 75/min 3. normal conduction 4. intermediate axis 5. normal p wave morphology 6. No pathologic Q or LVH. 7. ST elevation in II, III, AVF and V4-V6. ST depression in AVR. The ST vector is pointing downwards. * Conclusion: Distal LAD occlusion. |
|
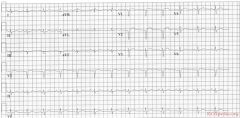
|
Culprit lesion: LAD
1. sinus rhythm 2. about 75/min 3. normal conduction 4. horizontal axis 5. normal p wave morphology 6. Microvoltages in the extremity leads. QS in V1, V2. 7. ST elevation in V1-V3 * Conclusion: Anteroseptal MI caused by an LAD occlusion. |
|
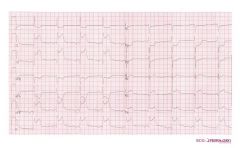
|
From ECGpedia
Jump to: navigation, search ST elevation in D2,D3,aVF,V5,V6,maybe V7-9 Bradycardia AMI of the inferio-posterior and basal posterior ==> RCA is blockage |
|
|
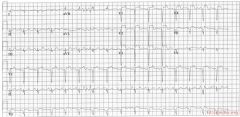
Culprit lesion: LAD
1. sinustachycardia 2. about 100/min 3. normal conduction 4. intermediate heart axis 5. tall p wave in II consistent with right atrial dilatation. (the sawtooth-basline between the 2nd and 3rd complex in AVR is probably a motion artefact). PTA depression in II 6. Loss of R waves throughout the anterior wall (V1-V6). QS complexes in V3-V5. 7. ST elevation in V1-V5 with terminal negative T waves * Conclusion: Large anterior MI due to LAD occlusion. Characteristics that suggest a large infarct in this case are: * Loss of R waves throughout the anterior wall (V1-V6). QS complexes in V3-V5. * Left and right sided decompensation, resulting in right atrial dilatation and ischemia * Tachycardia |
|
|
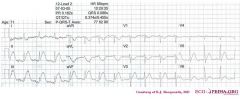
*
o Rhythm + This is a regular rhythm and every QRS complex is preceded by a p wave. The p wave is positive in II,III, and AVF and thus originates from the sinus node. Conclusion: sinus rhythm. o Hartfrequency + Use the 'count the squares' method (a bit less than 3 large squares ~> 300-150-100), thus about 90 bpm. o Conduction (PQ,QRS,QT) + PQ-interval=0.16sec (4 small squares), QRS duration=0.10sec, QT interval=360ms o Hartaxis + Positive in I, II, III, and AVF. Thus a normal heart axis. o P wave morphology + The p wave is difficult to assess, because of the (electrical) interference, but does not seem fulfill the criteria for left or right atrial dilatation. o QRS morphology + No pathologic Q waves. QRS duration < 0.12 seconds thus no bundle branch block is present. No left ventricular hypertrofy: S in V1 + R in V5 < 35mm. o ST morphology + Evident ST elevation in II,III, and AVF and also in V5. ST-elevation in AVL and V1-V2. o Compare with the old ECG (not available, so skip this step) o Conclusion? Acuut Inferior-Posterior Myocardial Infarction |
|
|
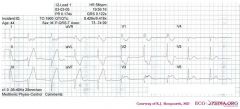
*
o Rhythm + In leads V1 to V3 there is apparantly no relationship between the P waves and the QRS complexes. Furthermore the QRS complexes are broad and have a RBBB pattern (V1:RSR), thus the rhythm is probably a ventricular escape rhythm. Leads V4-V6 however show a narrow complex preced by a P wave, probably the result of a rhythm change to sinus rhythm. o Hartfrequency + Use the 'count the squares' method (a bit less than 3 large squares ~> 300-150-100), thus about 58 bpm. o Conduction (PQ,QRS,QT) + During sinus beats: PQ-interval=250msec, QRS duration=0.11sec, QT interval=400ms (equals QTc at this rate). The wide complexes have a QRS duration of +- 160 ms. o Heartaxis + Negative in AVF and II, thus a left axis deviation. o P wave morphology + The p wave is rather difficult to discern. It seems normal in V4-V6 and positive in AVF and negative in AVR. o QRS morphology + RBBB pattern in V1 with ST changes (depression precordial leads). Leads V3 and V4 have probably been poled to the right chest. No pathologic Q waves. o ST morphology + ST elevation in II,III, and AVF and also in V3 (V3right). Hyperacute T waves with ST depression in V1-V2 an I, AVR and AVL. o Compare with the old ECG (not available, so skip this step) o Conclusion? Inferior-posterior myocardial infarction with complete AV block and ventricular excape rhythm with RBBB pattern and left axis, followed by sinus-rhythm. Probably RCA occlusion (ST depression in I) |
|
|
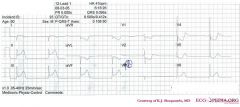
*
