![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
142 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Oral Surgery |
Type of dental specialist.
Primarily trained in surgery of the mouth and jaw.
Ex: extractions |
|
|
Prosthodontics |
Type of dental specialist.
Primarily concerned with the restoration and replacement of missing teeth and oral structures.
Ex: prosthetic partial, dentures, bridges |
|
|
Pedodontics |
Type of dental specialist.
primarily concerned with treating oral condition in children/adolescents. |
|
|
Periodontics |
Type of dental specialist.
primarily treats and diagnoses the diseases of the supporting and surrounding tissues of the teeth.
Gum specialist. |
|
|
Orthodontics |
Type of dental specialist.
primarily concerned with the guiding and correction of misaligned teeth. |
|
|
Endodontics |
Type of dental specialist.
primarily concerned with the health of the dental pump.
Root canals |
|
|
Patient Progress Notes |
Tracking, documenting ,legal documenting
Never erase anything. Simply cross it out, initial, then continue writing. |
|
|
Dentin |
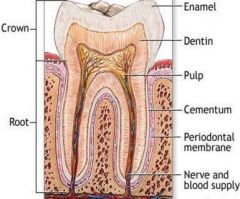
70% inorganic material
"Core of tooth" hollow yellow tube of tooth
Odontoblasts create dentin |
|
|
Enamal |
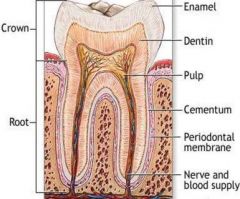
96 % inorganic material.
Hardest tissue of the body.
Covers the anatomic crown.
Made up of rocks and prisms.
Lines of retzius "incremental lines" |
|
|
Cementum |
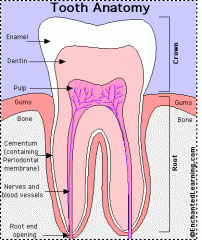
55 % inorganic material.
Bone-like tissue that covers anatomic root.
Attaches root to wall of alveolar socket |
|
|
Pulp |
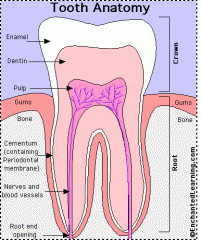
Provides nourishment (blood supply and lymphatic drainage) to dentin, sensations (nerve supply), and the formation of dentin. |
|
|
Apex |
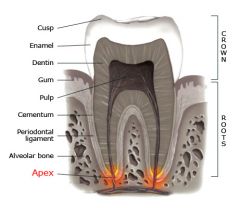
Tip of the root.
Apical Foramen- opening at apex to allow nerve. blood supply, and lymphatic draining system to enter the dental pulp. |
|
|
Odontoblasts |
Responsible for the formation of dentin. |
|
|
Frontal Bone |
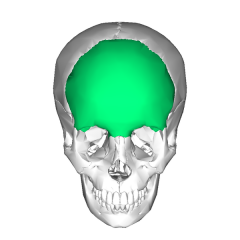
Makes up the forhead and part of the orbits and nasal cavity. |
|
|
Temporal Bone |
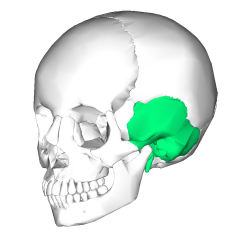
The left and right temporal bones comprise the base as well as the sides of the skill. Both bones contain glenoid fossa into which the mandible rests. |
|
|
Parietal Bone |
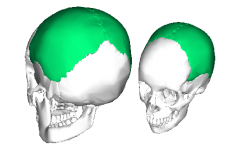
The left and right parietal bones form the largest portions of the roof of the skull and sides of the skull. |
|
|
Ethmoid Bone |
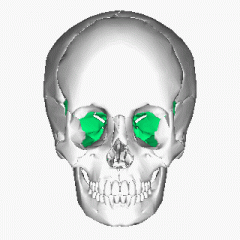
A thin bone located the the front portion of te craniums base. Situated between orbits. Forms the roof, septum, and sides of nose. |
|
|
Sphenoid Bone |
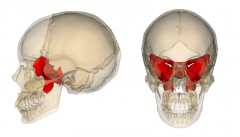
"Batwings"
Located in front portion of skulls base |
|
|
Mandible |
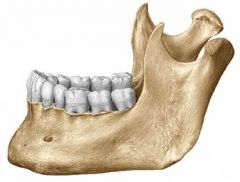
Skulls only movable bone and is the longest and strongest bone of the face. |
|
|
Maxillae |
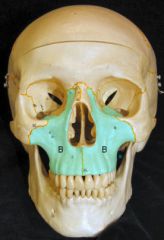
"Upper Jaw"
Largest bone in the upper face
Has 4 processes (Zygomatic, Palatine, Frontal, Alveolar) and 4 bones ( two zygomatic and two palatine) |
|
|
Incisors |
Single rooted teeth.
