![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the definition of labor?
|
contractions that result in cervical change
|
|
|
How many stages of labor exist?
|
three
|
|
|
Describe the events that characterize the beginning and end of the first stage of labor.
|
begins with onset of uterine contractions of sufficient frequency, intensity, and duration to result in effacement and dilation of the cervix
ends when the cervix is fully dilated to 10cm |
|
|
Describe the two phases of the first stage of labor.
|
Latent phase: begins with onset of labor and ends at approximately 4cm cervical dilation
Active phase: rapid dilation; begins at 4cm and ends at 10cm cervical dilation |
|
|
At what point in time is the latent phase of the first stage of labor considered to be prolonged?
|
nulliparous: prolonged if >20h
multiparous: prolonged if >14h |
|
|
Into what phases is the active phase of the first stage of labor further subdivided?
|
acceleration phase
phase of maximum slope deceleration phase These phases are classified according to the rate of cervical dilation |
|
|
At what degree of dilation does fetal descent begin?
|
7-8cm in nulliparas
|
|
|
What are the average rates of cervical dilation during the active phase of the first stage of labor for nulliparous and multiparous women?
|
nulliparous: up to 1.2cm/h
multiparous: up to 1.5cm/h these are average minimum rates; if slower: evaluate for adequacy of uterine contractions, fetal (mal)position, or cephalopelvic disproportion |
|
|
Describe the second stage of labor
|
begins when the cervix is fully dilated and ends with delivery of the fetus
|
|
|
Give the duration of the second stage of labor in nulliparous v. multiparous women, with and without an epidural
|
nulliparous: <2h (3 with epidural)
multiparous: <1h (2 with epidural) |
|
|
Describe the third stage of labor.
|
the main event in the third stage is placental separation
third stage begins immediately after delivery of the fetus and ends with delivery of fetal and placental membranes |
|
|
What is the normal duration of the third stage of labor?
|
10 min
considered prolonged if >30 min |
|
|
What are the three signs of placental separation?
|
gush of blood from vagina
umbilical cord lengthening fundus of uterus rises up and becomes firm |
|
|
What is the eponym for false labor?
What are the characteristics of false labor? |
Braxton Hicks contractions
contractions at irregular intervals intensity of contractions remains the same discomfort in lower abdomen no cervical change relieved by medications |
|
|
What are the characteristics of true labor?
|
contractions at regular intervals
increase in intensity of contractions discomfort in lower abdomen AND back cervical dilation not relieved by medications |
|
|
What history items must always be obtained from a laboring patient?
|
time of onset of contractions
frequency of contractions status of fetal membranes vaginal bleeding fetal activity Sx of preeclampsia Hx of allergies last PO intake (in case of c-section) medication use |
|
|
What are three indications for a sterile speculum exam in a laboring patient?
|
ROM is suspected
patient is in preterm labor bleeding suspicious for placenta previa is present |
|
|
What four signs on a speculum exam confirm rupture of membranes?
|
+ pooling
+ Valsalva + ferning + nitrazine |
|
|
What is the basis for ferning as a sign of ROM?
|
when places on a slide, crystallized NaCl in amniotic fluid shows characteristic fern-like pattern
|
|
|
What is the basis for the nitrazine test as a sign of ROM?
|
compared to vaginal fluid, amniotic fluid has a basic pH
nitrazine paper turns blue in presence of a basic pH fluid |
|
|
What can cause a false-positive nitrazine test?
|
vaginal infection with Trichomonas vaginalis
blood semen |
|
|
What is the significance of meconium in the amniotic fluid?
|
may indicate fetal distress
more common in term and postterm pregnancies than in preterm |
|
|
What are the events and consequences of meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS)?
|
1. fetal stress (e.g. hypoxia) leads to meconium in amniotic fluid
2. further fetal gasping leads to inhalation of meconium, which damages fetal lungs 3. at birth, infant presents with respiratory distress and may develop pulmonary hypertension 4. intubation helps little; ECMO may be necessary |
|
|
When does spontaneous rupture of membranes (SROM) most often occur?
|
during the course of active labor
|
|
|
Define: vernix
|
the fatty substance consisting of desquamated epithelial cells and sebaceous matter that normally covers the skin of the term fetus
|
|
|
Name the five parameters of the cervix that are measured
|
dilation
effacement station consistency position |
|
|
What does effacement describe?
|
length of the cervix
With labor, the cervix thins out and softens, and length is reduced. |
|
|
What is the normal length of the cervix?
