![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is SEC? |
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION: The legal authority to establish GAAP |
|
|
|
What determines GAAP since 1934? |
SEC (since 1934), CAP (1938-1959), APB (1959-1973), FASB (since 1973) |
4 |
|
|
What is FASB Accounting Standards Codification? |
The single source of authoritative GAAP since 2009 |
|
|
|
Are Accounting Standard Updates authoritative literature of the Code? |
No. They only provide background info, update the Code and describe the basis for conclusions on changes in the Codes. |
No |
|
|
Does SFAC mean GAAP? What does it do? |
They are not GAAP but they provide a basis for financial accounting concepts for business and non business enterprises. |
Basic reasoning |
|
|
What are the QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS of useful financial info? |
SFAC No 8. Chap 3. 1. Relevance (predictable value, confirming value, materiality) 2. Faithful Representation (Completeness - primary FS and notes, neutrality, freedom from error) |
"Passing confirms money" and "Complete neutral is free from error" |
|
|
How to enhance qualitative characteristics of of useful financial information? |
Comparability, verifiability, timeliness, understandability, cost constraint (benefits must be bigger than cost to obtain) |
Compare and verify in time to understand |
|
|
What is the process of issuing a new IFRS topic? |
1. (discussion paper) to get comments 2. Get approval from at least 9 members of IASB 3. Exposure Draft is issued for public comments. 4. Redeliberate on the issue after studying comments. 5. Draft the IFRS. |
At least 9 |
|
|
What are assumptions of financial statement preparation and presentation? |
Going concern and Accrual accounting |
2 |
|
|
Fundamental assumptions of GAAP's and IABS's Conceptual |
GAAP: entity, going concern, monetary unit, periodicity, historical cost, revenue recognitions, matching principal, accrual accounting, dull disclosure, conservatism principal IABS: accrual basis, going concern. |
|
|
|
Historical cost concept? |
Based on cost not current market value (GAAP) |
|
|
|
Conservatism practice |
Recognize revenue/gains when earning process is complete Recognize expenses/losses immediately Eg: used in recording of gain and loss contingencies |
Loss immediately, gain complete. |
|
|
Operating procedure for issuing FASB accounting standard update. |
1. Exposure drafts for public comments. 2. A majority vote of Board members is required 3. Review altenatives, prepare an accounting standard update. 4. Major vote by Board required for amendment. |
|
|
|
Replacement cost concept |
Is acquisition cost. The amount of cash or equivalent paid to acquire or replace an asset currently. |
|
|
|
Differences between managerial and financial accounting |
1. F is for external. M is for internal. F needs to follow GAAP, M doesn't. 2. M has future focus, F has past focus. 3. F is more precise. |
|
|
|
FABS Five elements of present value (economic value) measurement |
Estimate of cashflow (CF), expectations about timing variations of future cashflow (t), time value of money (I), the price of bearing risk (credit risk), others (liquititys, market imperfection) |
CF, I, N, t - UVOTE |
|
|
Matching principal |
All expenses incurred to generate a specific amount of revenue in a period are matched against the revenue. |
|
|
|
Accrual accounting |
Record rev and/or exp w/o exchange of cash |
|
|
|
Recognition vs Realization |
Realization: process of converting non cash resources and rights into money. (Rev and exp) Recognition: process of recording an item in the financial statements of an entity.
|
|
|
|
Measurement attributes for A & L |
Historical cost (PP&E) Current cost (inventory) Net realizable value (A/R) Current market value (Market securities) - for current a&l Present value future cash flows (long term debt) |
|
|
|
Loss from discontinued operation |
Net of tax. Includes impairment loss, gain/loss from actual operations, gain/loss on disposal in the period they occur. |
|
|
|
Impairment loss |
(FMV - Cost to sale) - Carrying value Recorded in the year of held for sale decision. If the estimation is different, make adjustment in the yr of realizing.
