![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define hypoxemia
|
decreased oxygen content in blood
|
|
|
Define hypoxia
|
Decreased level of oxygen in tissues
|
|
|
Define acidemia
|
Increased concentration of hydrogen ions in the blood
|
|
|
Define acidosis
|
Increased concentration of hydrogen ions in the tissue
|
|
|
Define asphyxia
|
Hypoxia with metabolic acidosis
|
|
|
What is fetal distress directly related to?
|
-Pre-existing status of the fetus
-Intensity and duration of stress -Ability of team to assess fetal condition accurately -Ability of team to react appropriately |
|
|
Why was fetal monitoring orginially introduced?
|
Original rationale for FHR monitoring was that it would serve as a screening test for asphyxia
Despite poor interobserver and intraobserver reliability, uncertain efficacy, and high false-positive rates, the technology continues to be utilized. |
|
|
When was the NICHD guidelines introduced and what was the purpose?
|
1997, National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Workshop
Purpose - to develop standardized and unambiguous definitions for FHR tracings Inability to determine outcomes when there is no standard definition of terms with fetal monitoring The prime focus of the workshop was for intrapartum patterns |
|
|
Describe the physiology of the placenta
|
-Placenta is a ‘semipermeable membrane’
-Can store nutrients and oxygen, which allows for some reserve -Oxygen is required to catabolize glucose the primary energy source -When oxygen is inadequate glycolytic metabolism is replaced at the pyruvic acid step with by-product production of lactic acid – accumulates over time and bicarbonate is consumed. -CO2 crosses placenta rapidly but lactic acid does not, therefore the decline in pH is progressive |
|
|
What is normal P02 in fetal oxygenation?
|
25-30mmHg
|
|
|
What is special about fetal hemoglobin?
|
Favorable dissociation curve provides for sufficient oxygen delivery
|
|
|
What happens to perfusion of the intervillous space during a contraction?
|
Perfusion of the intervillous space essentially ceases during contractions of normal intensity
|
|
|
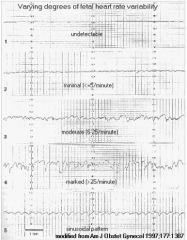
What is fetal heart rate variability related to? What are the different types of variability?
|
-Sympathetic and parasympathetic influences
-Short term/long term – absent, minimal, moderate, marked |
|
|
How is baseline FHR defined and what are the normal paremeters?
|
Baseline – average over 10 minutes, rounded to increments of 5 bpm. 110-160 = WNL
|
|
|
What are some causes of fetal tachycardia?
|
– hyperthermia; atropine, terbutaline; hypoxemia
|
|
|
What are some causes of fetal bradycardia?
|
Sleeping, analgesic agents – should resolve after about 20-30 minutes
|
|
|
What is the riteria for reactivity? What does it prove?
|
-2 accelerations of 15 beats per minute, each accel lasting 15 seconds.
-Presence virtually ensures the absence of fetal acidosis |
|
|
What do scalp stim and vibro acoustic stimulation prove if positive? When and how often would you do these two techniques of assessment?
|
Abcesnse of acidosis
Not sure look it up! See below picture & review: |
|
|
Define a later deceleration
|
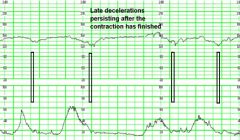
Late – gradual, with the onset of the Deceleration to its nadir taking at least 30 seconds and the nadir occurring after the peak of the associated contraction - sinister
|
|
|
Define an early deceleration
|

Early – gradual, but coincident with associated contraction – benign
|
|
|
Define an acceleration of the FHR
|
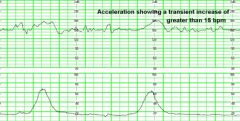
-Increase above baseline in a periodic fashion
-Increase 15 bpm x 15 secs for the near term and term baby -Increase 10 bpm x 10 secs for the <32 week fetus |
|
|
Define a variable deceleration, and state when it is concerning.
|
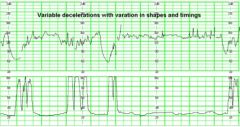
-Variable – response to cord compression
-Abrupt fall with abrupt rise usually related to contraction -Can be preceded and followed by brief accelerations (shoulders) – reassuring -Reflects respiratory acidosis, transient -Concerning when: *Persistent to less than 70 bpm lasting >60 seconds *Slow return to baseline |
|
|
Define what a sinusoidal pattern is.
