![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List different routes of med administration and identify fastest/slowest routes |
Oral (slow) Injection (subQ, ID, IM) (fast) IV (fastest) Topical (slow) Intradermal (slowest) Rectal (slow) Eyes/ears |
|
|
What is first pass effect |
First pass effect is when a med is processed by the liver for the first time. Liver breaks down some of the medication and whatever remains is bioavailable. |
|
|
List some factors that affect medication dosages and responses |
Body weight- Individuals with larger body mass require larger doses. think mg/kg Age- Liver/kidney function are immature in younger patients and decreased in older adults Gender- Hormones and fat content can affect med response Genetics- Generally the effect is either fewer benefits from med or increased toxicity Tolerance Accumulation- med concentration can increase due to inability to metabolize or excrete med fast enough. Older adults decreased kidney and liver function are primary culprits Diet- inadequate nutrition can hamper response due to lack of protein response |
|
|
List rights of med administration |
Right Client Right Medications Right Dose Right Time Right Route Right Documentation Also, Right Allergies, Expiration, and Right toRefuse |
|
|
How would you perform teaching/education for an infant? |
Teaching is directed toward parents Ask for information on the child’s strengths/limitations or likes/dislikes Provide detailed information to parents |
|
|
How would you perform teaching/education for a toddler |
Allow play and manipulation of objects Use puppets to express feelings Use repetition and imitation of information Respond to simple, step by step commands Teaching sessions no longer than 5 minutes Again teaching is primarily directed to the parents –encourage them to act as role models |
|
|
How would you perform teaching/education for a preschooler? |
Use calm approach build trust Again allow manipulation of objects and equipment Use simple drawings and stories Stimulate the senses: visual, auditory, tactile, motor Use positive reinforcement |
|
|
How would you perform teaching/education for a school aged child? |
capable of logical reasoning – “keep it simplestupid” Welcome active participation Teaching sessions can be extended to 30 minutesand spread apart to allow for comprehension of largeamount of info. Use diagrams, models, pictures, videos, computerand printed materials Clarify scientific and medical jargon Use analogies |
|
|
How would you perform teaching/education for an adolescent? |
Need for independence so let them share in decision making whenever possible Develop a mutually respectful, trustingrelationship Clarify terminology and medical jargon |
|
|
How would you perform teaching/education for a young/middle adult? |
Adults are self-directed. They often know whatthey want to know and expect to have some voice in theeducational process. Create a climate of mutual respect. Adults do notlearn well when they feel threatened. |
|
|
How would you perform teaching/education for an older adult and what special considerations should you be aware of? |
Adults are self-directed. They often know what they want to know and expect to have some voice in the educational process. Create a climate of mutual respect. Adults do not learn well when they feel threatened. OLDER ADULT SPECIFIC CONSIDERATIONS: Slower processing and reaction time Decreased short-term memory Increased test anxiety Altered time perception |
|
|
List and define the four developmental stages and appropriate ages for Piaget's theory |
Sensorimotor- 2 days-1 yr. Discovering relationships between their bodies and the environment. Preoperational- 1-6 years. During this stage, children begin to engage in symbolic play and learn to manipulate symbols Concrete operational 6-11 years. Children begin thinking logically about concrete events, but have difficulty understanding abstract or hypothetical concepts Formal operational- 12+ years. Develop the ability to think about abstract concepts. Skills such as logical thought, deductive reasoning, and systematic planning also emerge during this stage |
|
|
List and define eight stages of Erikson's theory of development and appropriate ages |
Infancy - Trust vs. Mistrust Toddler- Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt Late Pre school - Initiative vs. Guilt School Age - Industry vs. Inferiority Adolescence - Identity vs. Role Confusion Young Adult - Intimacy vs. Isolation Middle Adulthood - Generativity vs. Stagnation Maturity - Integrity vs. Despair |
|
|
List stages of growth and development and their appropriate ages |
Infancy- 2 days - 1 year Toddler- 1-3 years Pre-school- 3-6 years School age- 6-12 years Adolescence- 12-20 years Young adult- 20-35 years Middle adult- 35-65 years Older adult- 65+ years |
|
|
List some red flags for infants |
Unable to roll at 6 months or sit alone byage 9 months Unable to transfer objects from hand tohand by age 1 year Abnormal pincer grip or grasp by age 15months Unable to walk alone by 18 months Failure to speak recognizable words by 2years. |
|
|
List some red flags for toddlers |
Can’t walk ( at 18 mos) Doesn’t copy others Doesn’t know what to do with commonthings Doesn’t have at least 6 words Doesn’t mind when caregivers leaves or returns Loses skills he once had |
|
|
List some red flags for pre-schoolers |
Inability to perform self-care tasks, handwashing simple dressing, daytime toileting
Lack of socialization Unable to follow directions during exam Can’t tell what’s real or make believe Doesn’t draw |
|
|
List some red flags for school-age children |
School failure Lack of friends Social isolation Aggressive behavior: fights, firesetting, animal abuse |
