![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
dietary fiber is the ___1_ __2_
component of CHO and ___3_ found in __4_ food , __5_ in the __6_ gut may metabolize part it |
1. edible 2. nondigestible
3. lignin 4. PLANT 5. BACTERIA 6. LOWER |
|
|
2 CLASSIFICATIONS OF FIBER
|
CRUDE
TOTAL DETARY FIBER (SOL AND INSOL) |
|
|
FUNCTIONAL FIBER
|
isolated nonddigestable cho with beneficial physiological effects in human
|
|
|
how is soluble fibers beneficial
|
-attracts water, turning into gel and slowing digestion
-lowers chol (binds with bile acid) -delay glucose absoption |
|
|
how is insoluble fibers beneficial
|
speeds passage of food tru the stomach and intestine
-adds bulk to stool, reducing incidende of constipation |
|
|
put the following in order of solubility
1. lignin 2. cellulose 3 beta-glucans 4. gums 5. hemicellulose 6. pectins |
6. 4. 5. 3. 2. 1.
|
|
|
What is the main 2 extracts in legumes? 4 physiological effects? 3 health benefits?
|
1. hemicellulose, other polysaccharides 2. binds bile, inc viscosity, SCFA, fecal 3. decr chol, colon cancer, incr gluc tolerance
|
|
|
main sources of soluble fiber?
|
oat bran, barley, beans and lentils
|
|
|
main source of insoluble fiber
|
wheat bran, vegetables, whole grains
|
|
|
Cellulose is produced how?
|
During photosynthesis, sugars and glucose are manufactured from water and CO2.
|
|
|
How many glucose units does a long chain of cellulose can contain?
|
5000-10000
|
|
|
What are the 3 enzyme used for digestion when measuring fiber
|
Enzymatic digestion
i) α-amylase ii) protease iii) amyloglucosidase |
|
|
what is the formula to claculate total fiber after digestive testing
|
tot diet fiber = wt (residue)-wt(ash + protein)
|
|
|
i) α-amylase
ii) protease iii) amyloglucosidase |
i) α-amylase: gelatinize
ii) protease: remove protein iii) amyloglucosidase: remove starch |
|
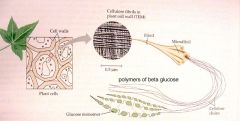
|
cellulose
|
|
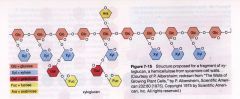
what is
|
hemicellulose
|
|
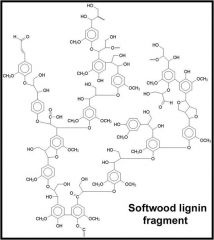
|
Lignin
|
|
|
difference between hemicellulose and cellulose?
|
- smaller molecules ~150
-produced from glucose and other sugars such as gal, man, xyl -can be straight or have short side-chains |
|
|
What aree the repeating units cellulose called?
|
cellobiose units
|
|
|
name one hemicellulose ex.?
|
glucoronoxylan
|
|
|
what are lignin classified as:
|
non-CHO
phenolics |
|
|
repeating units in fiber are called?
|
phenylpropane units
|
|
|
where are pectins found?
|
on pulp of apple and citrus
|
|
|
hydrolysis of pectin yields which 5 molecules?
|
2 sugArs: gAlactose & Aribinose
2 Acids: gAlacturonic acid and Acetic acid 3. Alcohol: methAnol |