Located at the front of mouth and designed to cut food.
Tooth #'s: 7-10 and 23-26 |
|
|
Molars (furcations) |
2 or 3 rooted teeth. (3 upper 2 lower)
Have more cusps than other teeth.
Widest chewing surface. |
|
|
Canines |
"Cuspids"
Longest and most stable rooth.
Located at corners of mouth.
Tooth #'s: 6, 11, 22, 27
|
|
|
Premolars |
"Bicuspids"
Have cusps for grasping and tearing food. Somewhat broad surface for grinding food. |
|
|
Ridges |
A linear elevation on surface of tooth.
Named according to its location and form.
Ex: buccal ridge, incisal ridge, and marginal ridge |
|
|
Mamelons |
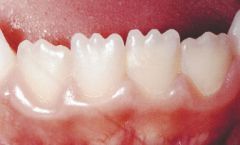
Elevations on the incisal edge of newly erupted incisors. |
|
|
Cingulums |
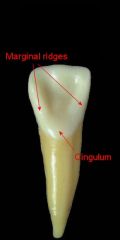
Bulge or elevation located on the cervical third of anterior teeth. |
|
|
Embrassures |
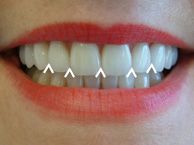
A triangular space in the gingival direction between the proximal surfaces of two teeth in contact. |
|
|
Soft Radiation |
Long wavelengths with less energy and less ability to penetrate matter. |
|
|
Hard Radiation |
Short wavelengths and high penetrating power. |
|
|
Scatter Radiation |
"Secondary waves"
Rays from primary beam that have been deflected by tissues or other objects. |
|
|
Rinn Holder |

Positioning device for x-rays for accuracy.
Prevents radiation exposure and adds stability. |
|
|
Lead Apron |
Used to protect patient from radiation exposure.
Lead thickness varies from 0.25-1.25 |
|
|
Collimator |
Increase film quality and decrease exposure. |
|
|
Alginate Impressions |
Commonly used for fabrication of diagnostic casts.
Ex: bleaching trays, mouth guards |
|
|
Polyvinylsolixane (lmp) |
Form of silicone rubber-base impression material used for detailed impressions.
Ex: crown, bridges, and full arch impressions |
|
|
Polysulfied (Impression) |
Older form of silicone impression material. Has a foul odor and is unpleasant but is used for detailed impressions.
Ex: crowns, bridges, and full arch impressions. |
|
|
FCC |
Full Cast Crown
Made of gold or metal alloy and designed to cover the entire anatomic crown of the tooth. |
|
|
Porcelain Fused to Metal |
Full metallic coping covered by porcelain or composite material. |
|
|
Inlay |

Can replace mesial, distal, occlusal, buccal, and lingual surfaces of posterior teeth and do not cover tips. |
|
|
Onlay |

Can replace mesial, disstal, occlusal, buccal, and lingual surfaces of posterior teeth and also include cusps of teeth. |
|
|
Implant |
Replacement of natural teeth which utilizes a titanium metal device embedded within the patient's bone. |
|
|
Root Canaled Teeth |
Attempt to save the tooth, but the tooth itself becomes more fragile so a crown is recommended. |
|
|
Removable Partial Denture |
Removable appliance that replaces missing teeth and soft tissue while preserving teeth and other oral structures. |
|
|
Rest ( in RPD) |
An acrylic or metallic projection that fits into a specifically prepared space on the abutment tooth. The rests prevent the RPD from seating tooth too far gingivally. |
|
|
Connector ( in RPD) |
Metal or acrylic bar which connects right side of the appliance to the left side. |
|
|
Clasp ( in RPD ) |
"Retainer"
Metal or acrylic attachments that encircle the abutment teeth to provide retention for the appliance. |
|
|
Saddle ( in RPD ) |
"Base"
Acrylic portion of appliance that rests on alveolar ridge, attached to RPD and holds artificial teeth. |
|
|
Flange (in RPD) |
The acrylic portion of the base that extends over the entire alveolar ridge.
