![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How far can you go in a bronch?
|
5 generations
|
|
|
What are lasers used for in a bronch?
|
to get rid of tumors
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of hemoptysis during a bronch?
|
chronic bronchitis
|
|
|
Why do you do a bronch with interstitial lung disease?
|
to get test samples to diagnose
|
|
|
What causes hypoxemia during a bronch?
|
The longer the procedure
|
|
|
What is 3ml 4% xylocaine used for in a bronch?
|
the nostril and above the vocal chords
|
|
|
What is 3ml 2% xylocaine used for in a bronch?
|
the nostril
|
|
|
What is 6ml 2% xylocaine used for in a bronch?
|
below the vocal chords
|
|
|
What is 15ml 0.9% NaCl used for in a bronch?
|
irrigation
|
|
|
What is a CVP line used for?
|
Right heart values, give medication,
|
|
|
Which type of pleural effusion has high protein content and is a result of disease processes such as pneumonia or TB when the pleural space is damaged?
|
exudate
|
|
|
Which type of pleural effusion is low protein and is the result of when the pleural space is undamaged, such as CHF? Common but small effusions
|
transudate
|
|
|
What occurs when you expand a pneumothorax too fast?
|
reexpansion pulmonary edema
|
|
|
ATP comes from where?
|
food
|
|
|
What is necessary for ATP to be reduced?
|
O2
|
|
|
What is the RQ
|
Ratio of O2 uptake/min : CO2 produced/min
|
|
|
What is BEE
|
Basal energy expenditure
|
|
|
What do you use to calculated the BEE?
|
Harrison-Benedict calculation
|
|
|
What are the requirements to calculate the BEE
|
absolute rest with no movement
|
|
|
What do we store in large quantities to meet our energy demands?
|
Glycogen
|
|
|
What are signs of starvation of the respiratory system?
|
Decreased surfactant production, emphysema like changes, gluconeogenesis (eats protein), low PFT's
|
|
|
List 4 PFT values that would be low if the respiratory system was being starved
|
FVC, FEV1, and DlCO
|
|
|
What is the RQ for fats?
|
0.7
|
|
|
What is the RQ for carbs?
|
1.0
|
|
|
What is the RQ for protein?
|
0.85
|
|
|
What are the detriments of a high carb diet?
|
retain CO2
|
|
|
What are the benefits of a high carb diet?
|
Increased endurance, performance work with less O2 demands
|
|
|
List three different ways to deliver nutrition
|
TPN, NG, orally
|
|
|
How long before starvation starts to occur with TPN
|
12-16 hours
|
|
|
What GCS score indicates intubation
|
<9
|
|
|
What GCS indicates non ICU
|
12-15
|
|
|
What GCS indicates moderate coma
|
9-12
|
|
|
What nerves stimulate gag reflex
|
vagus (9) and glossopharyngeal (10)
|
|
|
myasthenia gravis has what symptoms
|
Abnormal deep tendon reflex and impaired nerve impulse transmission
|
|
|
What does the Babinski sign indicate in adults?
|
Lesion of UMN or brain disease
|
|
|
At what age should the babinski sign disappear
|
12-18 months
|
|
|
What does PEERL stand for?
|
Pupils are equal round and reactive to light and accomodation
|
|
|
Which posture is thumb tucked under fists, rotation inward?
|
Decorticate
|
|
|
What posture is UMN lesion above the red nucleus?
|
Decorticate
|
|
|
What posture is arms rotated out
|
decerebrate
|
|
|
What posture is lesions below the red nucleus
|
decerebrate
|
|
|
If the ICP is high, what decreases?
|
CPP
|
|
|
What is the formula for PVR
|
(Mean PAP - PWP)/ CO x 80
|
|
|
What is the formula for SVR
|
(MAP-CVP)/CO x80
|
|

Where is the catheter located and what are the values?
|

Right atrium and 2-6mm HG
|
|
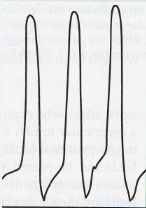
Where is the pulmonary artery catheter located and what are the values?
|
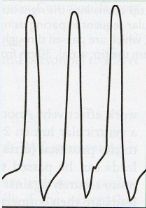
right ventricle 20-30/0-5
|
|

Where is this catheter located and what are its values?
|

pulmonary artery, normal pressures 20-30/6-15mmhg
Mean 10-20 mmhg |
|

What is the location of this catheter and its values?
|

Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, 4-12mmHg
|

