![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR) |
Infant weight below 10th percentile |
|
|
Major physiologic factor factor of IUGR |
Decrease in uterine plasma volume |
|
|
Maternal Conditions that affect plasma volume IUGR |
Poor nutritional status, smoking, multiple gestation Drug or alcohol abuse, TORCH infections, Severe anemia, Diabetes, Chronic renal disease, RH sensitization, Severe chronic asthma, Under 17 or over 35 Years of age, heart disease, high altitude |
|
|
Placental conditions IUGR |
Placental infarcts & hemangiomas, small placenta, Single umbilical artery, Abruptio placenta, Placental insufficiency. |
|
|
Fetal Conditions IUGR |
Genetic or chromosomal defects, intrauterine infection, Microceohaly. |
|
|
Growth restricted infants are born with diminished |
Stores of Fat and glycogen, and are likely to be hypoglycemic. |
|
|
Clinical signs of IUGR |
Uterus measuring small for dates and hx of maternal condition associated with IUGR. |
|
|
Symmetric IUGR |
Growth restriction affecting entire fetus. Etiology often genetic or due to maternal infection. Onset may be earlier in gestation. |
|
|
Sonographic findings of Symmetric IUGR |
Oligohydraminos, mature placenta earlier than expected, low BPP score, measure more than 2 weeks below expected GA. |
|
|
Asymmetric IUGR |
Occurs in the last 8-10 weeks of pregnancy. Hemodynamic patters in the fetus attempt to protect the brain, which receives the most nutrient rich blood first. There is symmetry between head size and abdominal size. |
|
|
Sonographic findings Asymmetric IUGR |
Asymmetry of head to body ratio (HC/AC)>2SD, AC measuring>2 weeks behind HC, oligohydraminos, mature placenta earlier than expected, many complex formulas exist for sonographically diagnosing. |
|
|
Doppler in IUGR |
Low predictive value, additional prenatal monitoring such as non-stress testing or BPP. Measurements of umbilical artery resistance are most widely accepted. |
|
|
Umbilical Artery in IUGR |
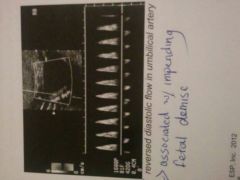
RI<.08, Systolic/diastolic ratio > 3.0 is abnormal after 30 weeks, ratios are higher if measured closer to fetal cord insertion. Absent or reversed diastolic flow is associated with impending fetal Denise. |
|
|
Erythroblastisis Fetalis |
Destruction of fetal RBCs by antibodies with subsequent fetal or neonatal complications. |
|
|
Causes of Erythroblastosis Fetalis |
Rh incompatibility, ABO incompatibility, isoimmune disease, other minor blood group incompatibly. |
|
|
Clinical manifestations of EF |
Congestive heart failure, fetal death, hydrops fetal is. |
|
|
Hydrops Fetalis |
Excessive accumulation of fluid in feral tissues and body cavities. Typically, diffuse interstitial edema, pleural and pericardial effusions and as cites. Two types immune and non immune. |
|
|
Immune Hydrops |
Due to Rh incompatibility aka Rh iso immunization. Occurs with Rh negative mother and Rh positive father (Rh positive fetus). Maternal antibodies recognize Rh antigens on fetal RBCs as foreign, and attack and destroy them. Erythroblastosis fetalis and fetal anemia results which results in hydrops. |
|
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) Doppler can help determine |
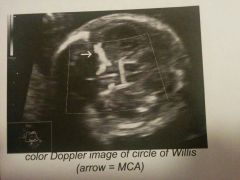
Likelihood of fetal anemia. MCA is examined close to its origin from internal carotid artery. |
|
|
MCA Doppler waveform in Rh-isoimumunized fetus |
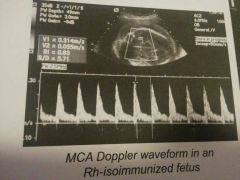
The angle of the ultrasound beam and direction of blood flow should be zero degrees. Risk of anemia is highest in fetuses with a pre-transfusion peak systolic velocity 1.5 times the median or higher. |
|
|
Non-Immune hydrops |
Hydrops due to any cause other than Rh sensitization. |
|
|
Causes of Non-Immune hydrops |
Cardiac anomalies/arrhythmia, infection, fifth disease), chromosome abnormalities, congenital hematologic disorders, abdominal or pulmonary masses leading to venous obstruction, twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome. |
|
|
Sonographic findings in hydrops fetalis |
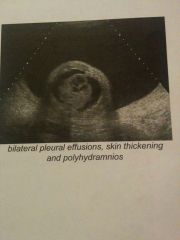
Pericardial effusion (earliest sign), ascites, fetal skin thickening (anasarca) >5mm, placental thickening > 5cm AP, pleural effusion, hepatosplenomegaly, polyhydraminos, enlarged umbilical vein (>1cm) |
|
|
Fetal Demise Sonographic appearance |
Absent cardiac activity, exaggerated fetal position, Roberts sign, Spaulding's sign, Duel's sign/halo sign. |
|
|
Robert's sign |
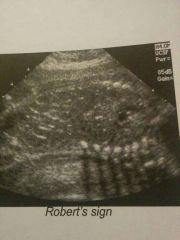
Echogenic foci (gas) in pulmonary vessels or abdomen- delayed finding(1 week after demise) |
|
|
Spaulding's sign |
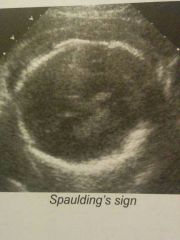
Overlapping skull bones |
|
|
Deuel's Sign/halo |
Halo effect seen radio graphically secondary to subcutaneous scalp edema in fetal demise. |

