![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Vitamin D, da hell is dat?
|
it is a fat soluble vitamin lol
Non essential (digestion); body synthesizes it |
|
|
Where are 3 places where Vitamin D comes from?
|
1) Body - vitamin D1, calcitrol
2) Plant sources - vitamin D2, ergocalciferol 3) Animal source - vitamin D3, cholecalciferol |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin D?
|
1) Enhances absorption of Ca and P from digestive to CV system
2) Reabsorbs minerals from bone when diet is insufficient |
|
|
What occurs with vitamin D deficiency?
|
Overt signs are relatively rare
Insufficiency is quite common |
|
|
How does Vitamin D deficiency affect bones in children versus adults?
|
RICKETS affects children, bones fail to calcify normally, bones bend.
OSTEOMALACIA affects adults, basically poor mineralization of bones (soft, flexible, brittle, deformed) |
|
|
Vitamin D toxicity is ________________. What are the associated symptoms?
|
Most likely of vitamins to have toxic effects
Raises blood Ca concentrations Forms stones in soft tissues May harden blood vessels |
|
|
What are some sources of Vitamin D?
|
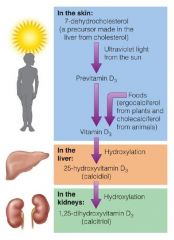
Few food resources- Oily fish, egg yolk, fortified milk
Sun exposure - no risk of toxicity, latitude, season, time of day |
|
|
Vitamin K is part of what family of compounds?
|
Quinones
|
|
|
What are K vitamins types (quinones)?
|
K1 - phylloquinone
K2 - menquinone K3 - menadione (considered unsafe), Synkayvite, Hykinone |
|
|
All quinones are stored in the ______ in small amounts, and are fat soluble except for _____ and ____.
|
liver; Synkayvite; Hykinone
|
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin K?
|
1) Blood clotting (carboxylates preprothormbin)
2) Bone health (carboxylated osterocalcin; becomes saturated with carboxyl groups) |
|
|
What is osteocalcin?
|
Osteocalcin is a protein in bone and dentin; contributes to mineralization, secreted by osteoblasts
|
|
|
What does osteocalcin act on?
|
1) Pancreatic beta cells; stimulates proliferation
2) Adipocytes; synthesizes and secretes ADIPONECTIN (hormone that increases body's sensitivity to insulin) |
|
|
What are sources of Vitamin K?
|
1) Absorbed with fat in small intestine (chylomicrons)
2) Storage = 10% phylloquinones, 90% menaquinones in liver 3) Raw, green leafy vegetables (turnip greens, spinach, cauliflower, cabbage, animal products very limited with Vitamin K) |
|
|
Vitamin K deficiency leads to:
|
Fat malabsorption condition (celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, colitis)
Prolonged use of antibiotics Megadoses of vitamin A and E |
|
|
What do newborns have to do with vitamin K?
|
Newborns receive vitamin K injections at birth
Body only needs small amounts, deficiencies are rare |
|
|
Toxicity associated with Vitamin K is
|
Rare! :D
|
|
|
Where is Vitamin K stored? What about it's excretion process?
|
In liver; excreted more readily than other fat-soluble vitamins
|
|
|
Vitamin C and E are ______ and deal with
|
Antioxidants; lipid peroxidation; production of unstable lipid molecules; major mechanisms of atherosclerosis
|
|
|
Where is Vitamin E stored in the body?
|
90% in adipose tissue, remaining is in cell membranes
|
|
|
In what forms does Vitamin E exist in?
|
Exists as 2 sets of 4 different compounds (Each)
|
|
|
What is the biologically active form of Vitamin E?
|
Alpha-tocopherol
|
|
|
What is the function of Vitamin E?
|
Anti-oxidant; deals with oxidative stress (excessive/beyond body's handling capacity; premature aging, cancer, atherosclerosis, cataracts)
|
|
|
What are Vitamin E recommendations discussed? (Food Sources)
|
Sunflower seeds (best source) - 1/4 cup = 100% RDA
Almonds, soybean & safflower oils, hazelnuts, fresh strawberries |
|
|
The food storage and preparation of Vitamin E includes
|
Refining wheat - removal of vitamin E - rich germ layer --> sell as supplement
Roasting almonds destroys 80% of vitamin E Ultraviolet light can screw up oils -- store oil in dark, cool place |
|
|
Vitamin A is 'CxHxOx'? (x = ?)
|
C = 20
H = 30 O = 1 |
|
|
What are the three active forms of Vitamin A?
|
1) Retinol - reproduction and bone health
2) Retinal - night and color vision 3) Retinoic Acid - cell growth and differentiation |
|
|
Where and how is Vitamin A stored?
|
90% in liver; stored as retinol linked to palmitic acid, liver maintains a reserve of vitamin A = if exceeded = toxic level
|
|
|
Function 1) What does vitamin A have to do with vision?
|
Retinal combines with opsin (receptor in retina) to form rhodopsin which increases sensitivity to light
|
|
|
Function 2: What does Vitamin A have to do with cell differentiation?
|
Retinoic acid induces gene transcription; involved in protein synthesis in stem cells
|
|
|
Function 3: Vitamin A and immune function?
|
Vitamin A maintains production of T-lymphocytes and induces IgG response in children after immunization
|
|
|
Function 4: Vitamin A and reproduction?
|
Involved in final stages of cell differentiation
|
|
|
Function 5: Vitamin A and bone development?
|
too little or too much (with supplementation) actives osteoclasts
|
|
|
What are Vitamin A food sources?
|
Chicken and beef liver
Cooked carrots Whole milk products (cheese and butter) Dark green or orange-yellow veggies |
|
|
Vitamin A toxicity is
|
Rare ... but occurs with large supplementation of fish oils. Children are more vulnerable
|
|
|
What are the symptoms associated with Vitamin A toxicity?
|
Fatigue, vomiting, skin disorders, vision problems, liver injury, birth defects
|