|
|
|
|
Time to calculate loss/gain from operation of held for sale unit? |
First yr is counted for 12 months even though the time period is not 1 yr full. Ex: even tho decision was made in April, from Jan to March is still counted as discontinued. |
|
|
|
Exit and disposal cost? |
Involuntary employee termination benefits, contract termination cost, others ( facility consolidation, employee allocation) |
|
|
|
Exit or disposal liability is recognized only when? How? |
ALL are met: 1. An obligation event has occurred 2. Obligation to transfer asset or provide service in the future 3. The entity has little or not discretion to avoid the future transfer of assets or services. When they occur. Measured at fair value. Disclosed in the notes. |
|
|
|
Advertising expense |
Selling expense. Freight out is selling expense. Freight in is cost of sales. |
|
|
|
Extraordinary items |
Both unusual and infrequent. Not included in continuing operation. Reported next of tax after continuing and discontinuing section. Either unusual or infrequent not both is reported separately as a component of income from continuing operation. Non operating.
IFRS doesn't allow reporting extraordinary. Extraordinary items r included in continuing operation.
|
|
|
|
Change of accounting principals, estimate, entity |
Reported in the adjustments in the beginning of retained earning statement.
|
|
|
|
Changes in accounting estimate (not error) |
Do not restate prior year -> prospectively not retrospectively. Implement in current period and continue in future period. |
|
|
|
Changes in accounting principles |
Adjust the beginning balance of RE in the earliest period balance for cumulative effects. Prior periods should be restated. If impractical to estimate, apply in the yr of change (change in inventory cost method) - prospectively If impossible to determine whether it is change in estimate or principal, chose change in estimate - prospectively Changes in depreciation method is considered change in estimate - prospectively. For IRFS, adjustment has to be made the beginning of prior yr RE. |
|
|
|
Change in accounting entity requires? |
Restate all previous statements. Full disclosure of reason of changes. IFRS does not have change in entity. |
|
|
|
Error correction. |
Restate previous periods. Errors, mistakes, change from non GAAP to GAAP. Reported as prior period adjustment to RE. |
|
|
|
Comprehensive income |
Represents all the Stockholder's equity that come from nonowner sources
=net income (continuing + discontinued+ extraordinary) + other comprehensive income.
Other comprehensive income (accumulatedly reported in equity section of BS): 1. Pension adjustments 2. Unrealized gain loss on available for sale securities and debt securities. 3. Foreign currency item 4. Effective portion of cashflow hedges 5. Revaluation surplus Includes all change of equity EXCEPT those from and to owners, investors. CAN be reported together or seperately. Calculated accumulatedly like RE. NOT REPORTED ON PER SHARE BASIS. Reported either net of tax or before tax. Reported in BOTH interim FS and year end fs. |
|
|
|
Disclosures requirement of risks and uncertainties? |
1. Description of the entity's major products or services and its principal market. 2. Use of estimates in the preparation of FS. 3. Disclose of effect of change if it is possible if an estimate will change in near term and the effect is MATERIAL. 4. Disclose concentrations if it exists in FS date, it makes the entity VULNERABLE to risk of a near term several impact, it is possible that the events that would cause severe impact will cover in near term. |
|
|
|
Interim financial report |
NOT required in both GAAP and IFRS. General rule: 1. all calculated by quarter. 2. Use the principals in the most recent annual report. 3. Report costs and expense in the period affected. Report revenues in the period earn and realized or realizable. 4. Report total comprehensive income in condensed FS to shareholders. 5. Estimate tax rate with the best info available at that time (use effective ANNUAL rate in the current quarter to the entire yr) . Multiply the year to date income by the rate and subtract the result from previous quarter -> income tax expense 6. Costs that benefit multiple period should be allocated equally to all the periods. TIMLINESS is emphasized over reliability. |
|
|
|
Disclosure of FS and Note to FS |
Significant accounting policies: Both require to include all significant policies in the INTERGRAL PART of FS. Not required to follow GAAP. Includes: 1. Measurement bases. 2. Accounting principles and methods 3. Criteria 4. Policies (basis of consolidation - which treated as cash equivalents, depreciation method, amortization of intangibles, inventory pricing, accounting for recognitions of profit on long term construction contract, recognition of revenue from franchising and leasing operations) 5. Pricing |
|
|
|
Disclose FS and notes to? |
Related parties ( affiliates, owners of more than 10% of voting interest and their immediate family members - only in GAAP, key management's, loan to officers...) DISCLOSE THE MOST RATHER THAN THR LEAST. |
|
|
|
Interim inventory evaluation requirements |
Gross profit method or retail inventory method Lower of cost of market method Only recognize permanent inventory losses from market declines not temporary (to be reverse at the end of the period, If not record loss at that point of realizing it is not reversed) |
|
|
|
Segment reporting |
To help users of FS (all public enterprises only) 1. Operating segments (annual and interim) 2. Products and services 3. Geographic areas 4. Major customers.
