![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
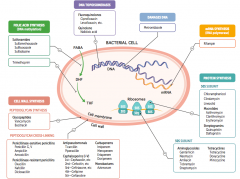
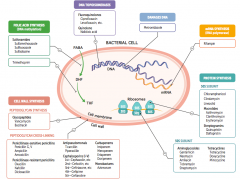
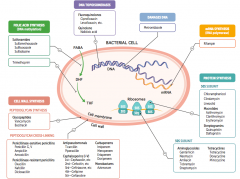
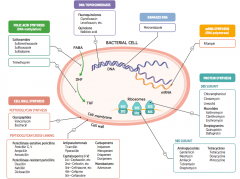
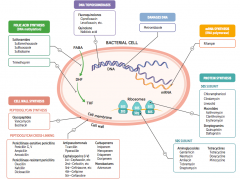
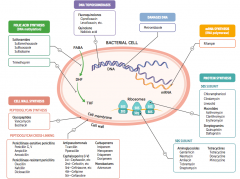
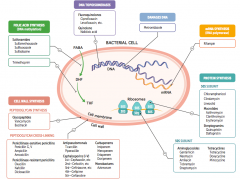
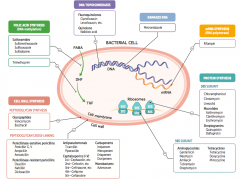
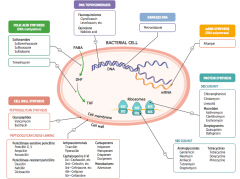
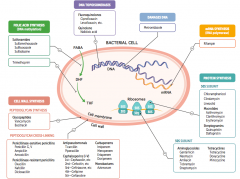
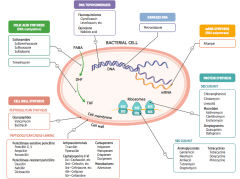
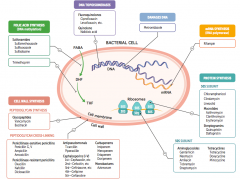
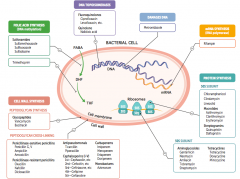
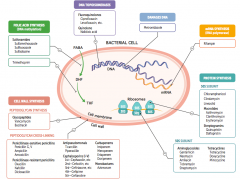
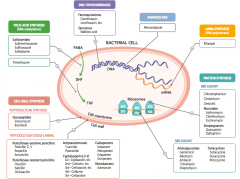
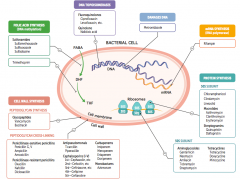
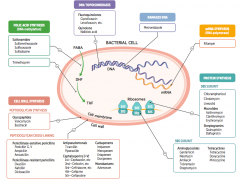
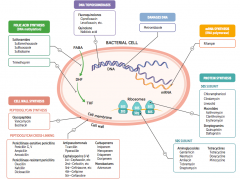
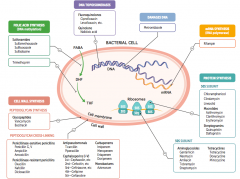
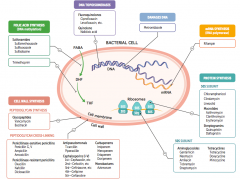
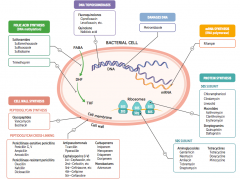
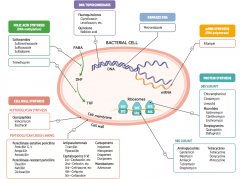
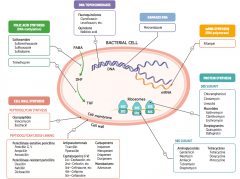
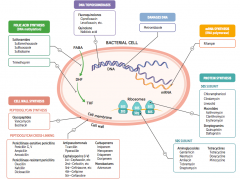
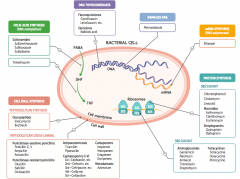
What parts of pathogens can anti-microbials target? |
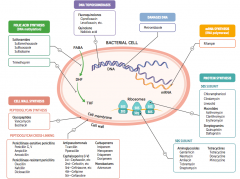
- Cell wall synthesis: peptidoglycan synthesis or cross-linking
- Folic acid synthesis (DNA methylation) - DNA topoisomerases - Damage DNA - mRNA synthesis (RNA polymerase) - Protein synthesis (50S or 30S subunit) |
|
|
Which types of drugs target peptidoglycan cross-linking? |
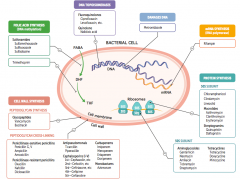
- Penicillinase-sensitive penicillins |
|
|
What are the penicillinase-sensitive penicillins that affect peptidoglycan cross-linking? |
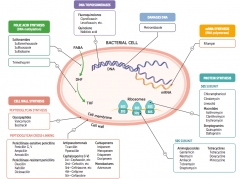
- Penicillin G, V |
|
|
What are the penicillinase-resistant penicillins that affect peptidoglycan cross-linking? |
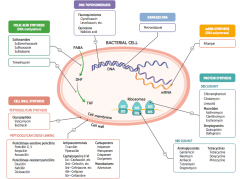
- Oxacillin
- Nafcillin - Dicloxacillin |
|
|
What are the antipseudomonals that affect peptidoglycan cross-linking? |
- Ticarcillin
- Piperacillin |
|
|
What are the cephalosporins that affect peptidoglycan cross-linking? |
1st - Cephazolin, etc |
|
|
What are the carbapenems that affect peptidoglycan cross-linking? |
- Imipenem |
|
|
What are the monobactams that affect peptidoglycan cross-linking? |
Aztreonam
|
|
|
Which drugs target peptidoglycan synthesis (cell wall)? |