|
|
|
Immediate Denture |
Dentures are fabricated prior to the extraction of teeth. On the day the teeth are extracted, the dentures are delivered. |
|
|
Endodontic Therapy |
Diagnosis and treatment of the tooth pulp and periapical tissues.
Patient Symptoms: Sever pain, lingering pain to sweets or thermal changes, pain to palpation, pain to percussion or mastication, absence of pain with swelling, radiolucent presentation at apex in radiograph. |
|
|
Molar Eruption Ages |
First Molar - Age 6- Tooth #'s 3,14,19,30
Second Molar- Age 12- Tooth #'s 2,15,18,31
Third Molars- Age 17-21- Tooth #'s 1,16,17,32 (Wisdom teeth) |
|
|
Hard Palate Bones |
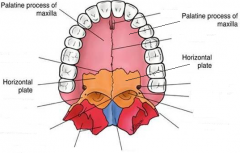
Made up of 4 bones: Palatine Processes of the maxillae (2) Horizontal plates of the palatine bones (2) |
|
|
Frontal Sinus |
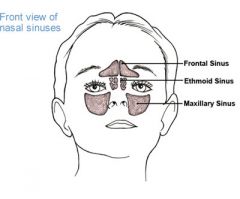
Located behind the superciliary arch which is just above the eyebrows.
Drains through the front nasal duct into the main cavity of the middle meatus.
|
|
|
Maxillary Sinus |
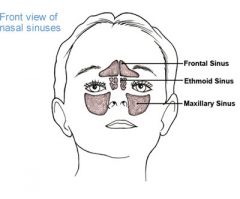
Can be seen in x-rays for maxillary teeth.
Largest accessory sinus of the nose, located in the body of the maxilla.
Situated below floor of the nose |
|
|
Anterior Ethmoid Cells |
numerous thin walled cavities
located between upper portions of the nasal sinuses and the orbits. |
|
|
Middle Ethmoid Cells |
numerous thin walled cavities
located between upper portions of the nasal sinuses and the orbits.
|
|
|
Spenoidal Sinuses |
Located within the body of the sphenoid.
Very large and can extend into the great wing of the sphenoid or the roots of the pterygoid process |
|
|
Interarticular Disc (TMJ) |
A disc that lies on the condyle, made of tough, fibrous tissue. Divides the space between the glenoid fossa and the condyle into two cavities which are filled with synovial fluid. |
|
|
Fibrous Capsule (TMJ) |
A sac that surrounds the interarticular disc. |
|
|
Omission |
Failure to act as a "resonable and prudent professional"
Ex: Failure to diagnose carious lesion on a patient that later needed a root canal. |
|
|
Commission |
An act that a "reasonable prudent professional" would not perform.
