![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
114 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a female worm produces 5000 eggs per day. Each animal in a herd is infected with 250 worms. How many eggs will a herd of 80 goats distribute on pasture in a week
|
5000*250*80*7
|
|
|
what can you suggest a producer do to clean pastures (with goats) heavily contamined with ressitant worm larvae?
|
rotate pastures, dual species grazing, burn/plow the pasture
|
|
|
anthelmintic strategies proprosed to support control of ruminant gi nematodes?
|
1) limit contact between hosts and infective larvae in the field thru grazing management methods 2) improving the host response against GIN infections relying on genetic selection between or within breeds of sheep or goats, crossbreeding of resistant and susceptible breeds and/or manipulations of nutrition. 3) control of GIN based on non conventional AH materials (plant/mineral compounds). AH materials can eliminate worms and/or negatively affect the parasite's biologgy
|
|
|
how to perform a mcMasters test
|
estimates EPG. 56ml sodium nitrate, 4 gm feces. Calibrated slide
|
|
|
Wisconsin test
|
estimates EPG, sugar solution, 5gm feces. More sensitive than mcmasters
|
|
|
what is considered a rescue dewormer when resistance on a farm is not known but immediate tx is necessary?
|
moxidectin
|
|
|
when might you recommend a dewormer other than the one most commonly used to rescue deworm small ruminants?
|
if a farm has been using moxidectin every 2 weeks and is stil having deaths from haemonchus
|
|
|
what type of eggs are typically present on a wisconsin or mcmasters slide when loking at fecals from cattle or small rums?
|
trichostrongyle eggs
|
|
|
what is the name of the dewormer (new class) in australia that we hope to one day have access to in the US
|
monepantel
|
|
|
what can you recommend be done to remove p. equorum eggs from the environment?
|
p. equorum eggs are very persistend and can live for several years in the environment. You can burn, but might not be successful
|
|
|
what is the recommended tx for foals with p. equorum?
|
fenbendazole paste (deworm foals every 2 months beginning at 60 days of age, until 18 months old)
|
|
|
is p. equorum harder or easier to kill with MCL than small strongyles?
|
harder- need a higher dose to kill the p. equorum eggs. P equorum is the dose limiting parasite
|
|
|
what characteristics of MCL anthelmintics may have contributed to selection for resistance to this drug class in p equorum populations?
|
mcl are more persistent (stay in the animal longer) than BZD. The low persistent dose contributes to resistance
|
|
|
what practice of the equine industry unrelated to parasite control likely contributes to the spread of MCL resistant populations of p. equorum?
|
requiring natural service for breeding exposes horses to the MCL resistant parasites, then the horses return home and shed the resistent parasites
|
|
|
to what class of anthelmintic do all hw preventatives currently on the market belong?
|
MCL
|
|
|
what percent of effiecay standard does FDA use for approval of new heartworm preventatives. Do you think this standard is appropriate?
|
100%- appropriate because HW is a potentially fatal dz
|
|
|
which of these preventatives would you expcet to be most persistent in the host and why?
|
moxidectin because it is given at a higher dose than other MCL
|
|
|
is MP3 a MCL resistent strain of D-immitis?
|
some say yes because some dogs are infected even when on MCL preventatives. Some say no because they think MP3 is just less susceptible to MCL and is harder to kill. Efficacy is still >95%
|
|
|
two papers on HW resistance, one with 100 infective larvae, one with 50 infective larva. Results?
|
1) 100 infective larvae and more infections- used 1 dose of tx. 2) used 50 L3 and got less infections; used 3 doses of tx (milbemycin and spinosad)
|
|
|
what is a non chemical control for heartworm?
|
protecting dogs from mosquitoes
|
|
|
a screening tool for heartworm strains that Ided resistant strains in the lab without having to infect dogs would be of great value in our ability to detect the prevalence of MLC resistant D immitis. (we have such screening tools for GI nematodes). Do you think such tools would be harder or easier to develop for D immitis? why?
