![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Kingdoms |
Animalia, plantae, fungi , protista, monera |
|
|
Carl Iinne |
Started naming everything |
|
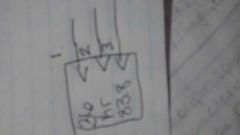
|
1. Atomic number-#of protons 2. Atomic symbol 3. Atomic mass- # of protons |
|
|
Energy shells |
1-2 2-8e 3-8e |
|
|
Bond |
Interactions of the outer electrons |
|
|
3 types of bond that creates molecules |
Non polar covalent bond- equal sharing of electrons. 2. Polar covalent bonds- unequal share of electrons 3 ionic bond- gain and loss of electrons |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds |
Between molecules Polar covalent bonding,,,, weak bonds |
|
|
Characteristics of water created by hydrogen bonding |
1. High specific heat 2. Capillary action 3. Surface tension 4. Less dense in a solid |
|
|
Monomers--> polymers |
Amino acids--> proteins Simple sugars -->carbohydrates Fatty acids-->lipids Nucleo tides-->nucleus acids |
|
|
Proteins |
Amino acids Function-structures and metabolism |
|
|
Lipids |
Fatty acids |
|
|
Fatty acids |
Saturated.- solid ex butter water Unsaturated- liquids oils |
|
|
Types of cell |
Prokaryotic cells- kingdom- monera Eukaryotic cells- all other kingdoms - Amelia, plantae, fungi, protista. |
|
|
Cell membrane .. |
Regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell |
|
|
Cell membranes movement |
1. Simple diffusion- high concentration to-> low concentration, through the phospholipid bilayer. 2. Osmosis - conc-> low concentration. Water, channel protein. 3. Fascilated diffusion high con -> low con.Carrier protein. 4. Active transport-low con-> high con carrier protein energy |
|
|
Organells |
Sperate chemical reactions in space and time |
|
|
Metabolism |
All the chemical reactions that allow a cell to acquire and use energy to synthesis, store, break apart, it eliminate substances that contributes to the survival or reproduction of the cell or organism. |
|
|
Metabolic pathways |
An orderly series of chemical reactions that must to a product |
|
|
Photosynthesis where, in , out |
Where: stroma In: co2, Rubp, A+P, NADPH Out: sugar RuBP |
|
|
Glycolysis- where, in, out |
Where: cytoplasm In: sugar A+ P Out- A+P , VADH, pyryuvale |
|
|
Transiting reactions where, in, out |
Where: matrix In: pyruvate Out: Acetylcea, NADH,Co2 |
|
|
Kerbs cycle where , in, out |
Where: matrix In: Acetyclo-a, oxgloarelate Out: NADH,A+P ,CO2 ,FabH2, oxgloarelate |
|
|
Mitosis |
creates somatic cells( all cells except sex cells) |
|
|
Meiosis |
Creates sex cells |
|
|
Autosomes |

|
|
|
Auto dominant inheritance |
1. Equally inherited between the sexes 2. Always expressed in the heterozygous condition. 3. Not lethal, not expressed until after maturity. |
|
|
X linked recessive inheritance |
1. Unequally inherited between the sexes 2. Always expressed in the male 3. Female- homozygous recessive |
|
|
Abnormal inheritance |
Autosomal recessive inheritance 1. Equally inherited between the sexes. 2. Not expressed in the heterozygous consortium. |
|
|
Gregor Mendel |
Father of genetics |
|
|
Test cross |
Use to determine the genotype of an individual showing the dominate phenotype |
|
|
Homeostasis |
Maintaining a constant internal environment |
|
|
Homeostasis parameters |
Temp- 98.7 f Blood sugars- 0.1% Blood pressure- 120/80 Blood ph- 7.4 |
|
|
Nervous system |
Central nervous system- brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system- nerve cell-neuron.. |
|
|
Types of neurons |
1. Sensory neuron 2. Association neuron 3. Motor neuron |
|
|
Know the respiratory system and the digestive system |

|
|
|
Guy hormones |
Made in one part of the body acts on a different part of the body. Hormonal control- begins in the Brian hypothalamus-gnrh. Pituitary gland-lh,FSH. Lh- release of testosterone Fsh- causes spermatogenesis. Testies-release testosterone, secondary male characteristics |
|
|
Female hormones |

|
|
|
Jean Baptiste lamark |
Theory of acquired characteristics |
|
|
Charles Darwin |
Much variation in all population |
|
|
Darwin/ Wallace |
Million years |
|
|
Lyell |
Geologist 8000 |
|
|
Alfred wegener |
Meteorologist Continental drift |
|
|
Robert dietz |
Plate techtonics |
|
|
Homologous structure |
Man, horse, whale, bat |
|
|
Avalogus structure |
Bird, bat, dragonfly |
|
|
Gene flow |
Immigration/ emigration. Ex squirrel and the dam |
|
|
Genetic drift |
Bottle neck event. Founders effect. |
|
|
Acid depletion |
Rain, Fogs, snow, dry particulates |