Ex: Dentist performed complicated procedure instead of referring the case to a specialist and the patient was injured. |
|
|
Negligence |
Failure to deliver due care to patient. |
|
|
Wilhelm Conrad Roentogen |
Discovered x-rays |
|
|
Otto Walkoff |
First dental x-ray |
|
|
C. Edmund Kells |
First to perform dental radiographs on a live patient and experimented on his hands causing cancer and an arm amputation. |
|
|
William Coolidge |
Invented the first x-ray tube. |
|
|
Amplitude |
Vertical height from top to bottom of a wave |
|
|
Wave Length |
The measurement of rays from the crest of a wave to the crest of another wave. |
|
|
Mesial |
Towards the midline |
|
|
Occlusal |
Chewing surface of posterior teeth |
|
|
Distal |
Surface farthest from the midline |
|
|
Buccal |
Facial surface of posterior teeth closest to the cheeks. |
|
|
Lingual |
Surface closest to the tongue. |
|
|
Periodontium |
Tissues that surround and support the teeth
Ex: alveolar process, periodontal ligament, and gingiva. |
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Cells responsible for bone formation |
|
|
Periodontal Ligament (PDL) |
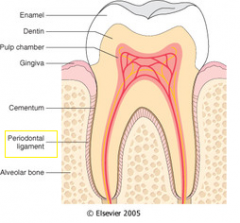
Tissues that support and anchor tooth in socket. |
|
|
Sulcus |
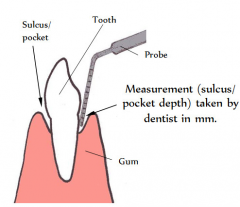
A groove or depression
Pocket depth used to measure for periodontal disease. |
|
|
Interdental Papillae |
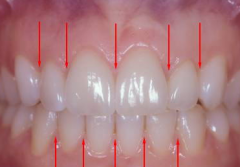
Triangular shaped crests of gingival tissue located between the teeth. The crests of tissue consists of free and attached gingiva. |
|
|
Free Gingival Groove |
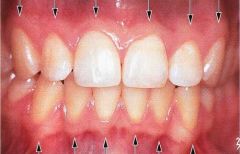
Located below the sulcus, this line seperates the free gingiva and the attached gingiva. |
|
|
Gingival Crest |
The peak of free gingiva. |
|
|
Free Gingiva |
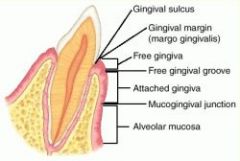
Moveable tissues that surrounds the crown of the tooth just above the CEJ of the tooth. |
|
|
Coronoid Process |
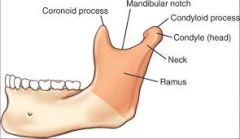
Part of the mandible.
Anterior
"Horn" |
|
|
Condyloid Process |
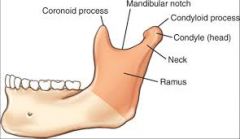
Posterior
Consists of a neck and condyle. The condyle fits into the glenoid fossa of the temporal bone. |
|
|
Sigmoid Notch Symphysis |
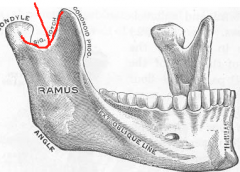
Depression between the coronoid and condyloid process. |
|
|
Regeneration and Repair |
Restoration of damaged tissue to original state. |
|
|
Systemic Inflammation |
Not limited to the area of injury |
|
|
Acute Inflammation |
Immediate localized protective response of the body to physical injury on the invasion of pathologic organisms |
|
|
Local Inflammation |
Limited to the area of injury. |
|
|
Chronic Inflammation |
A slow ongoing process that may lead to permanent tissue damage. |
|
|
Parotid Gland |
Largest salivary gland.
Bilateral infront and below the ear
Stenson's Duct enters the mouth oppostite the maxillary second molar.
|
|
|
Submandibular Gland |
Mixed gland.
Size of a walnut.
Bilateral on each side of the face beneath the lower jaw.
Whatons Duct on either side of lingual frenum
|
|
|
Sublingual Gland |
Smallest of the major salivary glands
Glands are all over the floor of the mouth |
|
|
Serous Gland |
Secretes serum |
|
|
Caries Stage I |
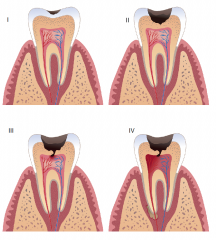
Smooth surface caries- triangular shaped decay that usually occurs between the teeth below the contact area.
