![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two modes of modern-day HPLC? |
1. Normal phase 2. Reversed phase |
|
|
What is the most common form of HPLC? |
Reversed-phase |
|
|
What are the phases in reversed-phase HPLC? |
1. Polar mobile phase 2. Hydrophobic stationary phase |
|
|
Name a common hydrophobic stationary phase |
Octadecylsilyl (ODS) |
|
|
What are the phases in normal phase HPLC? |
1. Non-polar mobile phase 2. Polar stationary phase |
|
|
In ion-exchance chromatography, what is the basis for separation? |
Separation based upon ion-exchanging with counter-ions and ionic interaction with bonde ionic group |
|
|
In size-exclusion chromatography, what is the basis for separation? |
Separation based upon analyte's molecular size and sieving action of the column packing |
|
|
Name two common mobile phases for NPC |
1. Hexane 2. Dichloromethane |
|
|
Name some common stationary phases in NPC |
1. Silica 2. Alumina 3. Amino- 4. Cyano- 5. Phenyl bonded phases |
|
|
What type of analytes is NPC useful for? |
Polar analytes |
|
|
What type of analytes is RPC useful for? |
Water-insoluble non-polar analytes |
|
|
Name two common polar mobile phases |
1. Methanol in water 2. Acetonitrile in water |
|
|
In RPC, do polar or non-polar analytes elute first? |
Polar analytes elute first |
|
|
How can ionic compounds be separated in RPC? |
Ion-pairing reagents or ion suppression (Heptanesulphonic acid) |
|
|
What is IEC used to separate? |
Ionic or ionizable analytes |
|
|
What is the stationary phase for IEC? |
Anionic (sulphonate) or cationic (quaternary ammonium) groups on polymeric materials or silica. |
|
|
What does the mobile phase in IEC consist of? |
Buffered solutions of different pH and ionic strength |
|
|
What are the three primary characteristics of HPLC mobile phases? |
1. Desirable physical properties 2. Strength 3. Selectivity |
|
|
Name eight desirable physical properties of a HPLC mobile phase |
1. High purity 2. Low cost 3. UV transparency 4. Non-corrosive 5. Low viscosity 6. Low toxicity 7. Non-flammable 8. Sample solubility |
|
|
What is the name of the scale used to characterise the strength of solvents? |
Hildebrand's scale |
|
|
How should solvents be treated before use? |
Filtered and degassed |
|
|
Name five common mobile phase modifiers and their use |
1. Buffers - stabilise pH of mobile phase under RP 2. Acidifiers - Suppress ionisation of acidic analytes under RP 3. Ionic strength - Control elution of ionic analyte under RP 4. Ion-pair reagents - Separation of ionic compounds under RP 5. Amine modifiers - Reduce tailing of basic analytes under RP |
|
|
Name three examples of mobile phase buffers |
1. Phosphate 2. Acetate 3. Citrate |
|
|
Name two examples of mobile phase acidifiers |
1. Phosphoric acid 2. Acetic acid |
|
|
What is commonly used to control the ionic strength of a solvent? |
NaCl |
|
|
What is a commonly used ion-pair reagent? |
Heptanesulphonate |
|
|
What is a common amine modifier? |
Triethylamine |
|
|
What is peak tailing, and what type of chromatography is it mainly a problem in? |
Assymetry of peaks - mainly a problem when separating amines using RP |
|
|
How is peak tailing caused? |
Interaction of polar amines with residual silanols on the RP column |
|
|
How do you work out the value of peak tailing on a chromatogram? |
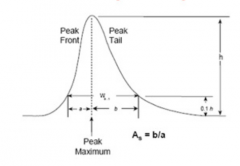
|
|
|
At what value does peak tailing become unacceptable? |
>2.0 |
|
|
Name three methods of overcoming peak tailing |
1. Lower pH (<3) 2. Add amine modifier 3. Endcapping |
|
|
What is an issue that can arise when lowering pH to overcome peak tailing? |
Can result in stripping of silica column |
|
|
How does adding an amine modifier help overcome peak tailing? What is one drawback? |
Competes with the analyte for the silnaols, therefore reducing analyte-silanol interactions. Drawback - stinks of fish. |
|
|
What is endcapping, and how is it accomplished? |
Endcapping is the reduction of residual silanols by 'capping' them to make them substantially less polar. Accomplished by adding Trimethylchlorsilane / Hexamethyldisilazane. |
|
|
How effective is endcapping at reducing silanols? |
Reduces by 50% |

