![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Aerial shot |
A shot from high above, usually from a crane or helicopter |
|
|
|
Angle |
The position of a camera of point of view in relation to the subject being shown. Seen from above, the subject will be shot from a high-angle; from below, it would be depicted from a low angle |
|
|
|
Animation |
A method used to make inanimate figures or objects come to life on the screen. This can be done by drawing on individual frames or by photographing an object one frame at a time will slightly changing the position of the object |
|
|
|
Aspect ratio |
The ratio of the width to the height of the film image. The traditional "academic ratio" is 1.33:1. Since the 1950s, widescreen ratios have become the norm, ranging from 1.66:1 - 2.55:1 |
|
|
|
Asynchronous sound |
Sound that does not have its source in the film image |
|
|
|
Backlighting |
Light that comes from behind the person or object being filmed, often creating a silhouette around that subject |
|
|
|
Chiaroscuro lighting |
The composition of light and dark in an image or picture |
|
|
|
Cinematography |
The technical term for the various stages of motion picture photography, from the manipulation of the film in the camera to the printing of that film |
|
|
|
Close-up (cu) |
An image in which the distance between the subject and the point of view is short, as in a close up of a person's face |
|
|
|
Composition |
The arrangement and relationship of the visual elements within a frame |
|
|
|
Computer graphics |
Images created electronically by a computer, often used for special effects or to manipulate photographic images |
|
|
|
Continuity editing |
An editing style that follows a linear and chronological moving forward, as if the image is simply recording the action. Because it creates the illusion of reality, is often called "invisible editing" |
|
|
|
Contrapuntal sound |
Sound that counterpoints or contrasts the image |
|
|
|
Crane shot (crs) |
An image depicting the subject from overhead, usually with the camera mounted on a mechanical crane |
|
|
|
Crosscutting |
An editing technique that alternates between two different actions or scenes |
|
|
|
Cutting (ct) |
Changing from one image to another; a version of this linkage is sometimes referred to as montage |
|
|
|
Deep focus |
A focus in which multiple planes in a shot are all simultaneously in focus |
|
|
|
Depth of field |
A range of planes within an image from foreground to background, all of which are in focus |
|
|
|
Direct sound |
Sound recorded at the same time as the image is filmed |
|
|
|
Dissolve |
An editing transition whereby one image fades out while another fades in |
|
|
|
Documentary |
The non-fiction film about real events and people, often avoiding traditional narrative structures |
|
|
|
Dubbing |
The recording of dialogue or other sound effects during the editing of a film |
|
|
|
DVD |
First developed around 1995, digital video discs have quickly become a primary vehicle for movie distribution and home viewing |
|
|
|
DVD technology |
The recording and playing of Bones as digital video discs, which can be viewed on DVD players or, increasingly, on computer drives. Besides the potential for higher quality sound and images, DVDs allow for manipulation of the image, such as screen format, and can offer supplemental materials, such as interviews with the stars |
|
|
|
Eyeline match |
The editing or joining of different shots by following the logic and direction of a character's glance or look |
|
|
|
Fade in |
An editing transition whereby an image gradually appears on a blackened screen |
|
|
|
Fade out |
And editing transition whereby an image gradually disappears on to a blackened screen |
|
|
|
Fast motion |
When action is filmed at less than 24 frames per second, the projection of that action at 24 frames per second will appear to move at a more rapid than normal pace |
|
|
|
Feature |
The main attraction when a group of films are shown. It can also refer to any film from 90 to 120 Minutes long shown exclusively at a theater |
|
|
|
Fill light |
Supplemental lighting that fills in or accentuates the key lighting on a filmed subject |
|
|
|
Film gauge |
The width of film stock measured in millimeters, ranging from 8mm (for home movies) to 70mm (for commercial blockbusters) |
|
|
|
Filmography |
A list of films with information that ranges from just the title to the complete details about the film, such as the director, producer, running time, and so forth |
|
|
|
Flashback |
An image, seen, or sequence that appears in a narrative to describe a past action or event |
|
|
|
Flashforward |
An image, see you in, or sequence that appears in a narrative to describe a future action or event |
|
|
|
Focus |
The clarity and detail of an image, produced by the type of lens used and the distance between the camera and the object being filmed |
|
|
|
Formalism |
A critical perspective that attends mainly to the structure and style of a movie or group of movies |
|
|
|
Frame |
The borders of the image within which the subject is composed |
|
|
|
Freeze Frame |
When the movement of the film image appears to stop so that it appears like a photographic still |
|
|
|
Full shot (fs) |
A shot that shows the whole body of the individual being filmed |
|
|
|
Genre |
A critical category for organizing films according to share themes, styles, and narrative structures; examples are horror films and gangster films |
|
|
|
Handheld shot |
A shot filmed from the shoulder of a camera person, usually creating the subjective perspective of an individual |
|
|
|
Highlighting |
Sharp or intense lighting used to concentrate or highlight a detail of a person or object |
|
|
|
Ideology |
An analytical approach that attempts to unmask the stated or unstated social and personal values that inform the movie or group of movies |
|
|
|
Intertitles |
Mostly associated with silent film, images that present printed information or dialog about the images before or after the intertitle |

|
|
|
Iris shot |
The expansion or contraction of a small circle within the darkened frame to open or close a shot or scene |
|
|
|
Jump cut |
A cut within the continuous action of a shot, creating a spatial or temporal jump or discontinuity within the action |
|
|
|
Key lighting |
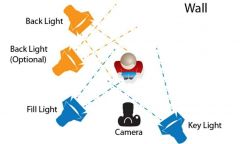
The primary source of false light on scene or subject. High key scenes are entirely lit by this source. Low key scenes have little artificial lighting |
|
|
|
Long shot (ls) |
An image in which the distance between the camera and the subject is great |
|
|
|
Match cut |
An edit that links two shots by a continuous sound or action |
|
|
|
Medium close up |

