![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the facial nerve?
|
CN VII
It is said to be the nerve to the muscles of facial expression (mimetic muscles), but has other functions as well. Passes through the facial canal. |
|
|
What are the components of the facial nerve?
|
-Special visceral efferent (SVE) motor fibers
-General visceral efferent (GVE) motor fibers -Special visceral afferent (SVA) fibers -General somatic afferent (GSA) |
|
|
What are the special visceral efferent (SVE) motor fibers?
|
VOLUNTARY CONTROL (has nothing to do with ANS). Motor fibers that innervate the muscles of facial expression. Their nerve cell bodies are in the motor nucleus of the facial nerve.
(Think of the oral cavity as a hollow organ associated with the digestive system) |
|
|
What are the visceral efferent (GVE) motor fibers?
|
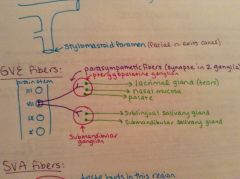
Provide parasympathetic innervation to the lacrimal gland, mucosa of the palate and nasal cavities, and the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands.
|
|
|
Where do the preganglionic nerve fibers of the GVE motor fibers synapse?
|
In two different parasympathetic ganglia:
-pterygopalatine ganglion -submandibular ganglion |
|
|
Where do the postganglionic nerve fibers from the pterygopalatine ganglion travel to?
|
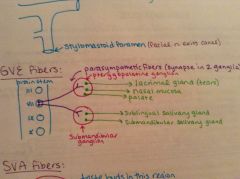
-lacrimal glands
-nasal mucosa -palate |
|
|
Where do the postganglionic nerve fibers from the submandibular ganglion travel to?
|
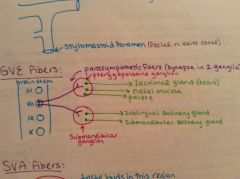
-sublingual salivary gland
-submandibular salivary gland |
|
|
What are the special visceral afferent (SVA) fibers?
|

Fibers for taste (from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue) are present in the chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve.
(Think special senses; hearing, taste, smell) |
|
|
What are the general somatic afferent (GSA) fibers?
|
Bring cutaneous innervation from a portion of the external auditory meatus and auricle. Proprioceptive fibers also provide for "position sense" for the facial muscles. Feel pain, temperature, touch, and pressure.
|
|
|
Where is the motor nucleus of the facial nerve?
|
The pons.
|
|
|
How does the facial nerve exit the cranial cavity?
|
Via the internal acoustic meatus, where it makes a sharp turn and enters the facial canal.
|
|
|
What are the branches of the facial nerve within the facial canal?
|
-the greater petrosal nerve
-nerve to the stapedius muscle -chorda tympani nerve |
|
|
Describe the chorda tympani nerve?
|

Passes through the middle ear, where it joins with the lingual nerve (CN V3). Distributed to the submandibular and sublingual glands. Also contains SVA fibers which bring taste from the anterior 2/3s of the tongue.
|
|
|
What are the branches of the facial nerve external to the skull?
|
-sends a sensory branch (GSA) to the external auditory meatus and the auricle
-terminal branches of the facial nerve supplying the muscles of facial expression |
|
|
What are the terminal branches of the facial nerve supplying the muscles of facial expression?
|
-temporal branches
-zygomatic branches -buccal branches -mandibular branch -cervical branch -posterior auricular branch |
|
|
What does the temporal branch of the facial nerve supply?
|
All of the superficial muscles above it, including the frontal belly of the occipitofrontalis, the corrugator supercilii, the orbicularis oculi and the anterior and superior auricular muscles.
|
|
|
What does the zygomatic branch of the facial nerve supply?
|
The muscles in the infraorbital area including the orbicularis oculi and all muscles associated with the upper lip, external nares, and part of the buccinator muscle.
|
|
|
What does the buccal branch of the facial nerve supply?
|
The buccinator and levators of the upper lip and angle of the mouth, depressors of the lower lip and angle of the mouth (both of which are also innvervated by the mandibular branch of CN VII).
|
|
|
What does the mandibular branch of the facial nerve supply?
|
Muscles of the lower lip and chin.
|
|
|
What does the cervical branch of the facial nerve supply?
|
The platysma.
|
|
|
What does the posterior auricular branch of the facial nerve supply?
|
Auricular muscles (which can only move the auricle in some people).
|
|
|
What happens if there is a lesion of the motor nucleus of the facial nerve?
|
Produces ipsilateral paralysis of the muscles of facial expression and eventually muscle atrophy as well. Can result from chilling of the face, middle ear infections, tumor and fractures (account for 75% of facial nerve Bell's palsy).
|
|
|
What causes weakness of facial muscles?
|
Results from injury to the branches of the facial nerve. Injury does not cause complete paralysis, b/c of the overlapping distribution of the branches.
|