Use SAME acct principals w the main FS. Intercompany transactions are not eliminated for reporting. -> sales to other segments determine operating income as well as sales to unaffiliated customers.
|
|
|
|
What are objective of General Purpose Financial Reporting? |
SFAC No 8. Chap 1: 1. Primary users are external users like investors, lenders or other creditors. 2. The financial information provided needs to meet the informative needs in accrual basis of accounting: the resources and the entity, claims against, the management abilities to use the resources. To access the future net cash flow. |
Disclose entity's performance |
|
|
Basis of asset in discontinued operation |
Net realizable value bcoz it is discontinued. If the asset is still in operation basis is historical cost. |
|
|
|
Cash basis vs actual basis |
Cash basis reporting is NOT an accounting principle under GAAP. Accrual basis reporting is. |
|
|
|
Reportable operating segments |
Segment is reported to CEO and Any of the 3 1. Basis of determining segment = 10% of the bigger of the absolute of TOTAL profit or TOTAL loss Segments that have the absolute of net profit/loss bigger or equal the basis are reporting segments. 2. Segments with assets => 10% of the total asset of all operating should be reported in FS. NOT the same for Lblt. 3. Rev greater than or equal 10% of TOTAL revenue of all segments. Including rev from unaffiliated and intersegment sales.
Unaffiliated sales and intersegment sales need to be disclosed seperately. |
|
|
|
Single step income statement |
Rev is total rev of all sales of goods, services and rental. Purchase discount is included in COGS. |
|
|
|
When company A buy company B |
A get the net value of assets, inventory, AR and has to pay the dealer price, mortgage, and AP. |
|
|
|
Assets in held for sale/ disposing unit |
Is valued at the lower of its book value or net realizable value ( FMV - cost to sell) Is still current asset until sold Is no longer depreciated. |
|
|
|
Cost of fixed asset for operations |
Allocated over the year full life even though bought at once. |
|
|
|
Development-stage enterprises |
Is either: primary operations have not commenced OR no significant revenue or loss.
Disclosure: 1. Same FS according to GAAP as other enterprises. 2. In balance sheet, cumulative net losses as "deficit accumulated during development stage" 3. In income statement and statement of CF, present both current amount for each period and cumulative amount from the company's inception. 4. In statement of shareholders equity, show # of share, dates, amount, if non cash consideration involved, a description of nature of consideration and basis for valuation.
|
|
|
|
First financial statements after transition to IFRS |
At least 3 balance sheets (end and beginning of prior period, end of current period) 2 income statement, 2 statement of CF, 2 statements of change in equity. Date of transaction is date of opening BS aka the beginning of prior period.
|
|
|
|
Debit and credit cheer sheet |
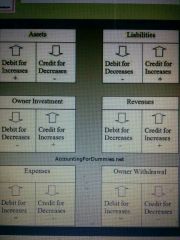
|
|