|
we can take microfilariae from a dog, put it in a dish, drop MCL in a dish and watch to see if the microfilaria die. The problem is we want to kill the l3 stage which needs to go through a mosquito vector (difficult to do in lab setting)
|
|
|
feature that can be used ID ostertagia?
|
cervical papillae
|
|
|
compare haemonchus and ostertagia
|
both have cervical papillae, but haemonchus is bigger
|
|
|
what causes the barber pole appearance of haemonchus contortus?
|
blood filled intesting wrapped around a white uterus
|
|
|
what type of worm is haemonchu and how do animals become infected?
|
nematode, ingestion of L3 on pasture
|
|
|
what clinical dz is haemonchus most likely to cause in goats? What causes the mortality?
|
anemia; bleed out of the abomasum
|
|
|
what 2 dewormers have haemonchus parasites been reported to have the highest level of resistance against?
|
fenbendazole and ivermectin
|
|
|
what is a rescue dewormer?
|
moxidectin
|
|
|
what is one other dewormer that can be used for haemonchus? What is its possible adverse effect?
|
levamisole; toxicity
|
|
|
what species can become infected with nematodirus spp?
|
sheep, cattle, llamas
|
|
|
is nematodirus common in small ruminants? How do animals become infected?
|
yes; ingestion of L3 on pasture
|
|
|
where do adults of nematodirus live?
|
small intestine
|
|
|
what features allow you to ID nematodirus to genus?
|
females= can see giant eggs in the uterus. Males=long spicules
|
|
|
can nematodirus cause disease in small ruminants/
|
yes- production loss (can hatch synchronously)
|
|
|
list 3 anthelmintics from 3 different classes that can be used to treat nematodirus. For each, what are cautions for treating sheep?
|
1) benzimidazoles - fenbendazole, albendazole (teratogenic) 2) tetrahydrapyrimidines- levamisole (toxicity if not dosed at 1.5x), pyrantels, etc. 3) MCL- ivermectin, moxidectin, doramectin, eprinomectin (in cattle)
|
|
|
what parasite is the famacha method used to control? Will it als aid in the control of other gi nematodes?
|
haemonchus contortus; it will not direclty aid In the control of other gI nematodes, but you do get the side effect of occasional deworming to control the GI nematodes
|
|
|
why do producers use FAMACHA?
|
1) decrease anthelmintic use to increase refugia (delay onset of resistance) 2) treat clinical dz
|
|
|
if there is resistance to fenbendazole and ivermectin what anhelmintic should be used to treat animals, based on the famacha scale?
|
levamisole- save moxidectin for rescue deworming
|
|
|
what disease does ostertagia ostertagi cause?
|
moroccan leather apperance from L4 emerging from abomasal mucosa
|
|
|
alternate names for ostertagia ostertagi?
|
small abomasal worm, brown stomach worm
|
|
|
what term is used to describe ostertagia disease syndrome?
|
type 1 ostertagiasis
|
|
|
what stage of ostertagis is responsible for the disease seen? How are they acquired?
|
larva. From the curent pasture/ingestion of L3.
|
|
|
what will you recommend to this rancher to address the immediate problem of ostertagiasis/
|
deworm, move pastures. In the future, deworm animals sooner using MCLs
|
|
|
how many cows do you need for an accurate FECRT and when do you peform?
|
we can take microfilariae from a dog, put it in a dish, drop MCL in a dish and watch to see if the microfilaria die. The problem is we want to kill the l3 stage which needs to go through a mosquito vector (difficult to do in lab setting)
|
|
|
what evidence is there that populations of cattle nematodes have become resistant to modern deowrmers?
|
research papers, but resistance is not as bad in cattle when compared to horses and small ruminants
|
|
|
trichostrongyle nematodes include
|
haemonchus, ostertagia, trichostrongylus, nematodirus, cooperia, oesophagostomum
|
|
|
levamisole treats
|
trichostrongyle nematodes
|
|
|
levamisole administration in goats
|
1.5x the dose given to sh instead of 2x (as with other dewormers) because of toxicity concerns (it is off label in goats0
|
|
|
can estimated weights be used to dose levamisole?
