![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Aspirin
Mechanism |
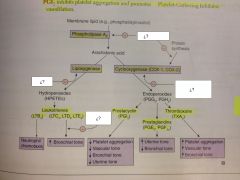
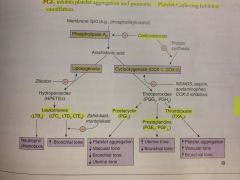
Irreversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX-1 & COX-2) by covalent acetylation, which decreases synthesis of Thromboxane A2 (TXA2) and prostaglandins.
Increase bleeding time until new platelets are produced (about 7 days) No effect on PT, or PTT A type of NSAID |
|
|
Aspirin
Clinical Use |
Low dose (<300 mg/day): Decrease platelet aggregation
Intermediate dose (300-2400 mg/day): Antipyretic and analgesic High dose (2400-4000 mg/day): Anti-inflammatory |
|
|
Aspirin
Toxicity |
Gastric ulceration
Tinnitus (CN VIII) Chronic use can lead to acute renal failure, interstitial nephritis, and upper GI bleeding. Risk of Reye syndrome in children treated with aspirin for viral infection Also stimulates respiratory centers, causing hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis |
|
|
Ibuprofen
what type of drug is it? |
NSAIDs
|
|
|
Naproxen
what type of drug is it? |
NSAIDs
|
|
|
Indomethacin
what type of drug is it? |
NSAIDs
|
|
|
Ketorolac (Toradol)
what type of drug is it? |
NSAIDs
|
|
|
Diclofenac
what type of drug is it? |
NSAIDs
|
|
|
NSAIDs
Mechanism |
Reversibly inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2)
Block PG synthesis |
|
|
NSAIDs
Clinical use |
Antipyretic
Analgesic Anti-inflammatory Indomethacin is used to close a PDA |
|
|
NSAIDs
Toxicity |
Interstitial nephritis
Gastric ulcer (PGs protect gastric mucosa) Renal ischemia (PGs vasodilate afferent arteriole) |
|
|
Celecoxib
What type of drug is it? |
COX-2 inhibitor
|
|
|
Meloxicam
What type of drug is it? |
COX-2 inhibitor
|
|
|
COX-2 inhibitor
Mechanism |
Reversibly inhibit COX-2, which is found in inflammatory cells and vascular endothelium and mediates inflammation and pain
Spares COX-1, which helps maintain the gastric mucosa (no gastric ulcers) and also spares TXA2 |
|
|
COX-2 inhibitor
Clinical Use |
Rheumatoid arthritis
Osteoarthritis Use in pts with gastritis or ulcers |
|
|
COX-2 inhibitor
Toxicity |
Increase risk of thrombosis
Sulfa allergy |
|
|
Acetaminophen
Mechanism |
Reversibly inhibitis cyclooxygenase, mostly in CNS
Inactivated peripherally |
|
|
Acetaminophen
Clinical use |
Antipyretic
Analgesic, but not anti-inflammatory Used instead of aspirin to avoid Reye syndrome in children with viral infection |
|
|
Acetaminophen
Toxicity |
Overdose produces hepatic necrosis
- Acetaminophen metabolite (NAPQI) depletes glutathione and forms toxic tissue adducts in liver - N- Acetylcysteine is antidote -> Regenerates glutathione |
|
|
Bisphosphonates. Alendronate, other -dronates
Mechanism |
Pyrophosphate analogs
Bind hydroxyapatite in bone, inhibiting osteoclast activity |
|
|
Bisphosphonates. Alendronate, other -dronates
Clinical Use |
Osteoporosis
Hypercalcemia Paget disease of bone |
|
|
Bisphosphonates. Alendronate, other -dronates
Toxicity |
Corrosive esophagitis (pts are advise to take with water and remain upright for 30 min)
Osteonecrosis of the jaw |
|
|
Chronic gout drugs (preventive) are...
|
Allopurinol
Febuxostat Probenecid |
|
|
Allopurinol
Mechanism |
Inhibits xanthine oxidase: Decrease conversion of xanthine to uric acid.
Also use in lymphoma and leukemia to prevent tumor lysis-associated urate nephropathy All but the highest doses depress uric acid clearance. Even high doses (5-6g/day) have only minor uricosuric activity |
|
|
Allopurinol
Side effects |
Increase concentrations of Azathioprine and 6-MP (both metabolized by xanthine oxidase)
Do not give salicylates |
|
|
Febuxostat
Mechanism |
Inhibits xanthine oxidase
|
|
|
Probenecid
Mechanism |
Inhibits reabsorption of uric acid in PCT (also inhibits secretion of PCN -> It will stay longer in the serum)
|
|
|
Acute gout drugs are...
|
NSAIDs: Naproxen or Indomethacin
Glucocorticoids: Oral or intraarticular Colchicine |
|
|
Colchicine
Mechanism Side effects |
Binds and stabilizes tubulin to inhibit microtuble polymerization, impairing leukocyte chemotaxis and degranulation
GI Side effects Acute and prophylactic value |
|
|
TNF-Alpha inhibitors
Side effects |
Predispose to infection, including reactivation of latent TB
TNF blockade prevents activation of macrophages and destruction of phagocytosed microbes |
|
|
Etanercept
What type of drug is it? |
TNF-Alpha inhibitor
|
|
|
Etanercept
Mechanism |
Fusion protein (receptor for TNF-alpha and IgG-Fc), produced by recombinant DNA
|
|
|
Etanercept
Clinical use |
Rheumatoid arthritis
Psoriasis Ankylosing spondylitis |
|
|
Infliximab
What type of drug is it? |
TNF- alpha
|
|
|
Adalimumab
What type of drug is it? |
TNF-alpha
|
|
|
Infliximab, adalimumab
Mechanism |
Anti-TNF-alpha monocloncal antibody
|
|
|
Infliximab, adalimumab
Clinical Use |
IBD
Rheumatoid Arthritis Ankylosing Spondylitis Psoriasis |
|
|
|