On surface of enamal |
|
|
Caries Stage II |
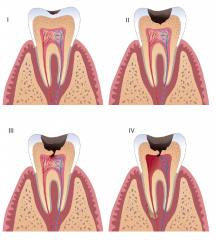
Decay triangle is still confined to the enamal, but has passed the halfway point |
|
|
Caries Stage III |
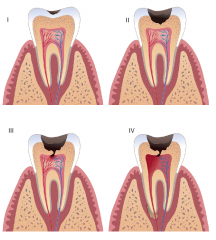
The decay triangle has passed the DEJ and entered the dentin.
Decay has not passed the halfway point between the DEJ and the pulp. |
|
|
Caries Stage IV |
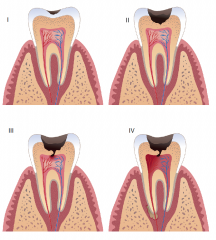
Decay triangle has passed the DEJ and has passed the halfway point between the DEJ and pulp. |
|
|
Cavity Varnish |
Seals open dentinal tubules
Purpose: 1. Prevent tooth sensitivity 2. Prevent discoloration of tooth structure |
|
|
Cavity Liner |
Similar to cavity varnish but contains calcium hydroxide or zinc oxide and is applied after cavity varnish.
Helps regenerate tooth structure
"Base"
|
|
|
Calcium Hydroxide |
Substance that is placed in the deepest part of cavity preperation closest to the pulp where it stimulates formation of secondary dentin.
Helps regenerate tooth structure
"Medicine" Can be used as a base |
|
|
Dental Cement |
cements crowns and bridges
can be used as a base
Types:
Zinc Phosphate- powder to liquid mixed on a cool glass tab Type 1-fine grain that easily flows into small irregularities of restoration Type 2- medium grain that can be used for posterior temporary restorations.
Zinc Polyacrylate- adheres directly to tooth structure through chelation. Attaches ortho brackets to tooth structure
Zinc Oxide-contains eugenol which is found in clove oil. |
|
|
Glass Ionomer Cement |
Properties: 1. can bond to enamel and dentin. 2. High strength and low solubility 3. Low film thickness 4. Biocompatible with tooth pulp. 5. Can be used as a base. |
|
|
Amalgam |
"dental alloy"
Oldest restorative material. Composed of silver alloy that is combined with mercury.
May contain silver (Ag), tin (Sn), copper (Cu), or zince (Zn) |
|
|
Informed Consent |
Requirement of parent or guardian to sign a form granting consent to perform any treatment. |
|
|
Sedation |
Extreme fear and resistance with the need for dental treatment often indicates the need for sedation.
Types: Conscious- oral sedative via pill or liquid form Inhalation- nitrous oxide, oxygen mix inhaled vio nose. offers fast onset and recovery with few side effects. General Anesthesia- loss of sensation, conciousness, protective reflexes, ability to obey commands, and maintain open airway. |
|
|
General Anesthesia |
loss of sensation, conciousness, protective reflexes, ability to obey commands, and maintain open airway. |
|
|
RPD Appoitments |
1. Exam and treatment plan 2. Tooth modification 3. Framework impression 4. Wax and framework try-in and bite registration 5. Delivery and adjustment. |
|
|
Partial Crowns |
A metallic, porcelain or composite resin restoration covering more than three but but not all surfaces of the tooth. |
|
|
Indirect Pulp Cap |
When there is a chance of nerve exposure, calcium hydroxide is placed on top of the area closest to the nerve and then permanent/ temporary restoration is placed. |
|
|
Direct Pulp Cap |
When nerve exposure occures during an operative procedure, calcium hydroxide is placed over exposure and a temporary or restoration is placed. |
|
|
Apexogenesis |
Process of performing a pulpotomy on an adult tooth with the goal of apex formation. |
|
|
Pulpectomy |
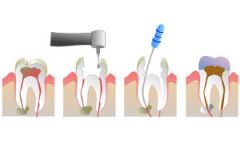
"Root canal treatment"