|
no, need exact so don’t underdose and increase chances or developing resistance. Also don’t want to overdose and induce toxicity
|
|
|
in sheep/goats, albendazole treats
|
trichostrongyle nematodes (adults and L4), cestodes, trematodes (adult f hepatic and f magna)
|
|
|
what can be done to increase efficacy of albendazole?
|
withhold feed, redose 12 hours later (keeps levels into kill zone for longer)
|
|
|
how should albendazole be dosed in goats compared to sheep?
|
2x the dose that is given to sheep
|
|
|
can albendazole be used in pregnant does?
|
no, teratogenic
|
|
|
in sheep/goats, ivermectin treats
|
trichostrongyle nematodes (adults and l4) , arthropods-all stages of oestrus ovis (nasal bot)
|
|
|
how should ivermectin be dosed in goats s compared to sheep?
|
2x the dose that is given to sheep
|
|
|
is ivermectin resistance in small ruminant nematodes common?
|
yes
|
|
|
in sheep/goats, moxidectin treats
|
trichostrongle nematodes (Adults and L4). Arthropods- all stages of oestrus ovis
|
|
|
how should moxidectin be dosed in goats compared to sheep?
|
2x the dose that is given to sheep
|
|
|
can moxidectin be used in pregnant does?
|
yes
|
|
|
fenbendazole treats (in cattle)
|
trichostrongyle nematodes (adults and L4), cestodes, hookworm
|
|
|
how is fenbendazole administered to cattle?
|
orally
|
|
|
hew persistent is fenbednazole after administration
|
not persistent
|
|
|
can febendazole be used in dairy cattle? Beef? Withdrawal times?
|
at the labeled dose, can be used in both dairy and beef cattle. No WDT in milk at labeled dose, but WDT of 1-2 weeks in beef cattle depending on the formulation
|
|
|
in cattel, albendazole treats
|
trichostrongyle nematodes (adults and l4), cestodes, trematodes (f hepatica)
|
|
|
can albendazole be used in pregnant cows?
|
no- potentially teratogenic
|
|
|
can albendazole be used in dairy cattle? Beef? Wdt?
|
can NOT be used in dairy, but can be used in beef cattle; WDT is 27 d
|
|
|
in cattle, levamisole treats
|
trichostrongle nematodes (Adults and L4).
|
|
|
can levamisole be used in dairy cattle? Beef? Wdt?
|
can not be used in dairy cattle of breeding age (residues in milk). Can be used in beef- WDT 2-9d depending on formulation
|
|
|
in cattle, MCLs treat
|
trichostrongyle nematodes (Adults and L4), arthropods
|
|
|
what is the major advantage of MCLs over the other classes listed for GI nematodes?
|
persistence
|
|
|
what is the disadvantage of persistence?
|
the persistence level trails off, and the lower levels selct for resistance
|
|
|
how is MCL administered to cattle?
|
injectable or pour on only
|
|
|
which MCLs can be used in dairy cattle?
|
moxidectin and eprinomectin pour on.
|
|
|
what is the primary causative agent of EPM in north america?
|
sarcocystis neurona
|
|
|
what diagnostic test should you perform, and what results would allow you to confirm a clinical diagnosis of EPM?
|
western blot or ELISA- compare Ab in CSF to Ab in serum (if CSF Ab > serum Ab, horse has EPM). **only test clinically ill horses**
|
|
|
how do horses become infected with sarcocystis neurona?
|
ingestion of sporocysts shed in opossum feces, usually from infected feed. Immediately infective upon shedding
|
|
|
common clinical signs of EPM?
|
asymmetrical muscle atrophy, lameness, ataxia, stiffness, training problems
|
|
|
what is the most effect treatment for EPM?
|
ponazuril, oral paste for 28 days
|
|
|
what disease is caused by babesia caballi?
|
piroplasmosis
|
|
|
how and where does a horse become infected with b. caballli?