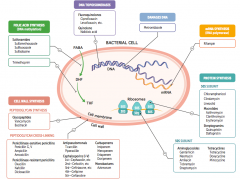
Glycopeptides |
|
|
What are the drugs that target folic acid synthesis (DNA methylation)? |
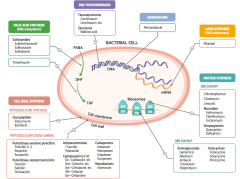
Sulfonamides |
|
|
What are the drugs that target DNA topoisomerases? |
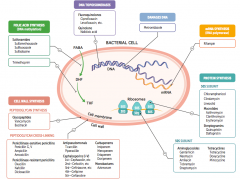
Fluoroquinolones |
|
|
What are the drugs that damage DNA? |
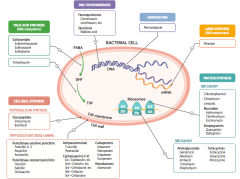
Metronidazole
|
|
|
What are the drugs that target mRNA synthesis (RNA polymerase)? |
Rifampin |
|
|
What are the drugs that target the 50S subunit in protein synthesis? |
Chloramphenicol |
|
|
What are the drugs that target the 30S subunit in protein synthesis? |
Aminoglycosides |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Ciprofloxacin - Levofloxacin |
Fluoroquinolones - inhibit DNA topoisomerases |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Metronidazole |
Damages DNA
|
|
|
Type / function of:
- Vancomycin - Bacitracin |
Glycopeptides |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Sulfamethoxazole - Sulfixoxazole - Sulfadiazine |
Sulfonamides |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Rifampin |
Inhibits mRNA synthesis (RNA polymerase)
|
|
|
Type / function of:
- Gentamicin - Neomycin - Amikacin - Tobramycin - Streptomycin |
Aminoglycosides |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Ticarcillin - Piperacillin |
Antipseudomonals |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Aztreonam |
Monobactam |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Trimethoprim |
Inhibits folic acid synthesis / DNA methylation
|
|
|
Type / function of:
- Chloramphenicol - Clindamycin - Linezolid |
Inhibit 50S subunit of protein synthesis
|
|
|
Type / function of:
- Tetracycline - Doxycycline - Minocycline |
Tetracyclines |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Imipenem - Meropenem - Ertapenem - Doripenem |
Carbapenems |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Azithromycin - Clarithromycin - Erythromycin |
Macrolides |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Oxacillin - Nafcillin - Dicloxacillin |
Penicillinase-resistant penicillins |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Penicillin G, V - Ampicillin - Amoxicillin |
