![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the oxygen indicator for the thioglycollate experiment |
Resazurin |
|
|
What does the prefix thio refer to in the thioglycollate |
Sulfur, means oxygen is replaced with sulfur |
|

Fill in the missing R group |
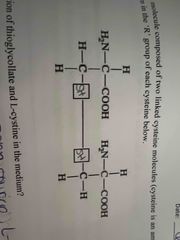
Back (Definition) |
|
|
what is the function of Thioglycollate and l-cystine in the medium? |
L-cystine and Thioglycollate are reducing agents, they remove molecular oxygen from medium and prevents accumulation of peroxides |
|
|
In thioglycollate Since cysteine is an amino acid, you can find it in peptides or proteins. What sources in the medium recipe contain protein |
L-cystine, casein, yeast extraction
|
|
|
at what percent is hydrogen peroxide used at for cleaning wounds? |
3% |
|
|
In thioglycollate What are the carbon and nitrogen sources in the medium |
casein and l-cystine are both carbon and nitrogen sources |
|
|
microbe classification: strict aerobes oxygen usage? enzymes present? |
oxygen usage: microbe requires oxygen enzyme present: superoxide Dismutatse and Catalase |
|
|
microbe classification: strict anaerobes oxygen usage? enzymes present? |
oxygen usage: oxygen is toxic to microbe enzymes present: neither enzyme; few exceptions |
|
|
microbe classification: microaerophiles oxygen usage? enzymes present? |
oxygen usage: microbe requires oxygen at less than atmospheric concentrations* enzyme present: Small concentrations of S.O.D and or catalase |
|
|
microbe classification: Aerotolerant oxygen usage? enzymes present? |
Oxygen usage: microbe may grow in presence or absence of oxygen; will not use oxygen even if its available enzyme present: S.O.D |
|
|
microbe classification: Facultative anaerobe oxygen usage? enzymes present? |
Oxygen usage: Oxygen usage: microbe may grow in presence or absence of oxygen; will use oxygen even if its available Enzyme present: Superoxide dismutatse, catalase |
|
|
how much nitrogen in the air we breathe? |
78.09% |
|
|
how much oxygen in the air we breathe? |
20.95% |
|
|
how much argon in the air we breathe? |
.93% |
|
|
how much carbon dioxide in the air we breathe? |
.039% |
|
|
what is the sodium Thioglycollate media? |
a method of determining how different species of bacteria may or may not use oxygen |
|
|
how to classify organism |
depending on the growth within the broth, based on their oxygen requirement |
|
|
what is the anaerobic jar used for |
its one method used to differentiate bacterial growth in aerobic or anaerobic conditions one plate is incubated under regular atmospheric conditions and the other is incubated inside of the jar that had majority of the free molecular oxygen reduced to water |
|
|
what does bacterial growth depend on |
microbes ability to handle oxygen |
|
|
some bacteria are able to tolerate ____ and use it as a _____ in the electron transport _____ |
1) oxygen 2) final electron acceptor 3) chain |
|
|
what is the leading anaerobe in human disease? |
B. fragilis (ETBF), causes diarrheal disease in people abdominal pain, tenesmus, inflammatory diarrhea |
|
|
what is the purpose of the Oxoid product in anaerobic jar |
oxygen reducer , contains ascorbic and activated carbon, which react on contact with air. |
|
|
what is normal flora |
zoo of bacteria that colonize your skin, mouth, and along your digestive tract from the day you are born. necessary in maintaining good health by occupying space so that microbes/pathogens have a dfficult time colonizing and producing disease |
|
|
what bacterial species is part of the normal flora? |
Staphyloccocus aureus because it can tolerate and thrive on the salty environment found on our skin |
|
|
MRSA and when was it discovered |
methicillin resistant staphyloccocus aureus ,1961 |
|
|
what is an opportunistic pathogen? |
microbes that usually do not cause disease in healthy people, but may become virulent with immunocompromised and unhealthy individuals |
|
|
what is bacterial meningitis |
an infection of the membranes and cerebrospinal fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
nitrogen, vitamin and carbon sources in sheeps blood agar? |
nitrogen vitamin and carbon: enzymatic digest of casein, enzymatic digest of animal tissue vitamin: yeast extract |
|
|
what does sodium chloride do in the sheeps blood agar medum |
maintains the osmotic balance of the medium |
|
|
what is the solidifying agent in the sleeps blood agar |
Agar |
|
|
why do few student in class exhibit plates with b-hemolysis? are they ill? explain? |
if plate exhibits b-hemolysis student is not ill, it means they are carriers of streptococcus pyogenes |
|
|
if the students are not presently ill could they be carriers what is a carrier? explain |
yes they are carriers meaning they have streptococcus pyogenes in the back of their throats and can give strep throat to to others that they get in concat with via kiss or sharing drinks |
|
|
if these students are not presently ill, could they have been ill in the recent past or near future? would this show up on the plate? |
since they are carriers it means they are asymptomatic and though they have it, they will never get sick from it, but it still shows in the plate since it is present in their throats |
|
|
what is bioluminescense? |
the chemical production of light by living organisms. |
|
|
what is GFP |
green flourescent protein |
|
|
define bacterial transformations |
a process of horizontal gene transfer by which some bacteria take up foreign genetic material (naked DNA) from the environment. allows the bacteria to express new traits and characteristics |
|
|
what is arabinose and what is it used for in pGLO experemint |
arabinose is an aldopentose/ monosaccharide used as an inducer for the expression of GFP, it acts as an allosteric regulator of araC |
|
|
what is araC for in the pGLO plasmid |
Dna binding protein encodes the regulatory protein that binds to the pBAD promoter |
|
|
what is the purpose of the proteins, araB, AraA and AraD? |
code for 3 digestive enzymes involved in the breakdown of arabinose, are clustered together in what is known as the arabinose operon |
|
|
what is Pbad used for? |
it is a promoter region. binds to araC which then binds to the pBAD region activating GFP transcription |
|
|
what is the purpose of LB/amp (+)DNA |
transformed bacteria will grow |
|
|
LB/amp/arabinose with (+)DNA |
transformed bacteria will express GFP protein and exhibit green flourescents |
|
|
LB/amp with (-)DNA |
negative control, identifies false positive results |
|
|
LB with (-)DNA |
negative control ensures the medium doesnt interfere with bacteria control |
|
|
what are ethical considerations when making genetically modifies organisms |
environmental impact and safety development of antibiotic resistant bacteria potential to cause ecological damage creation of new allergins and toxins |
|
|
list 3 tpes of gmos |
GMo crops such as corn cotton and soybeans produced to feed growing populations, prevent pest infecting crops, make drought resistnt crops geetically engineered foo like salmon, engineered to grow faster and bigger than natural salmon, bigger population, more people fishing, less fish, genetically engineering bigger fish and more, to fee growing population genetically modifies bacteria to create insulin for diabetics, contains human insulin gene inserted into bacteria , insuling gene translates and produces recombinent insulin |
|
|
what is the kirby-bauer disc diffusion test |
it is designed to analyze wether a given species of bacteria is susceptible or resitant to an antibiotic the bacteria will grow in the presence of the antibiotic or growth ill be inhibited forming a zone of inhibition |

