![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four main functions of the epithelia?
|
Protection, secretion, absorption, surface transport
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is the epidermis of the skin?
|
Stratified squamous keratinised epithelium
|
|
|
What are the three cell types in the skin's epidermis?
|
Keratinocytes, pigment cells and epidermal macrophages
|
|
|
What is keratinisation?
|
An ordered process involving mitosis, cell differentiation and apoptosis. Proceeds from the basal layer upwards, giving a layered architecture to the epidermis
0005181010 - Weekend (: |
|
|
What is the nomenclature of the epidermal layers of the skin?
|
Prickle, granular, keratinised, desquamating
|
|
|
What is the content of the skin's epidermis? (4)
|
Keratinocytes, macrophages, pigment cells, nerve endings
|
|
|
What is the content of the skin's dermis? (8)
|
CT, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, smooth muscle-arrector pili, blood vessels, nerve endings
|
|
|
What is a sebaceous gland?
|
Glands in the skin which secrete an oily/waxy matter, called sebum
|
|
|
What is the purpose of sebum?
|
To lubricate the skin and hair of mammals
|
|
|
What is the content of the skin's hypodermis? (4)
|
CT, adipocytes, hair follicle roots, sweat glands
|
|
|
What are the two divisions of the skin's dermis?
|
Subepithelial/papillary
Deep |
|
|
What is in the papillary dermis?
|
Loose CT containing MICROCIRUCLATION (nutritional blood supply to the skin) and sensory nerve endings
|
|
|
What is in the deep dermis? (5)
|
Fibrous CT (mainly coarse collagen and elastin bundles) with scattered fibroblasts, blood vessel plexuses (A network of nerves or vessels in the body), sensory nerve endings
|
|
|
What are the eight types of epithelium?
|
Simple/Stratified: Squamous, cuboidal and columnar, pseudostratified, transitional
|
|
|
What are the three cell types of the pseudostratified epithelium?
|
Goblet, ciliated columnar and basal
|
|
|
What is the function of a goblet cell?
|
To secrete mucin, which dissolves in water to form mucus
|
|
|
What is simple squamous epithelium located? What's a special name for it?
|
It lines the lumen of blood vessels. It is called 'endothelium'.
|
|
|
What does squamous mean?
|
Flat
|
|
|
Where is simple cuboidal epithelium found?
|
The kidney medulla, in the collecting ducts
|
|
|
Where is simple columnar epithelium found?
|
Cells that line the interior surface of the gastrointestinal tract
|
|
|
Columnar cells are usually highly secretory, how is their structure adapted to this? What do they secrete?
|
They have a very elongated cytoplasm, capable of producing and holding a large quantity of secretory products. They secrete mucus
|
|
|
Where is stratified squamous epithelium found?
|
Lumen of the oesophagus
|
|
|
What is a 'strata'?
|
A layer
|
|
|
Epithelia *always* stands on...
|
Basal Lamina
|
|
|
What is the function of the basal lamina wrt epithelia?
|
BL links epithelia to CT
|
|
|
How is epithelium classified?
|
By the shape of the outermost (luminal/superficial) cell
|
|
|
What is the top part of the epithelia called? What is the bottom part called?
|
Apical = Top
Basal = Bottom |
|
|
Where is stratified cuboidal found?
|
Large ducts - salivary gland, sweat gland
|
|
|
Stratified columnar is rare, but where is it found?
|
Large ducts
|
|
|
Epithelium is polar true/false
|
True
|
|
|
Epithelia regenerates well, however, it can undergo metaplasia as a result of this. What is metaplasia?
|
Where tumours can form due to abnormal change in the nature of a tissue
|
|
|
How are epithelial cells connected?
|
By specialised 'junctions'
|
|
|
Remember: PSEUDOstratified is just that! It looks stratified, but isn't. Where is it found?
|
Mainly respiratory epithelium
|
|
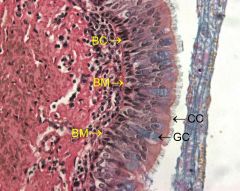
|
Pseudostratified
|
|
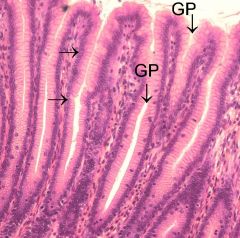
|
Simple Columnar
Note how the top half of the cell is lightly stained (where it is full of mucus being prepared for secretion) |
|
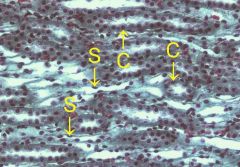
|
Simple cuboidal
he ducts and the thick limbs of the loops are constructed from simple cuboidal epithelium (C). The capillaries and the thin limbs of the loops are constructed from simple squamous epithelium (S) |
|
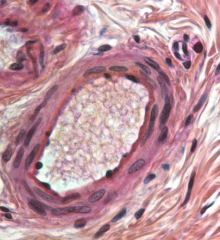
|
Simple Squamous (inner layer)
|
|
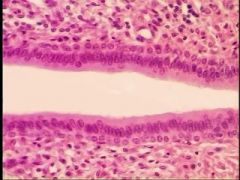
|
Stratified columnar
Rare - found in the ocular conjunctiva of the eye, in parts of the pharynx and anus, the female's uterus, the male urethra and vas deferens. |
|
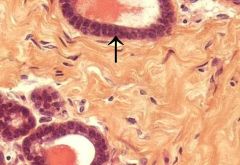
|
Stratified Cuboidal
It is commonly found in exocrine glands, where it forms the larger ducts |
|
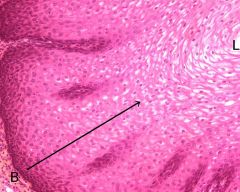
|
Stratified squamous
|
|
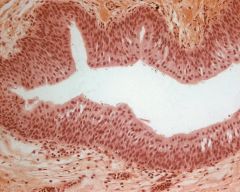
|
Transitional
Visible intercellular spaces Small basal cells, lying closest to the basement membrane |

