![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fertilization
|
Successful fusion of the male and female gamete cells.
Normally occurs in the ampullary region of uterine tube, near the ovaries |
|
|
Capacitation
|
Necessary removal of glycoproteins surrounding the sperm head before fertilization.
|
|
|
Corona radiata
|
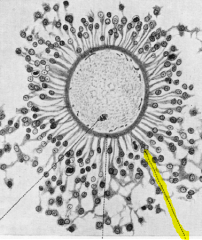
Also called the cumulus oophorus
Outer layer of the ovum |
|
|
Sperm penetration
|
Controlled by acrosomal enzymes released by the tip of the spermatozoa
|
|
|
Sperm fusion
|
Sperm head and tail enter the ovum, allowing the second meiotic division to complete.
The extra chromosomal information is expelled in the second polar body. |
|
|
Mechanisms to block polyspermy
|
Fast block - change in membrane potential that prevents further sperm fusion events
Slow block - at the time of sperm entry, the ovum undergoes an event called the cortical reaction. |
|
|
Cortical reaction
|
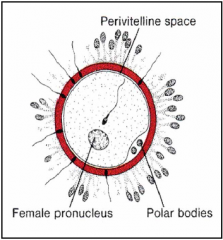
This forms a space between the egg membrane and the zona pellucida, called the Perivitelline space, where digestive enzymes are released.
Prevents additional sperm from entering. |
|
|
Pro-nucleus
|
The decondensed head of the sperm formed after tail degeneration.
The ovum nuclei also called pro-nucleus. Pro-nuclei fuse to form the diploid nucleus. |
|
|
Zygote
|
The diploid cell formed after fertilization and the joining the the two haploid pro-nuclei.
|
|
|
Zygotic cell division
|
Divides every 16-24 hours.
Early divisions happen without cell growth -> more, smaller cells Zygotic cells will become both the embryo and extraembryotic tissues. |
|
|
Morula
|
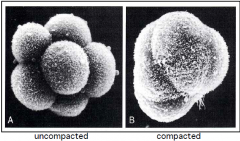
"Mulberry" stage
The 8-16 cell stage after fertilization Initially loosely associated (can split into twins), but then compact |
|
|
Blastocyst
|
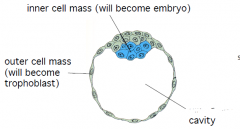
Between 32 and 128 cell stage.
Cells organize around a blastocele (cavity) |
|
|
Implantation
|
As the embryo continues to develop, it will move along the uterine tube towards the uterus.
At day 5-6, in the blastocyst stage, the embryo will implant. |
|
|
Trophoblast
|
Formed from the outer layer of cells in blastocyst
Become 2 forms: Cytotrophoblast, which are mononucleated, and Synctiotrophoblasts |
|
|
Syncytiotrophoblast
|
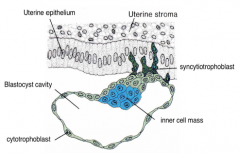
Formed from trophoblast cells near the inner cell mass.
Multinucleated, highly invasive cells. The retroviral-derived protein, syncytin, is essential for formation. Binds with L-selectin to begin implantation. Eventually these cells surround the entire embryo after implantation. |