|
unclear. Possibly tick bites, most likely in southern US
|
|
|
what is the next step in managing a diagnosis of b. caballi
|
report to USDA
|
|
|
recommended TX for piroplasmosis in the US?
|
None- euthanize. In other countries- imidocarb, but horse remains a carrier
|
|
|
what tick has recently been associated with transmission of b. caballi in N. America?
|
amblyomma cajennense- other ticks assoc included rhipicephalus/boophilis microplus, dermacentor albipictus/nitens/variabilis
|
|
|
what type of worm is monieza?
|
cestode
|
|
|
how do goats become infected with monezia?
|
ingestion of oribatid mite containing a cysticercoid
|
|
|
are monezia parasites likely causing any clinical dz in the goats?
|
no, but there is controversy
|
|
|
recommended TX for monezia?
|
albendazole
|
|
|
how is t. foetus infected best diagnosed?
|
culture inPouch or PCR of pouch (best option)
|
|
|
what needs to be done to confirm a diagnosis?
|
diagnosis confirmed if both tests are positive
|
|
|
what is the recommended tx to eliminate t. foetus infection in the herd?
|
no tx- slaughter
|
|
|
what recommendations can be made to prevent t. foetus infection?
|
use young virgin bulls/test negative bulls, good biosecurity, practice herd management, cull infected animals, vaccinate (not 100%, decreases clinical dz but does not eliminate infection)
|
|
|
clinical signs of eimera infection in goats?
|
severe watery dairrhea that is flecked with blood
|
|
|
how does a goat become infected with eimeria?
|
ingestion of sporulated oocysts from the environment
|
|
|
why would only one animal in a herd become clinically ill with eimeria?
|
pecking order- not receiving the coccidiostats in feed, malnourished, etc
|
|
|
recommended TX for eimeria?
|
amprolium for 5days.
|
|
|
is eimeria zoonotic? Contagious to other animals?
|
no.
|
|
|
how does f. hepatic cause dz in cattle?
|
juveniles migrate in the parenchyma of liver. Adults cause inflammation and fibrosis in bile ducts (pipe stem liver)- overall, decrease feed efficiency, growth and fertility
|
|
|
how do cattle become infected with f. hepatica, and when during the year is transmission occuring?
|
ingestion of metacercaria on infected pasture (NOT from ingestion of snail); fall to winter in south, summer in north
|
|
|
what role do WTD play in f. hepatica transmission?
|
none
|
|
|
what is the recommended treatment and when during the year will you treat to best control f. hepatica?
|
clorsulon or albendazole. Nothing is effective against migrating juveniles; early fall (Before snails come out) b/c transmission stops in summer and starts again when weather cools
|
|
|
how is a calf most likely infected with cryptosporidium parvum
|
ingestion of oocyst (immediately infective upon shedding)
|
|
|
is cryptosporidium parvum zoonotic?
|
yes
|
|
|
treatment for c. parvum?
|
no effective tx- supportive care and isolation
|
|

|
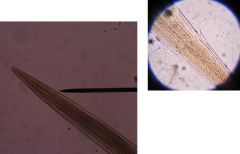
Ostertagia spp.
|
|
|
Haemonchus
|
|

|
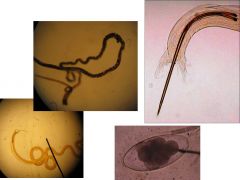
haemonchus contortus
|
|
|
nematodirus spp.
|
|

|
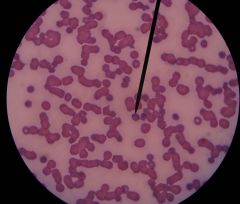
ostertagia ostertagi
|
|
|
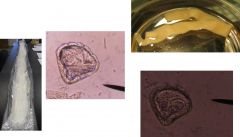
babesia caballi
|
|
|
monezia
|
|
|
tritrichomonas foetus
|
|
|
eimeria spp
|
|

|
fasciola hepatica
|
|
|
cryptosporidium parvum
|