|
Visually apparent, smooth, sine wave–like undulating pattern in FHR baseline with a cycle frequency of 3–5/min that persists for 20 minutes that persists for 20 minutes
|
|
|
Describe criteria for a category one FHR tracing
|
Cat I:
-Baseline rate: 110–160 beats per minute (bpm) -Baseline FHR variability: moderate -Late or variable decelerations: absent -Early decelerations: present or absent -Accelerations: present or absent |
|
|
Describe criteria for a category two FHR tracing
|
-Category II FHR tracings include all FHR tracings not categorized as Category I or Category III. Category II tracings may represent an appreciable fraction of those encountered in clinical care.
Examples of Category II FHR tracings include any of the following: -Baseline rate *Bradycardia not accompanied by absent baseline variability *Tachycardia -Baseline FHR variability *Minimal baseline variability *Absent baseline variability not accompanied by recurrent -Decelerations *Marked baseline variability -Accelerations *Absence of induced accelerations after fetal stimulation -Periodic or episodic decelerations *Recurrent variable decelerations accompanied by minimal or moderate baseline variability *Prolonged deceleration 2 minutes but 10 minutes *Recurrent late decelerations with moderate baseline variability *Variable decelerations with other characteristics, such as slow return to baseline, “overshoots,” or “shoulders” |
|
|
Describe criteria for a category three FHR tracing
|
Category III FHR tracings include either:
-Absent baseline FHR variability and any of the following: *Recurrent late decelerations *Recurrent variable decelerations *Bradycardia *Sinusoidal pattern |
|
|
How is uterine contractions evaluated when looking at a strip, and what is considered a normal active pattern, and what is considered not normal?
|
-Quantified as the number of contractions present in a 10-minute window, averaged over 30 minutes.
-Terminology *Normal: 5 contractions in 10 minutes, averaged over a 30-minute window *Tachysystole: 5 contractions in 10 minutes, averaged over a 30-minute window |
|
|
Define tachysystole in relation to contractions and what are charting aspects and prevention measures important to know when encountering this pattern?
|
-Tachysystole: 5 contractions in 10 minutes, averaged over a 30-minute window
-Tachysystole should always be qualified as to the presence or absence of associated FHR decelerations. -The term tachysystole applies to both spontaneous or stimulated labor. -The clinical response to tachysystole may differ depending on whether contractions are spontaneous or stimulated. -The terms hyperstimulation and hypercontractility are not defined and should be abandoned Interventions: *Maternal positioning *Tachysystole – oxytocin with rising resting tone *Initiate tocolysis *Increase IV fluids *Initiate oxygen therapy, 10-12 L preferably with rebreather mask *Improper coaching *Possibly amnioinfusion? |
|
|
List fetal heart rate patterns associated with adverse fetal outcomes
|
-Minimal/absent variability for an hour or more as a single finding without known cause
-Recurrent late decelerations or repetitive moderate to severe variables and minimal or absent variability -Persistent tachycardia or bradycardia and minimal/absent variability -Persistent or progressive bradycardia below 80 beats per minute |
|
|
List common terminology when describing FHR patterns and their definitions: recurrent pattern, periodic changes, episodic changes prolonged deceleration, sinusoidal pattern
|
-Reassuring/Non-reassuring
-Recurrent pattern – with >50% in any 20 minute window of time -Periodic changes (w/ctx), episodic (w/out ctx) -Prolonged deceleration: abrupt decrease to levels below baseline that lasts >2 min to <10 min -Sinusoidal pattern – smooth, undulating pattern, lasting at least 10 minutes |
|
|
List basic steps in evaluation and management of a FHR pattern
|
-Determine etiology
-Attempt to correct through measures aimed at improving fetal oxygenation and placental perfusion -Consult with team -Scalp pH or SaO2?? -Refer/transfer |
|
|
List the recommended documentation intervals according to AWHONN, ACOG, SOGC, & RCOG
|

|
|
|
What are the ACNM recommendations when doing intermittent FHR auscultation?
|
-Determine baseline by listening between contractions, without fetal movement
-Subsequently count the FHR after UC for 30-60 seconds every 15-30 minutes in active labor and every 5 minutes in 2nd stage -Note accelerations and decelerations using multiple-count strategy (count for 5-15 seconds during the total time segment) |