A shot that shows an individual from the Torso to the Head |
|
|
|
Medium long shot |

I shot that reveals the entire body of a person or object along with a large part of the surrounding scene |
|
|
|
Medium shot (ms) |

A shot that shows an individual from the waist up |
|
|
|
Mirror shot |
I shot that reveals a person or scene through its reflection in a mirror |
|
|
|
Mise-en-scène |
The arrangement of the theatrical elements (sets, lighting, costumes, and props) before they are actually filmed |
Think "messy scene" and what goes into making a scene on stage out in film look like a messy teenagers room |
|
|
Model shot |
I shot that uses small constructions or miniatures to create the illusion of real objects |
|
|
|
Montage |
A specific kind of editing in which objects and figures are linked in a variety of creative or unexpected ways. Usually this kind of editing aims to generate certain effects or ideas |
|
|
|
Narrative |
The way of story is constructed through a particular point of view and arrangement of events |
|
|
|
Off-screen space |
Areas that are not shown by the image but sometimes suggested by actions or words within the image |
|
|
|
180 degree system |
I traditional rule for filming action so that the camera does not cross an imaginary 180° line. It is meant to create a stable spatial orientation for all action filmed |
|
|
|
Pan (ps) |
The shot that pivots from left to right or right to left without the camera changing its position |
|
|
|
Parallel action |
Two or more actions that are linked by the film to appear simultaneous |
|
|
|
Point of view (pov) |
The position from which an action or subject is seen, often determining its significance |
|
|
|
Point-of-view shot |

A subjective shot that reproduces a character's optical point of view, often proceeded / followed by shots of the character looking |
|
|
|
Process shot |
The shot that employs special effects during or after the filming of the shot |
Think "a shot to be/that is processed" |
|
|
Rack Focus |

A quick change of focus within a shot so that one object appears suddenly out of focus and another appear suddenly in focus |
|
|
|
Reaction shot |
A shot that cuts from an object, person, or action to show another person or persons' reaction |
|
|
|
Resolution |
The degree of sharpness in an image |
|
|
|
Scene |
The space within which a narrative action takes place; it is composed of one or more shots |
|
|
|
Score |
The musical soundtrack for a movie |
|
|
|
Screenplay |
The literary description of film that maybe a description of characters, dialogue, and actions or may contain exact shots and scenes |
|
|
|
Sequence |
A series of scenes or shots unified by a shared action or motif |
|
|
|
Set |
The place or location used for a specific scene or shot in a film |
In theater this is the arrangement of items on stage, but in film this is the ___________ of the shot/scene. |
|
|
Shallow Focus |
A shot in which on the objects and persons in the foreground of the image can be seen clearly |
Shallow focus is like near-sightedness |
|
|
Shot |
A continuously exposed and unedited image of any length |
|
|
|
Shot/reverse shot (s/rs) |
An editing pattern that cuts between individuals according to the logic of their conversations |
|
|
|
Slow motion |
When action is filmed at a speed faster than 24 frames per sec that action appears unusually slow when projected at normal speed |
|
|
|
Soft focus |
By using filters on the camera lens, objects and individuals will appear blurred or with hazy definition |
|
|
|
Sound effects |
Any number of uses of sound other than music or dialogue |
|
|
|
Soundtrack |
Using either optical or magnetic recording technology, the dimension of film that includes music, noise, dialogue, and any other aural effects |
|
|
|
Special effects |
The term used to describe a range of technological additions to the film to manipulate or alter what has been filmed |
|
|
|
Subjective camera |
A technique that recreates the perspective of a single individual |
|
|
|
Swish pan |
The pain shot that moves rapidly from right to left or left to right, creating a blurring effect |
|
|
|
Synchronous sound |
Sound whose source is identified by the film image |
|
|
|
Take |
The recording of an image on film (usually used in writing as a temporal measure, such as a "long take" or a "short take") |
|
|
|
Title shot |
I shot that moves vertically up or down without changing the position of the camera |
|
|
|
Tracking shot (trs) |
The movement of the image through a scene, photographed by camera mounted on tracks. A dolly shot creates the same movement with a camera mounted on a mechanical cart, while a handheld camera is mounted on a cameraperson's shoulder |
|
|
|
Videotape |
Magnetic tape used to record films for distribution and playing on VCRs; The quality of both the film sound and image usually deteriorate on videotape |
|
|
|
Voice over |
The voice of someone, not seen in the narrative image, who describes or comments on that image |
|
|
|
Widescreen |
An aspect ratio that exceeds the traditional 1.33:1 ratio of width to height. The most common widescreen ratios are 1.66:1 and 1.85:1 |
|
|
|
Wipe |
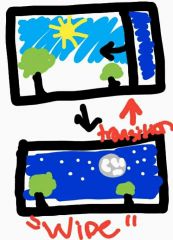
An editing technique whereby a line crossing (or "wiping") one image replaces it with another image |
The Star Wars transition |
|
|
Zoom shot |
The movement of the image according to the focal adjustments of the lens, without the camera being moved |
|

