![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
AAs are/are not good physiological buffers. Why are/aren't they?
|
Are not. No pK values near physiological pH.
|
|
|
Which type of optical isomer is predominant in bodily amino acids?
|
L-isomer
|
|
|
Remember CORN law: If H towards you COO-, R, and NH3 are clockwise around
|
.
|
|
|
What type of bonds do hydrophilic AAs have?
|
=O, OH or NH (i.e. they can form H bonds with water)
|
|
|
What type of bonds do acidic AAs have?
|
COO-
|
|
|
What type of bonds to basic AAs have?
|
NH
|
|
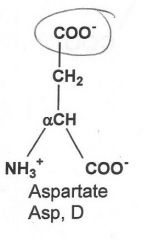
|
Acidic
|
|
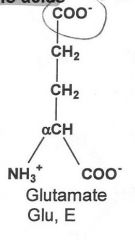
|
Acidic
|
|
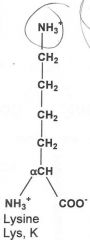
|
Basic
|
|
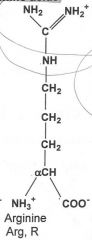
|
Basic
|
|
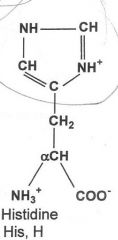
|
Basic
|
|
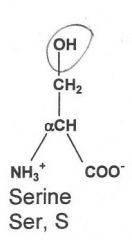
|
Hydrophilic
|
|
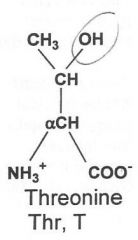
|
Hydrophilic
|
|
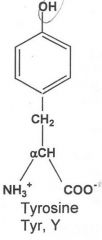
|
Hydrophilic
|
|
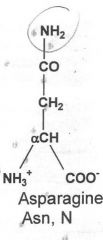
|
Hydrophilic
|
|
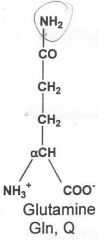
|
Hydrophilic
|
|
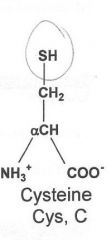
|
Hydrophilic
|
|
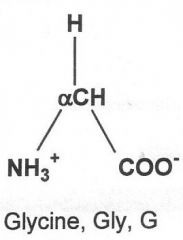
|
Hydrophobic
|
|
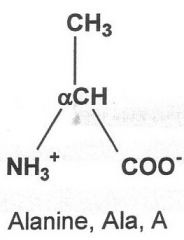
|
Hydrophobic
|
|
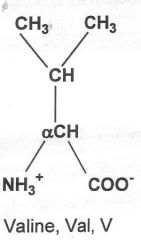
|
Hydrophobic
|
|
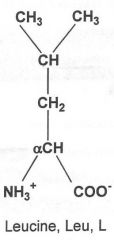
|
Hydrophobic
|
|
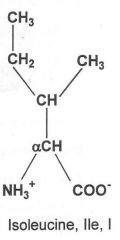
|
Hydrophobic
|
|
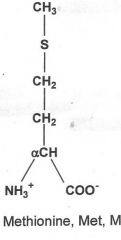
|
Hydrophobic
|
|
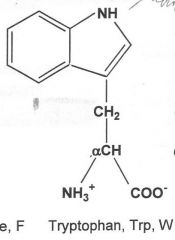
|
Hydrophobic
|
|
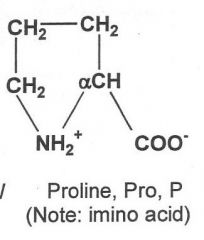
|
Hydrophobic
|
|
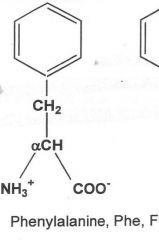
|
Hydrophobic
|
|
|
What are the two acidic amino acids? (GA)
|
Glutamate and Aspartate
|
|
|
What are the three basic amino acids? (LAH)
|
Lysine, Arginine and Histidine
|
|
|
What are the six hydrophilic amino acids? (CT-STAG)
|
Cysteine, tyrosine, serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine
|
|
|
What are the nine hydrophobic amino acids? (TIM V GLAPP)
|
Tryptophan, Isoleucine, Methionine, valine, glycine, leucine, alanine, proline, phenylalanine
|