Penicillinase-sensitive penicillins |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Nalidixic Acid |
Quinolone |
|
|
Type / function of:
- Quinupristin - Dalfopristin |
Streptogramins |
|
|
Type / function of: |
Cephalosporins (I-V) |
|
|
What parts of pathogens can anti-microbials target? |
- Cell wall synthesis: peptidoglycan synthesis or cross-linking
- Folic acid synthesis (DNA methylation) - DNA topoisomerases - Damage DNA - mRNA synthesis (RNA polymerase) - Protein synthesis (50S or 30S subunit) |
|
|
MECHANISM: Penicillin G, V |
1. Binds penicillin-binding proteins (transpeptidases) 2. Block transpeptidase cross-linking of peptidoglycan 3. Activate autolytic enzymes |
|
|
CLINICAL USE: Penicilling G, V |
1. Most: G(+) → S. penumoniae, S. pyogenes, Actinomyces 2. N. meningitidis + T. pallidum 3. Bactericidal: G(+) cocci; G(-) cocci; G(+) rods; spirochetes 4. Penicillinase Sensitive |
|
|
TOXICITY: Penicilling G, V |
1. Hypersensitivity Rxn 2. Hemolytic Anemia |
|
|
RESISTANCE: Penicilling G, V |
Penicillinase (β-lactamse) cleaves β-lactam ring |
|
|
LIST: AMINOPENICILLINS, Penicillinase-SENSITIVE Penicillins |
Ampicillin + Amoxicillin |
|
|
MECHANISM: Ampicillin + Amoxicillin |
1. Binds penicillin-binding proteins (transpeptidases) 2. Block transpeptidase cross-linking of peptidoglycan 3. Activate autolytic enzymes 4. Wide spectrum; Penicillinase sensitive 5. Combine with CALVULANIC ACID
|
|
|
CLINICAL USE: Ampicillin + Amoxicillin |
1. H. Influenzae 2. E. Coli 3. Listeria Monocytogenes, 5. Proteus Mirabilis 4. Salmonella 6. Shigella 7. Enterococci
MNEMONIC: HELPSS |
|
|
TOXICITY: Ampicillin + Amoxicillin |
1. Hypersensitivity Rxn 2. Pseudomembranous Colitis 3. Rash |
|
|
RESISTANCE: Ampicillin + Amoxicillin |
Penicillinase (β-lactamse) cleaves β-lactam ring |
|
|
LIST: Penicillinase-RESISTANT penicillins |
Dicloxacillin Oxacillin Nafcillin
MNEMONIC: DON |
|
|
MECHANISM: Dicloxacillin, Oxacillin, Nafcillin |
1. Binds penicillin-binding proteins (transpeptidases) 2. Block transpeptidase cross-linking of peptidoglycan 3. Activate autolytic enzymes 4. Narrow Spectrum 5. Penicillinase RESISTANT (d/t bulky R goup) |
|
|
CLINICAL USE: Dicloxacillin, Oxacillin, Nafcillin |
S. aureus EXCEPT MRSA |
|
|
TOXICITY: Dicloxacillin, Oxacillin, Nafcillin |
1. Hypersensitivity Rxn 2. Interstitial Nephritis |