|
|
List some red flags for adolescents |
Anorexia Attention deficit Anger issues Suicidal tendencies/self harm |
|
|
List some red flags for young adults |
Not resolving conflict (intimacy vs isolation) The young adult must be willing to be openand committed to another individual. |
|
|
List gross/fine motor skill development in infants |
1 month- demonstrates head lag, grasp reflex 2 months- lifts head off mattress,holds hand in open position 3 months- lifts head and shoulders off mattress, diminished head lag, no grasp reflex 4 months- rolls from back to side, grasps objects w/ both hands, puts objects in mouth 5 months- rolls from front to back, palmar grasp 6 months- trolls from back to front, holds bottle 7 months- bears weight on feet, sits supported by hands, moves objects from hand to hand 8 months- sits unsupported,pincer grasp 9 months-pulls to a standing position, dominant hand evident 10 months- changes from prone position to sitting 11 months- cruises, walks with hand held, fine pincer grasp, puts objects into container 12 months- sits down unassisted, turns pages in book, can stack two blocks unsuccessfully |
|
|
List gross/fine motor skill development in toddlers |
15 months- walk w/o assistance, creeps up stairs, uses cup, builds two block towers 18 months- assumes standing position, jumps with both feet, manages spoon w/o rotation, turns pages in book 2-3 at a time 2 years- walk up/down stairs, builds towers w/ 6-7 blocks 2.5 years- jumps with both feet, stand on one foot, draw circles, good hand/finger coordination |
|
|
List gross/fine motor skill development in preschooler |
3 yo- ride tricycle, jump off bottom step 4yo- skip/hop on one foot, throw ball overhead 5 yo- jump rope, walk backwards, move up/down stairs easily |
|
|
List some therapeutic communication techniques |
Silence General leads Restating orparaphrasing Seeking clarification Offering self Providing information Acknowledging Clarifying time or sequence Presenting reality Focusing• Reflecting Summarizing & planning Open-ended questions Touch |
|
|
List some communication barriers (non-therapeutic) |
Stereotyping Agreeing and disagreeing Being defensive Challenging Probing (“Why...) Testing Giving Advice Excessive or irrelevantquestioning Changing topic orsubject Unwarranted or Falsereassurance Passing judgment Offering personal opinion Sympathy |
|
|
What tasks cannot be delegated by a RN? |
PACET- Planning, Assessment, Collaboration, Evaluation, Teaching (Initial) |
|
|
What tasks can be delegated to LPN |
Follow Up Monitoring Reinforce Teaching |
|
|
What tasks can be delegated to a UAP? |
VAPER- Vitals, Ambulation, Positioning, Eating, Recording |
|
|
What are the levels of prioritization? |
A = airway – has the highest priority. We cannot livewithout oxygen, which enters our airway. B = breathing – is the next highest priority. Oxygenenter the body by breathing. C = circulation – is the third highest priority. Oxygenmust be moved to the tissues where it is needed, inorder for the cells to survive.
D = Potential for disability – 4th highest priority |
|
|
List five cycles of sleep and some characteristics of each cycle |
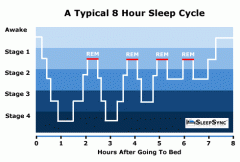
Stage 1- very light sleep, generally only a few minutes long Stage 2- deeper sleep, lasts for 10-20 mins Stage 3- initial stage of deep sleep, 15-30 mins Stage 4- Deepest sleep, 15-30 mins REM- Difficult to awaken, cog. restoration takes place, lasts ~20 mins |
|
|
List some common sleep disorders |
Insomnia- inability to fall asleep or stay asleep. may be acute or chronic Sleep apnea- a cessation of breath for more than 10 seconds during sleep. Can be related to obstruction of airways or CNS Narcolepsy- Sudden attacks of sleep or excessive sleepiness during waking hours |
|
|
List appropriate hours of sleep across the lifespan |
Infants (4-12 Months) = 12 to 16 Hours Toddlers (12 - 24 months) = 11 to 14 Hours Preschoolers (3y – 5y) = 10 to 13 Hours School-Age (6y – 12y) = 9 to 12 Hours Teenagers (13y – 18y) = 8 to 10 Hours Young Adults (18y – 25y) = 7 to 9 Hours Adults (26y – 64y) = 7 to 9 Hours Older Adults (65y +) = 7 to 8 Hours |
|
|
What are some nursing considerations regarding sleep? |
Establish a bedtime routine & rituals Limit waking – “Cluster Care” Light Carbohydrate meal Promote comfort Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) for those with sleep apnea. Sleep Study Referral? Teaching/Evaluating – Sleep diary, Sleep Hygiene Sleep promoting OTC products (melatonin, valerian, chamomile) |
|
|
List 5 steps of the nursing process |
Assessment Analysis/connections Planning Implementation Evaluation (remember you are evaluating the patients response to the nursing interventions) |
|
|
List Gordon's 11 functional patterns |
Cognitive Activity & exercise Elimination Nutrition/metabolic Sleep/rest Health perception/management Self-perception/concept Sexuality Coping & stress tolerance Role/relationship Value/belief |
|
|
List the three levels of illness prevention |
Primary prevention – prevent problem from ever happening (education, healthy lifestyle, vaccinations)
Secondary prevention – early detection and treatment (Acute care, exams/screening tests,daily, low-dose aspirins and/or diet and exercise programs to prevent further heart attacks or strokes) Tertiary prevention – long-term treatment |
|
|
List three different types of exercise |
Isotonic- exercise utilizing the contraction and lengthening of muscles. think running and swimming Isometric- exercise against an immovable object. think pushing your hands against each other Isokinetic- moving an object with weight/resistance. Think using weight machines |