What is its length when it is said to be 50% effaced? |
3 to 4 cm
1.5 to 2 cm |
|
|
How is effacement determined?
|
Palpation and estimation of length from internal to external os
|
|
|
Describe the two separate systems used to report station
|
1. ischial spine is zero station; areas above and below divided into thirds (-3 to +3)
2. ischial spine is zero station; areas above and below measured in cm intervals (-5 to +5) |
|
|
Describe the anatomic landmarks of the two separate systems used to report station
|
ischial spine is zero station for both systems
+3 is introitus for "thirds" method +5 is introitus for "5cm" method |
|
|
How is station determined for a vertex fetus?
|
determined by location of BPD, not tip of the head
|
|
|
How is cervical consistency described?
|
firm --> medium --> soft
in preparation for dilation and labor |
|
|
How is cervical position described?
|
posterior: difficult to palpate because it is behind the presenting part, and usually high in the pelvis
midposition anterior: easy to palpate, low in the pelvis |
|
|
What is the usual progression of cervical position during labor?
|
posterior to anterior
|
|
|
Name two labor-inducing agents
|
vaginal prostaglandins: inserted for ripening (softening) of cervix
IV pitocin: oxytocin analogue, increases strength and frequency of contractions |
|
|
Describe the elements of the Bishop scoring system
|
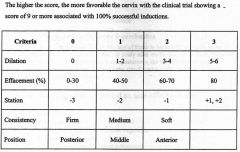
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Leopold maneuvers?
How many parts are there? |
to determine which way the baby is presenting in the uterus
four |
|
|
Name the four questions answered by the four parts of the Leopold maneuvers
|
1. What fetal part occupies the fundus?
2. On what side is the fetal back? 3. What fetal part lies over the pelvis inlet? 4. On which side is the cephalic prominence? |
|
|
What four fetal properties are described from the Leopold maneuvers?
|
lie
presentation position attitude |
|
|
What does lie describe?
|
long axis of the fetus relative to the mother
longitudinal: long axis of fetus parallel to mother's transverse: long axis of fetus perpendicular to mother's oblique: long axis of fetus oblique to mother's |
|
|
What is described by presentation?
What is the most common type of presentation? |
portion of the fetus that is foremost within birth canal
vertex (posterior fontanel is presenting part) |
|
|
Give the reference point to determine position for the following presentations:
1. vertex 2. breech 3. face |
1. occiput
2. sacrum 3. chin |
|
|
What percentage of term births are vertex presentation?
Describe the posture of the fetus in a term, vertex presentation. |
96%
head is flexed so chin is in contact with chest; posterior fontanel is presenting part, creating smallest diameter of fetal skull to pass through the pelvis |
|
|
What percentage of babies presenting OP will spontaneously rotate to OA position?
|
90%
|
|
|
What is the brow presentation, and what are its complications?
|
eyebrows present first, forcing a large diameter through the pelvis
vaginal delivery impossible; must be converted to face or vertex |
|
|
What is the incidence of breech presentation?
|
3.5% at or near term
14% in pre-term many found in early pregnancy will spontaneously convert to vertex |
|
|
Name seven risk factors for breech presentation.
|
low birth weight
congenital anomalies (e.g. hydrocephalus, anencephaly) uterine anomalies multiple gestation placenta previa hydramnios, oligohydramnios multiparity |
|
|
Name three types of breech presentations and give the incidence of each.
|
1. frank breech: 65%
2. complete breech: 25% 3. incomplete (footling) breech: 10% |
|
|
Describe the three types of breech presentation.
|
frank breech: thighs flexed, knees extended
complete breech: thighs flexed, knees flexed incomplete (footling) breech: one or both hips are not flexed so that a foot lie below the buttocks |
|
|
How are breech presentations diagnosed (3)?
|
Leopold maneuvers
ultrasound vaginal exam |
|
|
Malpresentation is not uncommon and not significant before ____ weeks.
|
34
|
|
|
Define: external cephalic version
|
procedure that maneuvers the infant to a cephalic position by applying pressure through the maternal abdomen
|
|
|
Under what conditions can external cephalic version be attempted?
What is the success rate? |
May only be done if:
1. breech is diagnosed before the onset of labor 2. gestational age is 35-37 weeks success rate 50% |
|
|
What are the risks of external cephalic version?
|
placental abruption
fetal heart rate abnormalities reversion |
|
|
Name the cardinal movements of labor.
|
engagement
descent flexion internal rotation extension external rotation expulsion |
|
|
Briefly describe each of the following cardinal movements of labor:
engagement descent flexion internal rotation extension external rotation |
engagement: descent of biparietal diameter through pelvic inlet
descent: when fetal head passes into pelvis; occurs discontinuously flexion: when fetal chin apposes thorax internal rotation: turning of the head to move occiput toward symphysis pubis extension: moves the occiput toward the fetal back external rotation: after delivery of head, moves occiput and spine into same plane |