o Rhythm + Regular rhythm with narrow QRS complexes without P waves. Probably a nodal escape rhythm with either atrial standstill or atrial fibrillation with AV block o Heart rate + 41 bpm o Conduction (PQ,QRS,QT) + PQ: not applicable QRS: 100ms QT: 450ms QTc: 370ms o Heartaxis + Negative in I, positive in II and AVF, thus a right axis deviation. o P wave morphology + No P waves present. o QRS morphology + Narrow QRS, no pathologic Q waves, normal precordial R wave progression. A notch is seen in the terminal part of the QRS complex in V5/V6. o ST morphology + ST elevation in I, II, III, AVF, V6. ST depression in AVR, AVL, V1-V5. No ST deviation in V4R o Compare with the old ECG (not available, so skip this step) o Conclusion? Inferior-posterior-lateral myocardial infarction with a nodal escape rhythm - probably due to RCX occlusion |
|
|
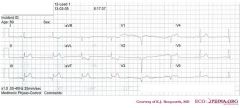
*
o Rhythm + Regular rhythm with normal P waves (positive in I, II, negative in AVR), followed by QRS complexes. Sinusrhythm o Heart rate + 46 bpm. Thus sinusbradycardia o Conduction (PQ,QRS,QT) + PQ: 170ms QRS: 110ms QT: 420ms QTc: 370ms o Heartaxis + Positive in I and AVL: normal heart axis o P wave morphology + P wave positive in II, bifasic in V1. Not well discernible in AVF. Seems normal. o QRS morphology + Pathologic Q waves in III and AVF. Slow R wave progression. Some aspecific intraventricular conduction delays (QRS 110ms). o ST morphology + ST elevation in II, III (III>II), AVF, V5 (1 mm elevation V4 and V6). ST depression in I and AVL. Lead V3 shows V4R and is not elevated. o Compare with the old ECG (not available, so skip this step) o Conclusion? Inferior myocardial infarction with Q waves in the inferior leads; probably due to RCA occlusion (III>II, depression in I) |
|
|
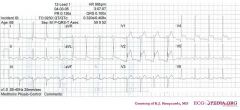
*
o Rhythm + The ECG shows a regular rhythm with normal P waves (positive in I, III and AVF, negative in AVR), followed by QRS complexes. Sinusrhythm o Heart rate + 100 bpm o Conduction (PQ,QRS,QT) + PQ: 140ms QRS: 100ms QT: 320ms QTc: 410ms o Heartaxis + QRS positive in I and AVF: normal heart axis o P wave morphology + The P waves have normal morphology. o QRS morphology + Narrow QRS. No left ventricular hypertrophy. No pathologic Q waves. o ST morphology + ST elevation in V1-V4 and lead I. ST depression in II, III, AVF and V6. Lead V3 shows V4R which is not elevated o Compare with the old ECG (not available, so skip this step) o Conclusion? Sinusrhythm with anteroseptal infarction. Ischemic vector is pointing upwards (ST depression in AVF), a sign of proximal LAD occlusion. |
|
|
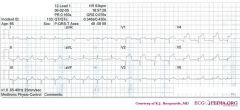
*
o Rhythm + The ECG shows a regular rhythm with normal P waves (positive in I, III and AVF, negative in AVR), followed by QRS complexes. Sinusrhythm o Heart rate + 90 bpm o Conduction (PQ,QRS,QT) + PQ: 160ms QRS: 80 ms QT: 340ms QTc: 416ms o Heartaxis + QRS positive in I and negative in II and AVF: left heart axis deviation o P wave morphology + P wave positive in II, III and AVF, biphasic in V1. The P waves have normal morphology. o QRS morphology + Narrow QRS. QS in V1-V2. Q in V4. Reduced R wave progression. o ST morphology + ST elevation in I, AVL, V1-V5 (V3=V4R and not elevated). ST depression in III and AVF. o Compare with the old ECG (not available, so skip this step) o Conclusion? Sinusrhythm with anteroseptal infarction. Ischemic vector is pointing upwards (ST depression in AVF), a sign of proximal LAD occlusion. |
|
|
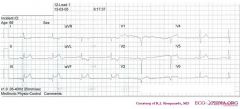
*
o Rhythm + The ECG shows a regular rhythm. Every P wave is followed by a QRS complex. P waves are positive in I and AVF. Normal sinus rhythm o Heart rate + 40 bpm o Conduction (PQ,QRS,QT) + PQ: 160ms QRS: 90ms QT: 420ms QTc: 360ms o Heartaxis + QRS positive in I and AVF: normal heart axis o P wave morphology + Normal P wave morphology o QRS morphology + Pathologic Q waves in III and AVF. QS in V1 and V2. No ST elevation in V3 (=V4R). o ST morphology + ST elevation in II, III, AVF and V5. ST depression in I, AVL. o Compare with the old ECG (not available, so skip this step) o Conclusion? sinusbradycardia with inferior-lateral myocardial infarction. |