Involves removing the entire pulp from a tooth. Treatment with zinc oxide-eugenol and a permanent restoration. |
|
|
Pulpotomy |
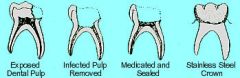
Involves the removal of pulp tissue up to the canals
Treatment with formocresol or calcium hydroxide, and restoration. |
|
|
Apicoectomy |
Involves removal of the apical portion of a tooth and surrounding tissue. |
|
|
Anterior Superior Alveolar (ASA) |
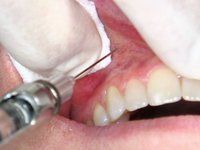
Injection site
Mesial to the maxillary canine, at the apex, in the muccobucal fold. |
|
|
Greater Palatine Injection |
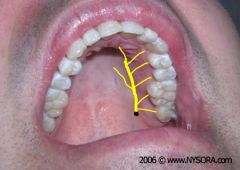
Distal to the second molar, halway between the gingival margin and the midline |
|
|
Middle Superior Alveolar ( MSA) |
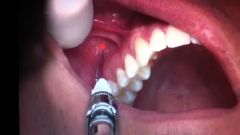
At the apex of the maxillary second premolar in the muccobucal fold. |
|
|
Posterior Superior Alveolar (PSA) |
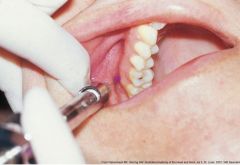
Just distal to the apex of the maxillary second molar in the muccobucal fold |
|
|
Buccal Injection |
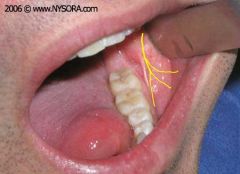
On the buccal side, distal to the most distal tooth in the arch. |
|
|
Inferior Alveolar Injection |
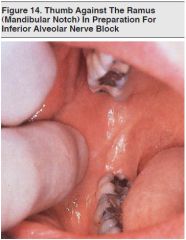
Distal, superior, and slightly lingual to the retromolar pad. |
|
|
Mental Injection |
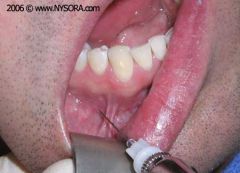
Between the first and second premolars,anterior to the mental foramen in the mucobuccal fold. |
|
|
Infiltration Injection |
Maxillary- apex of any tooth at mucobuccal fold
Mandibular- at apex of each incisor at mucobuccal fold. |
|
|
Occlusion Development |
Ever changing process that continues throughout life. |
|
|
Centric Occlusion |
Maxillary and mandibular jaws are closed, teeth are in maximum contact and the heads of both condyles are in the most retruded, unrestrained position in the glenoid fossa. |
|
|
Retractors |
Instrument used to retract tongue, cheek, lips to allow visibility |
|
|
Hyperventillation |
rapid breathing brought on by a stressful situation |
|
|
Allergic Reaction |
occures when a sensitivity to an allergen develops within an individual and a stimulant is placed. |
|
|
Oral Prophylaxis |
Removal of stains, plaque, foreign debris and calculus from the teeth |
|
|
Clinical Crown |
Crown portion of tooth that is visible in the oral cavity |
|
|
Disclosing Solution |
Special dye used to detect plaque in the oral cavity |
|
|
Fluoride |
Reduces tooth decay and promotes general oral health |
|
|
Coronal Polishing |
Process of removing stained and soft deposits from the clinical crown of a tooth |
|
|
Periodontitis |
Early- 2-4 mm
Moderate- 5-7mm
Advanced- 8+ mm and tooth mobility |
|
|
Gingivectomy |
Involved the removal of inflamed and diseased tissue |
|
|
Gingivoplasty |
Involves the removal of excess tissue and re-contouring the gingiva. |
|
|
Gingival grafting |
Type of periodontal surgery involving the removal of tissue from one part of the mouth to another area where it is needed. |
|
|
Osteoplasty |
Surgical reshaping of alveolar bone. |
|
|
Alveoplasty |
Removal of bone with a high speed handpiece and surgical buur, ronegeur forceps or bone files following surgery or extraction.
"re-contouring bone" |
|
|
Biopsy |
Removal of a sample of irregular tissue to be sent to a lab for analysis. |
|
|
Frenectomy |
Surgical procedure to remove the lingual or facial frenum attachment. |
|
|
Alveolitis |
"Dry Socket"
Absence of a blood clot in the socket following extraction. |

