![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the 6 different cell types found in Connective Tissue
|
Fibroblasts, Macrophages, Plasma Cells, Mast Cells, Leukocytes, and Adipocytes.
|
|
|
Name the two types of Extracellular Matrix
|
Fibers and Ground Substance
|
|
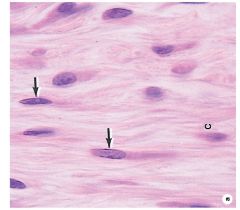
|
Fibroblasts
|
|
|
What are the 3 proteins of Fibers?
|
The three proteins of fibers are: Collagen, Reticular, and Elastic
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of Ground Substance?
|
The three types of Ground Substances are: Glycosaminoglycans (GAGS), Proteoglycans, and Multiadhesive glycoproteins.
|
|
|
What are the 3 Major Classes of Components that make up Connective Tissue?
|
The 3 major classes of components are: Cells, Extracellular Matrix, and Tissue Fluid
|
|
|
What kind of cell does Fibroblasts originate from?
|
Undifferentiated Mesenchymal Cells
|
|
|
What kind of cell does Macrophages originate from?
|
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
|
|
|
Plasma cells, where does it originate from?
|
originate from Hematopoietic Stem Cells
|
|
|
What kind of cell does Leukocytes originate from?
|
Undifferentiated Mesenchymal Cells
|
|
|
What kind of cell does Adipocytes originate from?
|
Undifferentiated Mesenchymal Cells
|
|
|
What is the function of Fibroblasts?
|
They are responsible for the synthesis of Extracellular Matrix Components
|
|
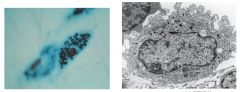
|
Macrophages and Lysosome
|
|
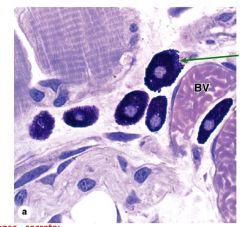
Name the cell...and what is the filling?
|
Mast cells filled with basophilic secretory granules
|
|
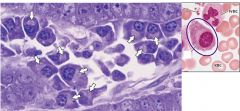
|
Plasma Cells
|
|
|
What is the function of Plasma Cells?
|
They are responsible for producing antibodies
|
|
|
Why are mast cells needed?
|
For defense-they secrete:
|
|
|
What are the 5 components that Mast cells secrete and what are their functions?
|
Heparin-anticoagulant
Histamine-Increased vascular permeability; smooth muscle contraction Serine Proteases-Activate Mediators of inflammation Chemotactic Factors-Attract Leukocytes Leukotrienes-Trigger Smooth Muscle Contraction |
|
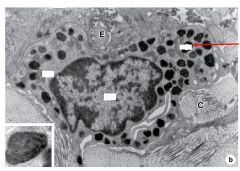
What is type of cell is this and what is the arrow pointing to?
|
Mast Cell
Arrow is pointing at secretory granules |
|
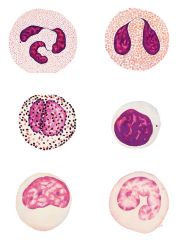
Name left to right; row by row
|
Leukocytes
Neutrophil Eosinophil Basophil Lymphocyte Monocyte Monocyte |
|
|
What is Diapedesis?
And describe the process.... |
When leukocytes cross walls of venules and capillaries.
Cytokines are released at sites of injury, infection, and inflammation. Vascular permeability and chemotaxis (guide) leukocytes to cross over. |
|
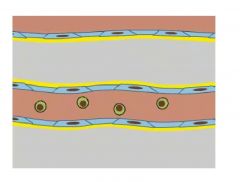
What is this process called?
|
Diapedesis
|
|
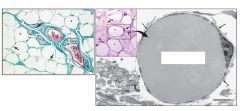
What is this?
What is in the middle? |
These are adipocytes with a large lipid droplet in the middle
|
|
|
What are the 4 categories of collagen?
And what type of collagen are in each category? |
1. Collagen that form Long Fibrils = Type I, II, III, V, and XI (SIX)
2. Fibril-Associated Collagen = Types IX, XII, XIV 3. Collagen that form Anchoring Fibrils= Type VII 4. Collagen that form Networks: Type IV |
|
|
How prevalent is Collagen Type I and what does it do?
|
Most abundant and widespread; provides tensile strength
|
|
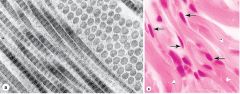
|
c = collagen bundles
|
|
|
Which type of fiber has mainly Collagen Type III?
What kind of support does it provide? Describe its meshwork. |
Reticular Fibers
It is heavily glycosylated; forms delicate branched, flexible "reticular" supporting meshwork in highly cellular tissue. |
|
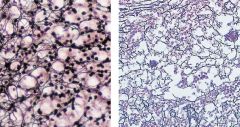
|
Fiber-Reticular Fibers in the
Adrenal Cortex (left) Lymph Nodes (right) |
|
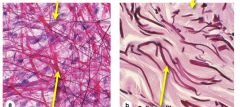
|
Left Photo:
Top Arrow: Elastic Fibers Bottom Arrow: Collagen Fibers Right Photo: Top Arrow: Elastin Fibers Bottom Arrow: Collagen Fibers |
|
|
What are elastic fibers made of?
(IF you miss this, slap yourself!) |
Elastin and Fibrillin
|
|
|
What are some characteristics of Elastic Fibers?
What are some differences between collagen verses elastic fibers? |
Highly hydrophobic protein
Similar to Collagen: rich in proline and glycine Different from Collagen: not glycosylated and contains little hydroxyproline |
|
|
Describe 4 characteristics of Ground Substance
(including the macromolecules that make up GS) |
1. Viscous
2. Highly hydrated complex mixture of macromolecules: -glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) -Proteoglycans -Multiadhesive Glycoproteins 3. Resists Compressive forces 4. Aqueous phase permits rapid diffusion of nutrients, metabolites, and hormones between the blood and the tissue cells |
|
|
What are GAGS?
|
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Long unbranched polysaccharide chains composed of repeating disaccharide units (generally a uronic acid and an amino sugar) |
|
|
What are Proteoglycans?
|
Core proteins to which GAGs are covalently linked
|
|
|
What are multi-adhesive glycoproteins?
|
protein chains bound to branched polysaccharides
|
|
|
Name 4 Multiadhesive Glycoproteins
|
Fibronectin
Laminin Entactin Tenascin |
|
|
What is the function of Multiadhesive Glycoproteins?
|
Function as links between cells and ECM constituents = help to mediate normal cell adhesion and migration
|
|
|
When does Edema occur?
|
When fluid movement is blocked by osmotic pressure
|
|
|
What are the 2 categories of Connective Tissue? And describe their resistance to stress and their physiological appearance
|
Loose (areolar):
-not very resistant to stress -Greater proportion ECM , cells -Fewer Fibers -Flexible, well-vascularized Dense can be broken down to A. Irregular: Without definite orientation B. Regular: With definite orientation -Resistant to stress -Clear predominance of collagen fibers |
|
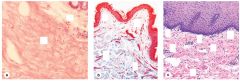
|
Mammary Gland:
Dense is on the left Loose is on the right Skin- Loose irregular on the top Dense on the bottom Tendon with long, parallel bundles of collagen fibers between elongated nuclei of fibrocytes. -Loose on the top -Dense on the bottom |
|
|
Name 4 functions of Connective Tissue
|
1. Support
2. Defense 3. Repair and Regeneration 4. Nutrition and Storage |

